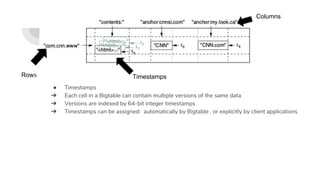
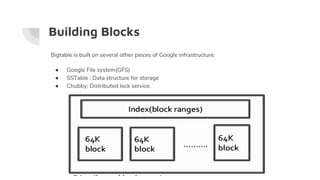
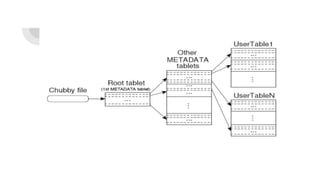
Bigtable is Google's cloud-based data storage service that provides scalable, high-performance storage for large analytical and operational workloads. It uses a distributed, parallel architecture to store data across thousands of commodity servers and provides low-latency access. Many Google services such as Gmail, YouTube, Google Maps, and Google Analytics use Bigtable to store and access massive amounts of data.