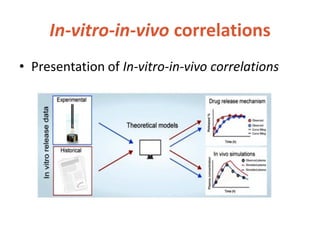
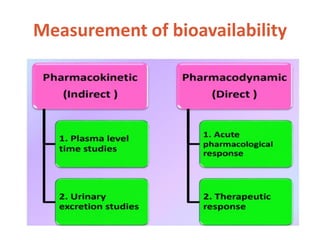
This document discusses bioavailability and bioequivalence. It defines bioavailability as the rate and extent of drug absorption into systemic circulation from its dosage form. Bioequivalence is established when two similar dosage forms reach systemic circulation at the same relative rate and extent. The objectives, significance, and various study designs of bioavailability testing are described, including absolute vs relative bioavailability. Methods for measuring bioavailability and various in vitro drug dissolution models are also summarized.












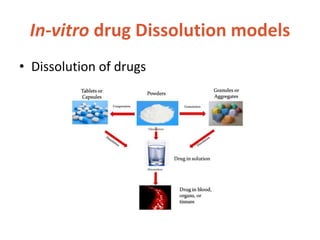
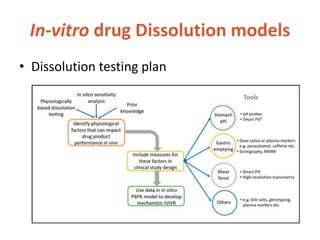


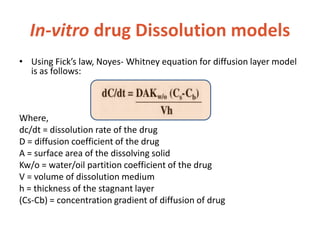


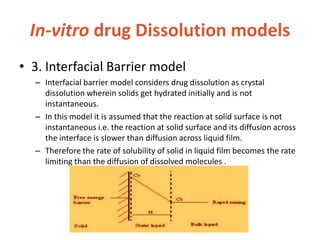



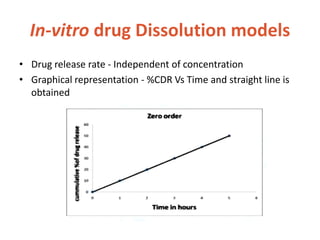

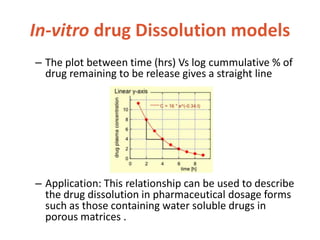

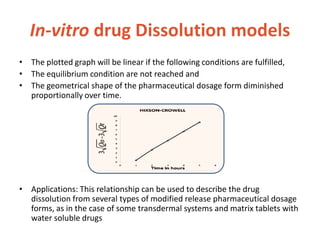
![In-vitro drug Dissolution models
• The study of dissolution from a planar system
having a homogeneous matrix can be obtained by
the equation:
A=[D(2C-Cs)Cs X t]1/2
Where, A = amount of drug released in time ‘t’ per unit
area
D = diffusivity of drug molecule in the matrix substance
C = initial drug concentration
Cs = drug solubility in the matrix media.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilitybioequivalance-200902183227/85/Bioavailability-Bioequivalance-32-320.jpg)
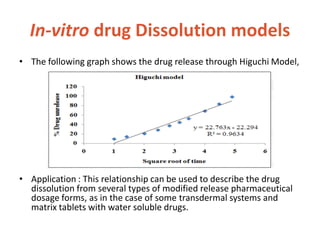


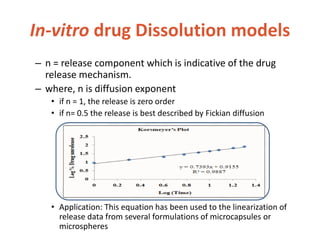


![In-vitro drug Dissolution models
• 10. Wiebull Model
– Wiebull model is generally applied to drug dissolution
or release from pharmaceutical dosage forms These
accumulated fraction of drug M in solution at time t is
given by Wiebull equation,
M= Mo[1-e-(t-T/a)b]
– Where, m = % dissolved in time ‘t’ a= scale parameter
which defines the time scale of the dissolution
process Ti = lag time( generally zero) b = shape factor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilitybioequivalance-200902183227/85/Bioavailability-Bioequivalance-40-320.jpg)