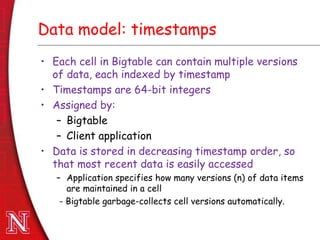
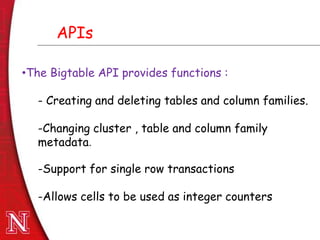
Bigtable is a distributed storage system developed at Google to manage large amounts of structured data across thousands of servers. It provides a flexible data model with rows and columns that can be queried and modified in real time. Bigtable was designed as Google needed a system that could scale enormously without compromising performance. It has been successfully used by many Google products and services that require fast access to very large datasets, such as web search, Google Maps, and Google Analytics.