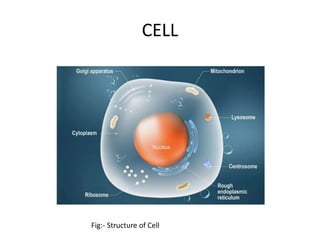
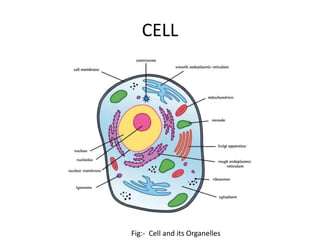
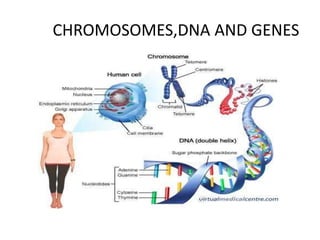
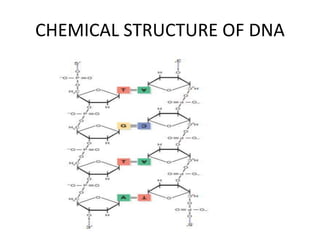
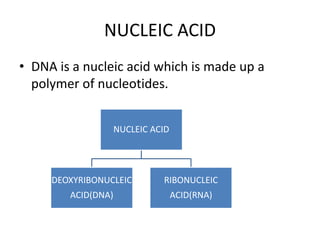
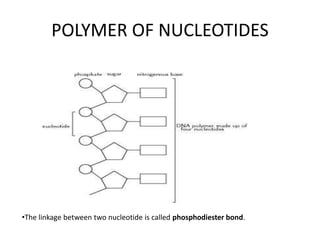
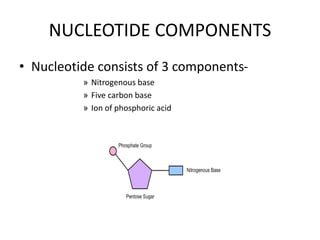
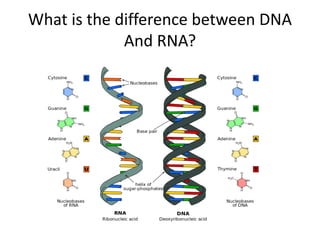
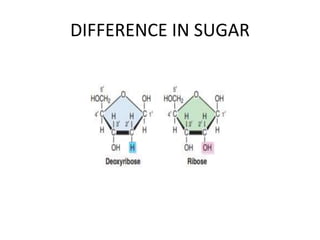
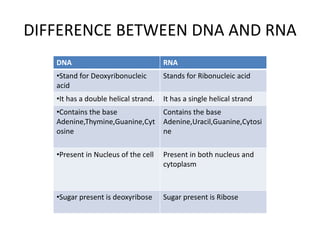
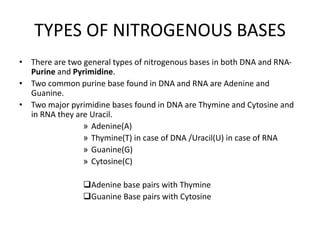
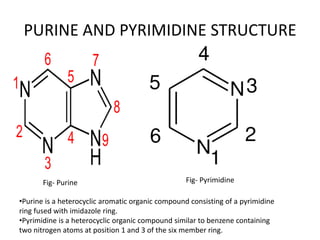
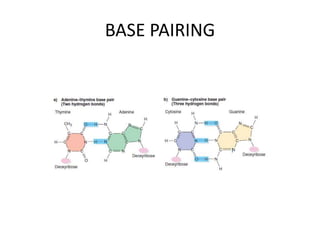
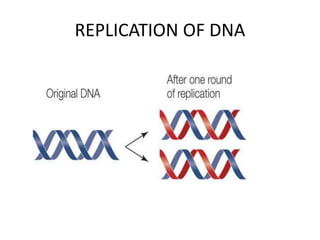
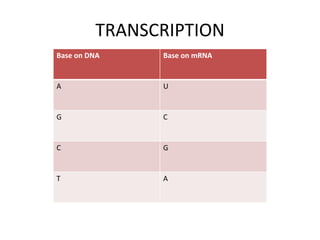
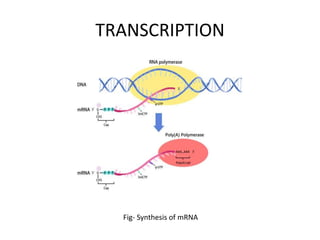
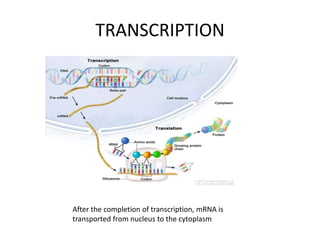
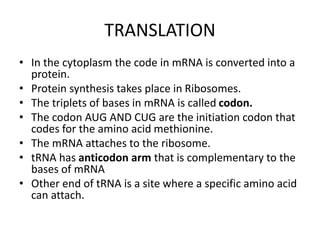
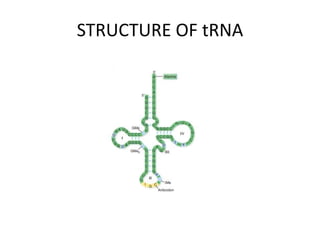
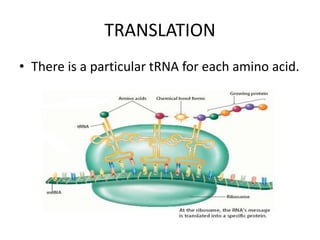
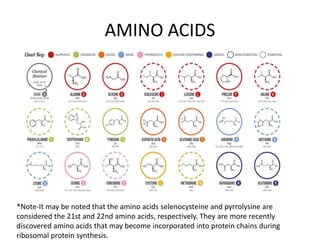
The document discusses DNA, its structure and function. It describes how DNA is made up of nucleotides containing nitrogenous bases, sugars and phosphates. The four bases in DNA are adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine. DNA replication and protein synthesis are also summarized. DNA replication involves unwinding of the DNA double helix followed by synthesis of new strands along the existing strands. Protein synthesis occurs via transcription of DNA to mRNA in the nucleus, and translation of mRNA to proteins on ribosomes in the cytoplasm using transfer RNA.