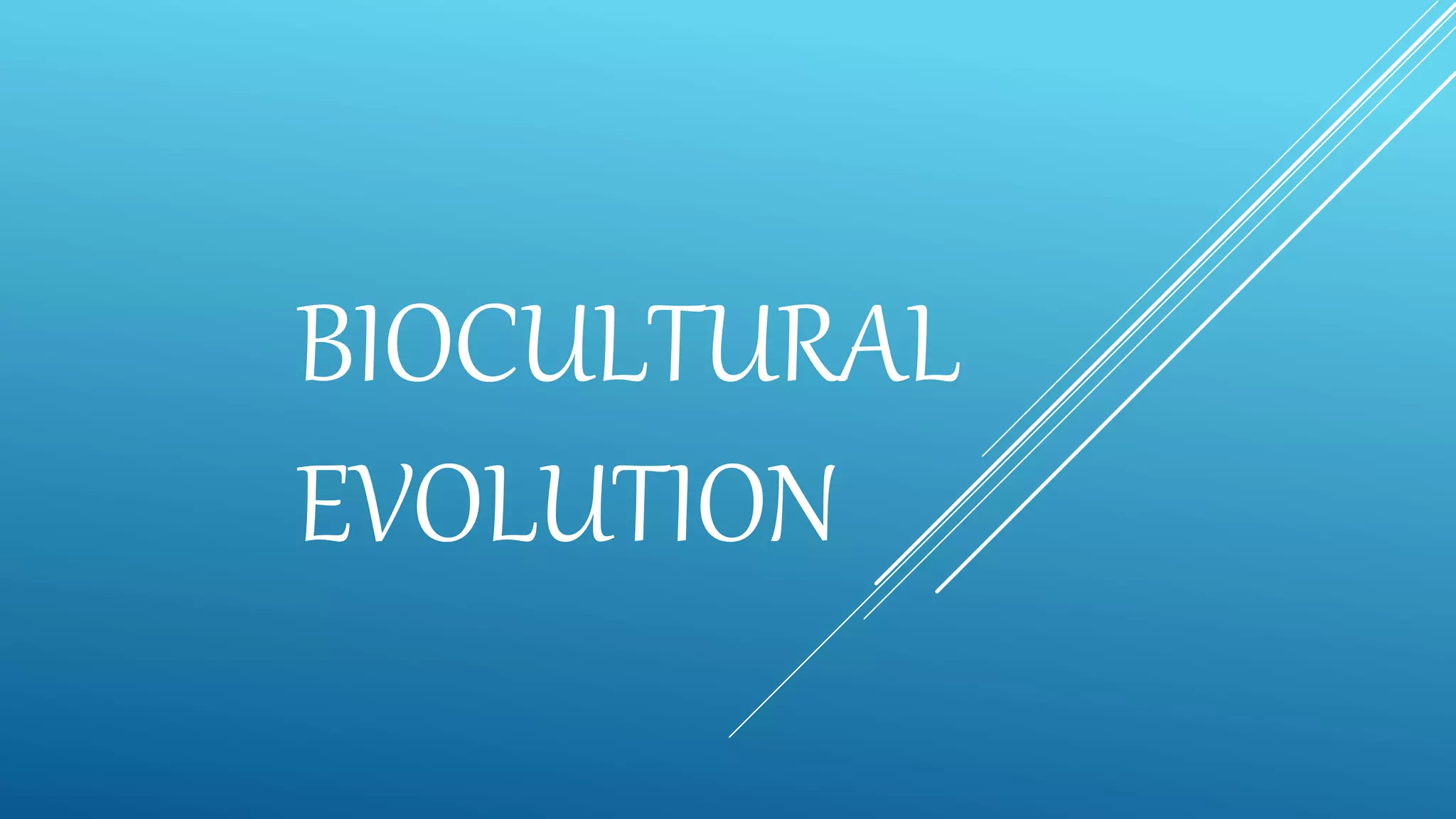
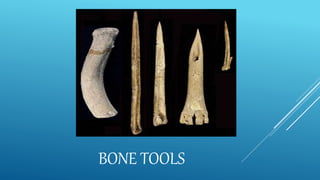
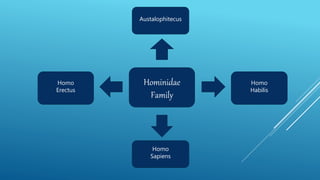
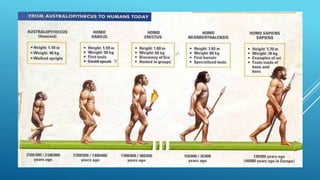
The document discusses biocultural evolution and early hominids. It describes Darwin's theory of natural selection and how early hominid species like Australopithecus were capable of bipedalism. It then outlines some of the main hominid species, including Homo habilis which used tools for scavenging, Homo erectus which existed around 1.8 million years ago and moved from Africa to Asia, and Homo sapiens which evolved from Homo erectus around 500,000-200,000 years ago.