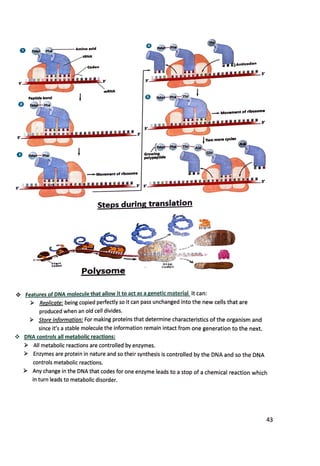
This document discusses nucleic acids and protein synthesis. It begins by describing the structures of DNA and RNA, which are made up of nucleotides containing phosphate, sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and nitrogenous bases. DNA contains the bases adenine, cytosine, thymine, and guanine, while RNA contains adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. The document then explains DNA replication, which involves unwinding the DNA double helix and using each strand as a template to synthesize a new complementary strand. It also describes transcription of DNA into mRNA and translation of mRNA into proteins, which occurs on ribosomes and involves transfer RNA bringing amino acids to be joined into polypeptide chains according to
![1
/ Sugar-phosphate backbone
s• end/ (on blue background)
Nucleoslde
r--"--.
Nitrogenous bases
Pyrimidines
,,t,_,.CH3
HN
O'~ 'W' H
H
Nitrogenous
base Cytosine (C) Thymine (T, In ONA) Uracil (U, In RNA)
-o-Lo-~~-
b
- ,.
Phosphate
group 3· 2·
Sugar
(pentose)
' ,i..._________
OH
3' end
(al Polynucleotlde, or nuclelc acid
(bl Nudeotlde
Formation of a polynucleotide:
NH2
hN..._c)<:::-N
Hl II I
N,..<:'.,N#CH
H
Adenine (A)
s·
HOC~H
2 OH
•· H ,.
H 1•
1
. H
OH H
·Sugars
Oeoxyrib(lse Un DNA}
Guanlne(G)
s·
H
t.J,~
~
w-
OH OH
Rlbose (In RNA)
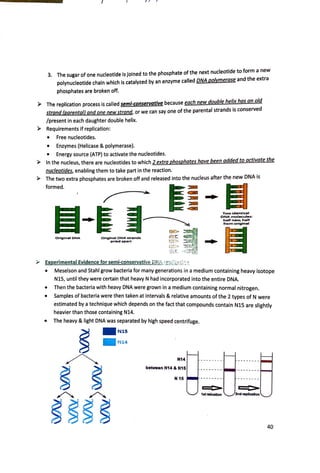
During the interphase (period between 2 succes$!Ve divisions), many nucleotides are linked
together (by a condensation reaction) to form a.120.lY!]ucleotide.
They are linked by a phosphodiester bond between.!: of one nucleotide and~ of the other.
The polynucleotide chains are made of alternating sugars and phosphates linked together, with
the nitrogen bases projecting sideways.
The strand is said to have 3'and S'end.
The Structure of DNA molecule (by Watson &Crick)
It's made of two polynucleotide strands lying side by side, the two strands are held together by
H bond between the nitrogen bases according to the rule of base pairing c=G& A=T
The two strands twist around each other to form a double helix, they run in opposite
directions/antiparallel to allow the bases to fit exactly with each other.
In each base pair, one base belongs to the double ringed purines while other belongs to the
single ringed pyrimidines. The A & T pair has 2 H bonds, while C & G pair has 3H bonds.
The base pairing helps to:
• Stabilize the molecule.
• Allows the DNA to replicate.
• Gives the DNA the 3 dimensional configuration.
The width of the DNA molecule is about 2nm, each twist contains 10 pairs of nucleotides and
measures 3.4nm in length.
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnastructureandproteinsynthesisfaculty-240216180153-86146ac0/85/DNA-structure-and-protein-synthesis-pdf-2-320.jpg)
![3.4 nm
]~.34 nm
The structure of DNA
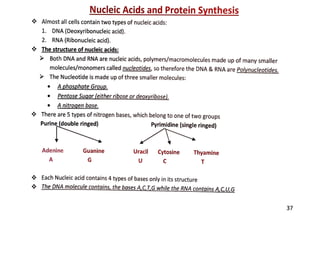
Differences between DNA and RNA:
P.O.C.
ar
structure
Location
Re lication
Stabili
Existence
Molecular mass
Ratio between
bases
Amount
DNA Replication:
DNA
oeo ribose
Doubl
Nucleus/s
More stable
Permanent
Up to 150 X 10'>7
A/T, G/ C = 1
Constant forall cells
(except gametes)
H
"'- " · ••••0
~ ., " "
••·•
•
H
-,~
o sugar
Adenine (A) Thymine (T)
H
I
o
~~--
-~~
Q
I
N- H• •· ··O Sugar
H
Guanine (G) Cytosine (C)
Base pairing in DNA.
RNA
Ribose
A,G,U,C
/ nucleus
can't
Less stable
Tem porary
Up to 2 X 10
A/U , G/C varies
varies from cell to cell
accordingto metabolic
activities
Before a cell divides, its DNA is replicated (in the interphase) so that each new cell receives a
complete copy of the original genetic information.
Mechanism of DNA Replication
1. The Two strands unwind/unzip, due to the breakdown ofH bonds between the bases by
Helicase enzyme.
2. Each one ofthe two strands acts as a template to which a complementary set of nucleotides
(always present in the nucleus) would attach according to the rule of base pairing by H bonds
39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnastructureandproteinsynthesisfaculty-240216180153-86146ac0/85/DNA-structure-and-protein-synthesis-pdf-3-320.jpg)