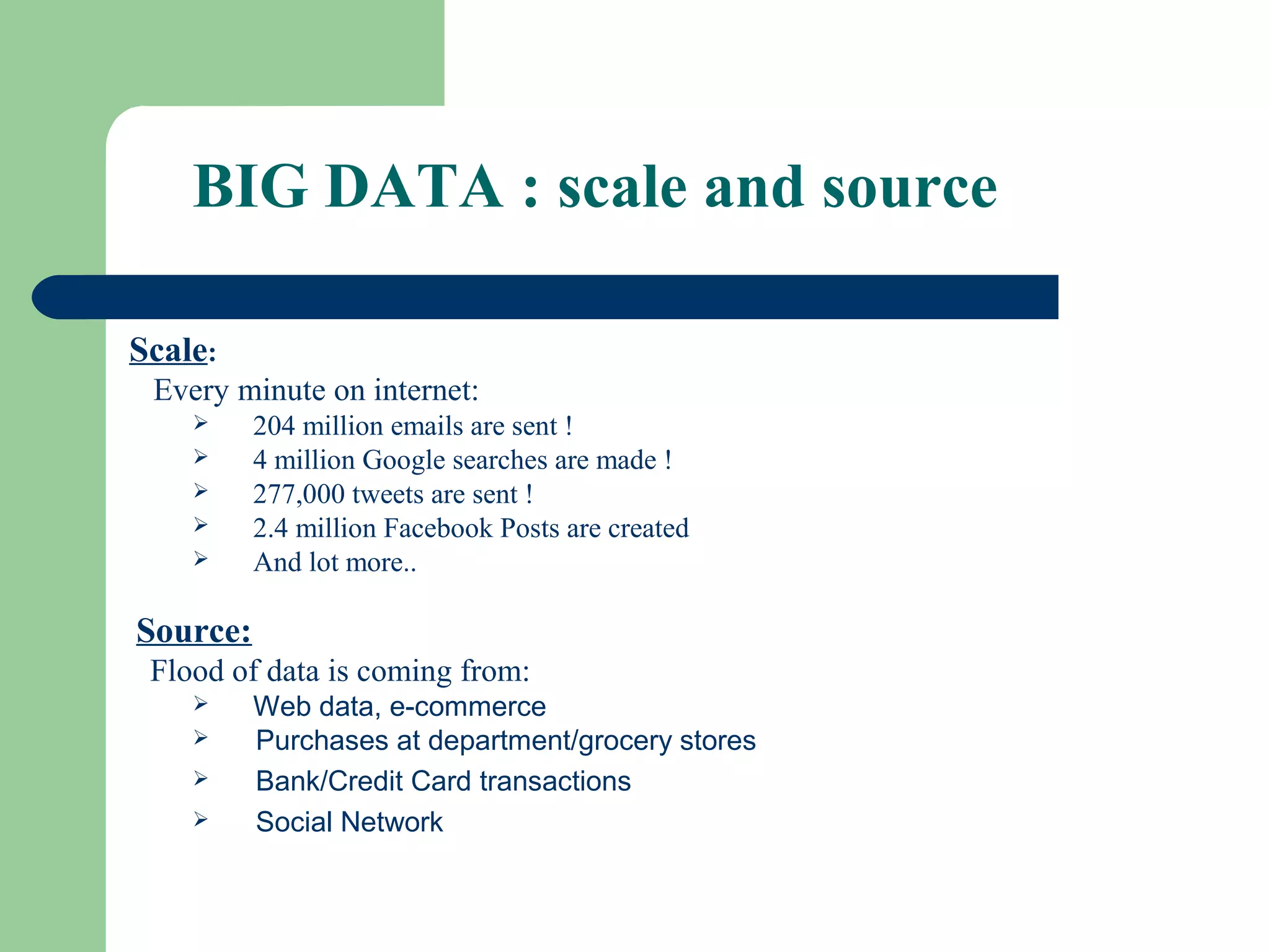
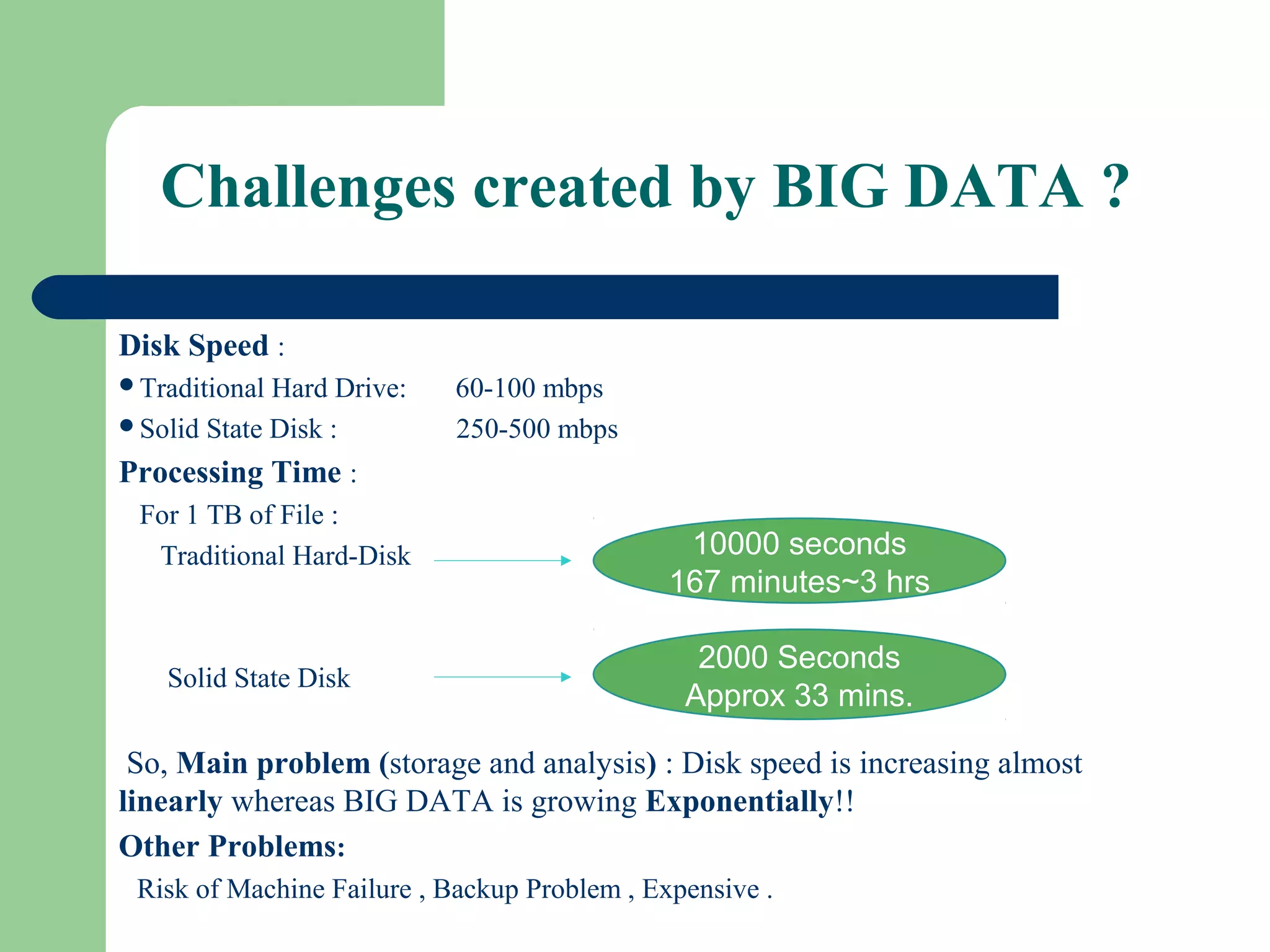
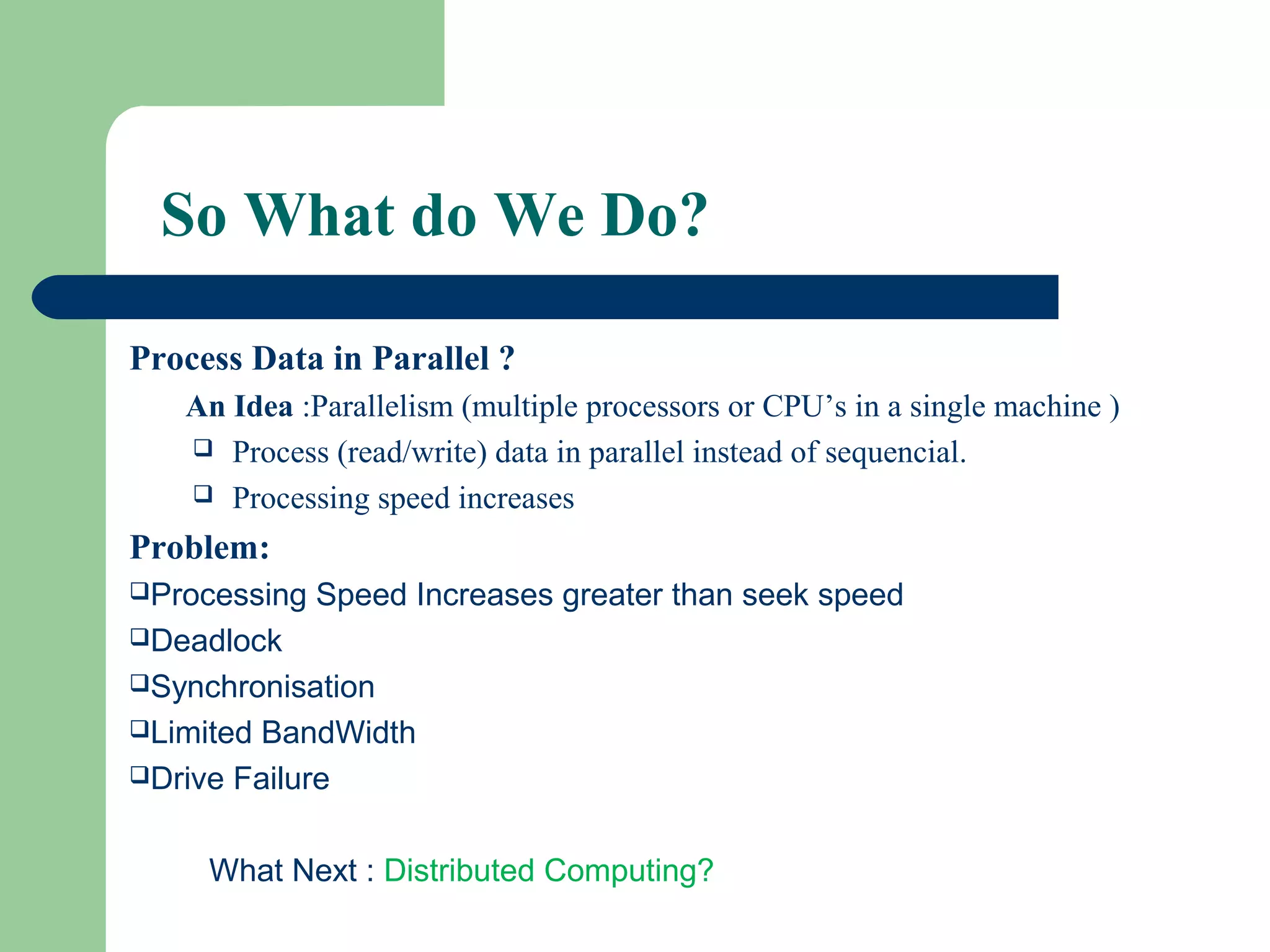
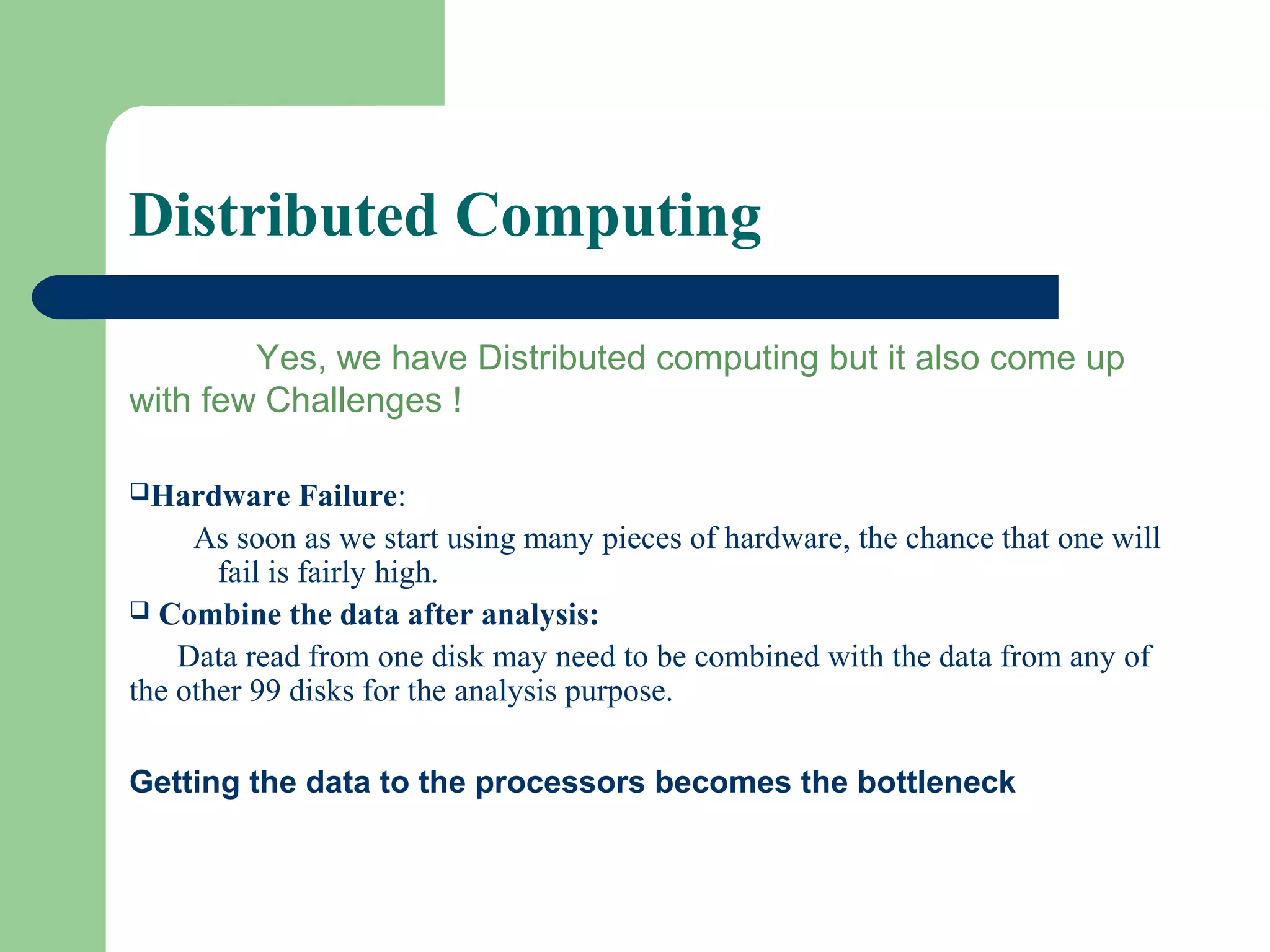
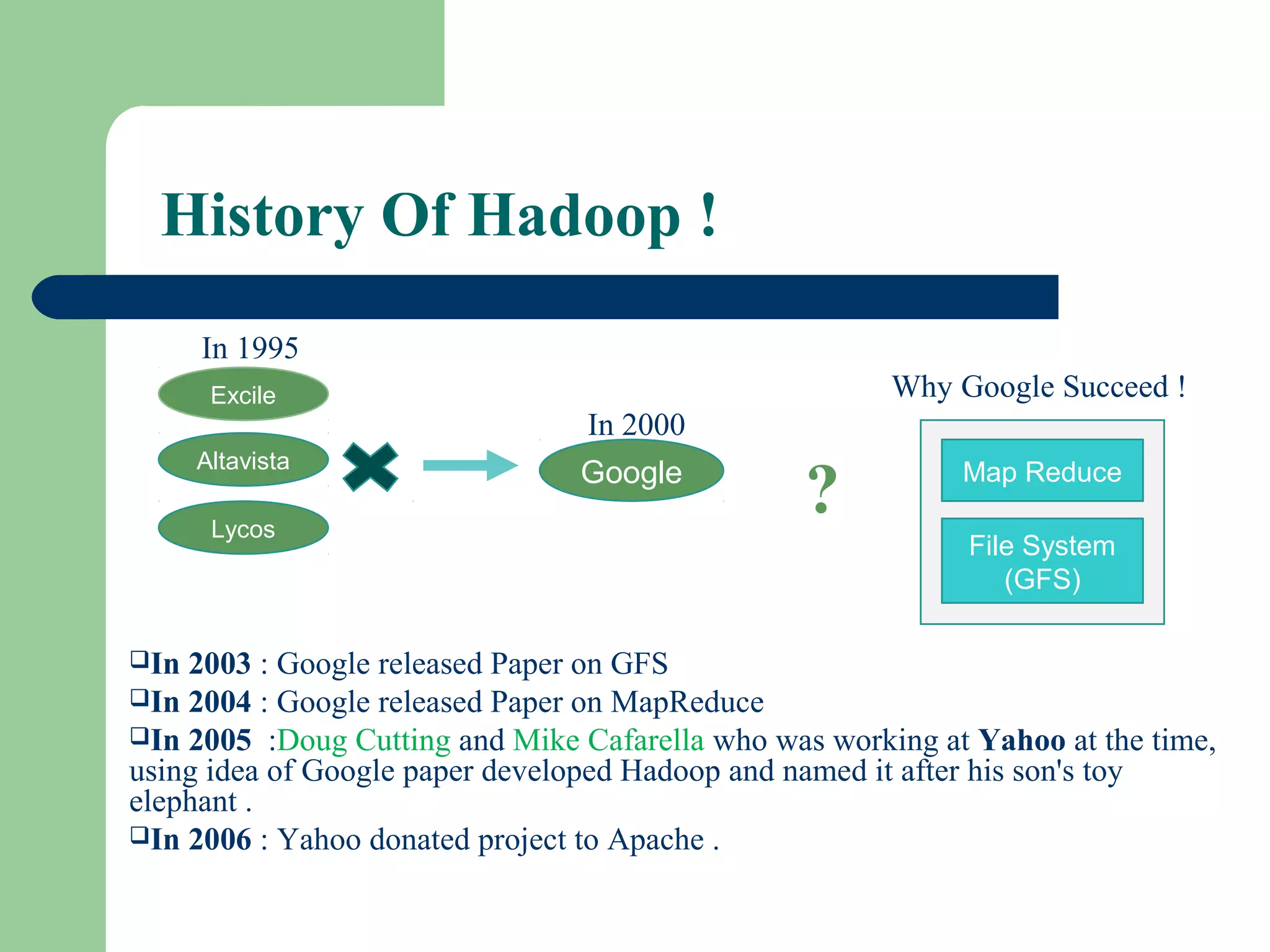
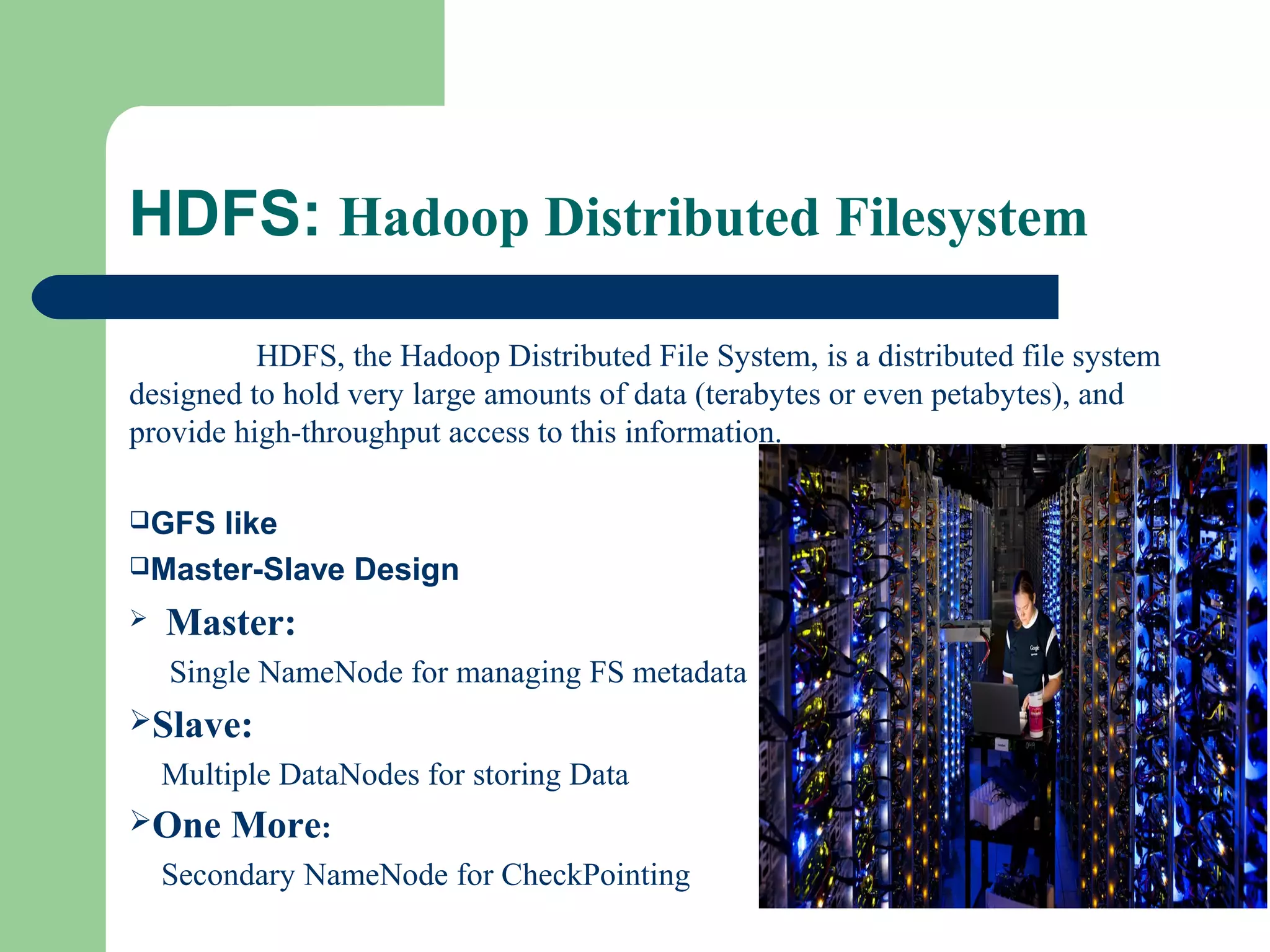
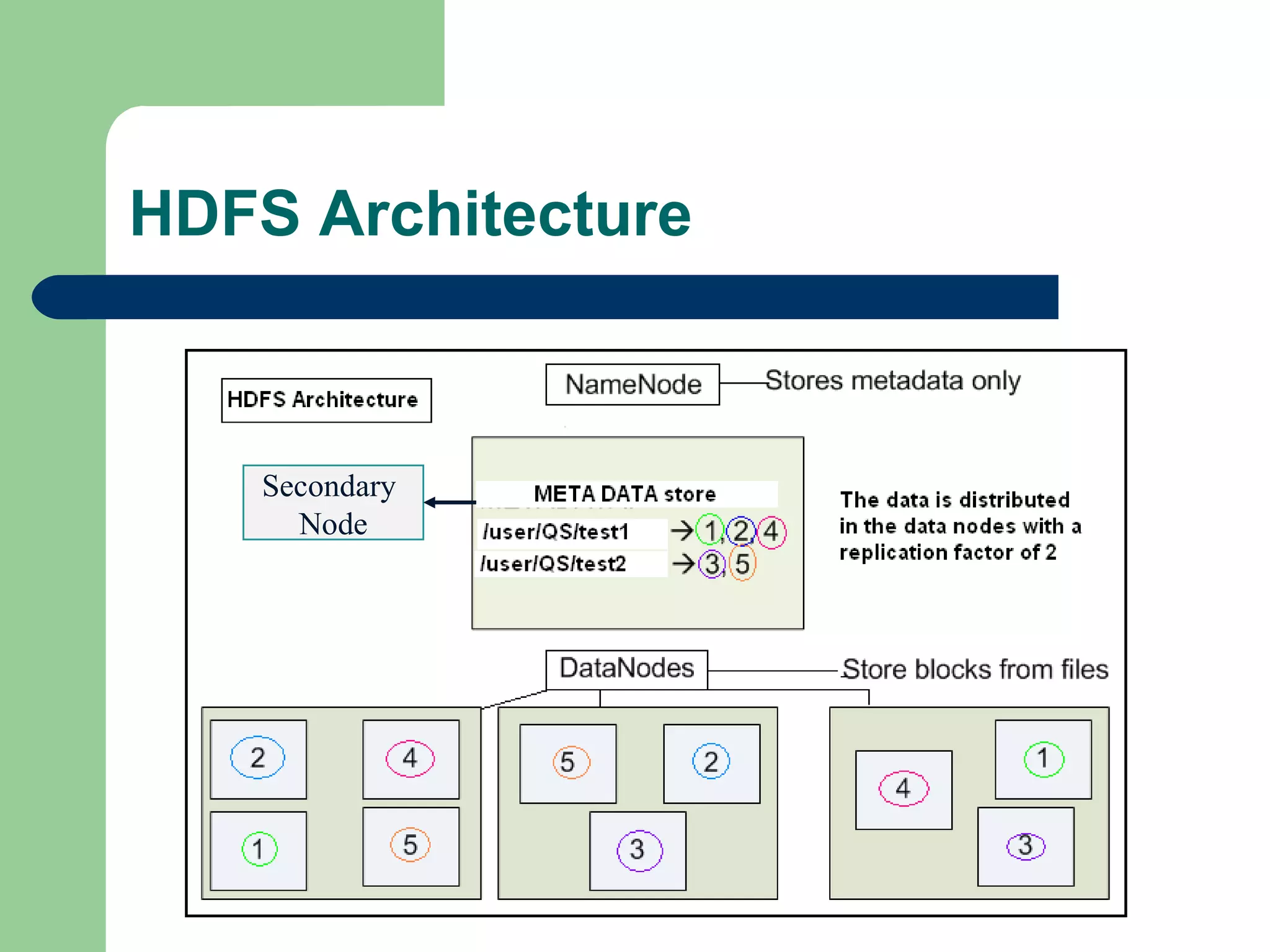
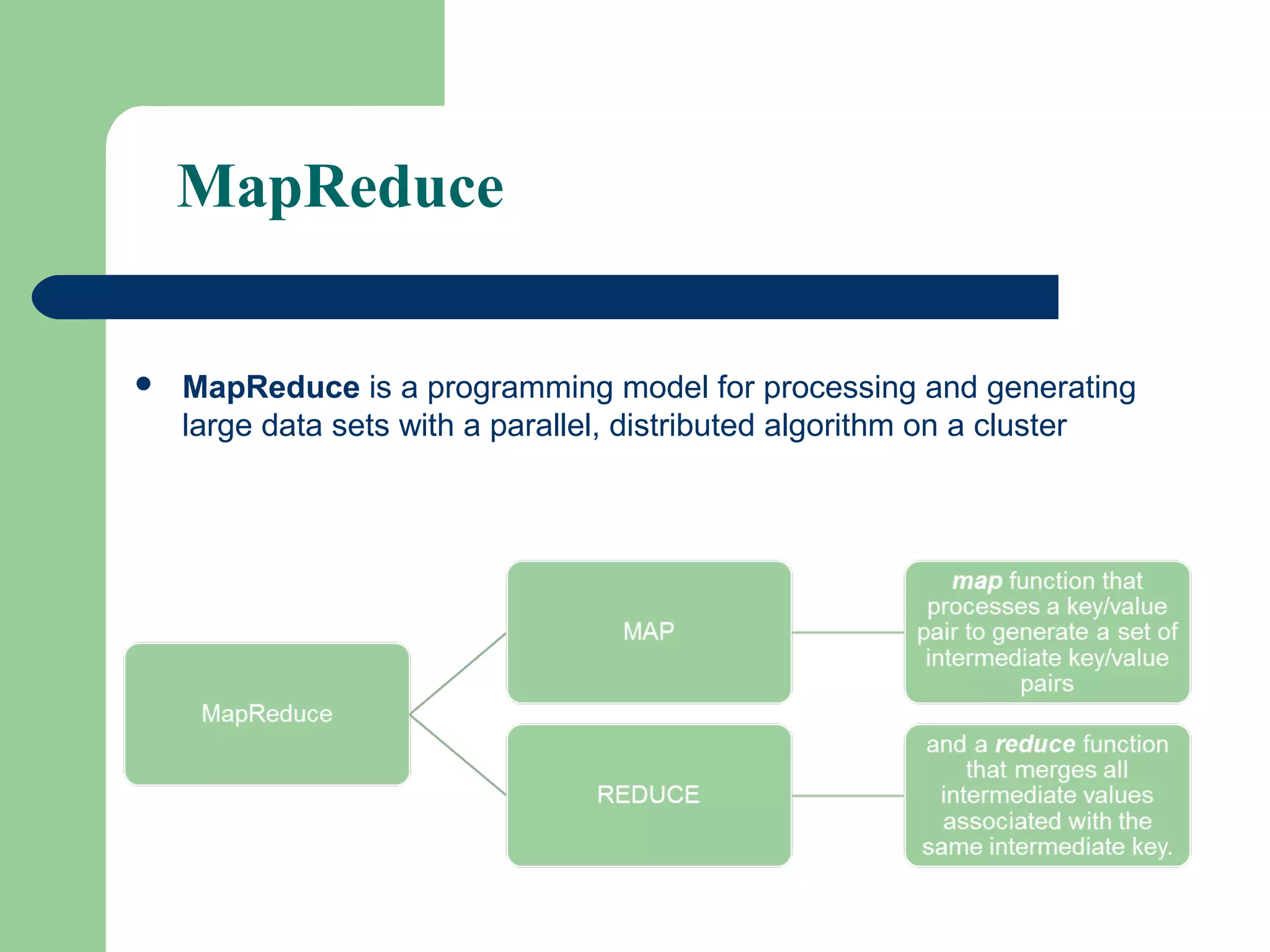
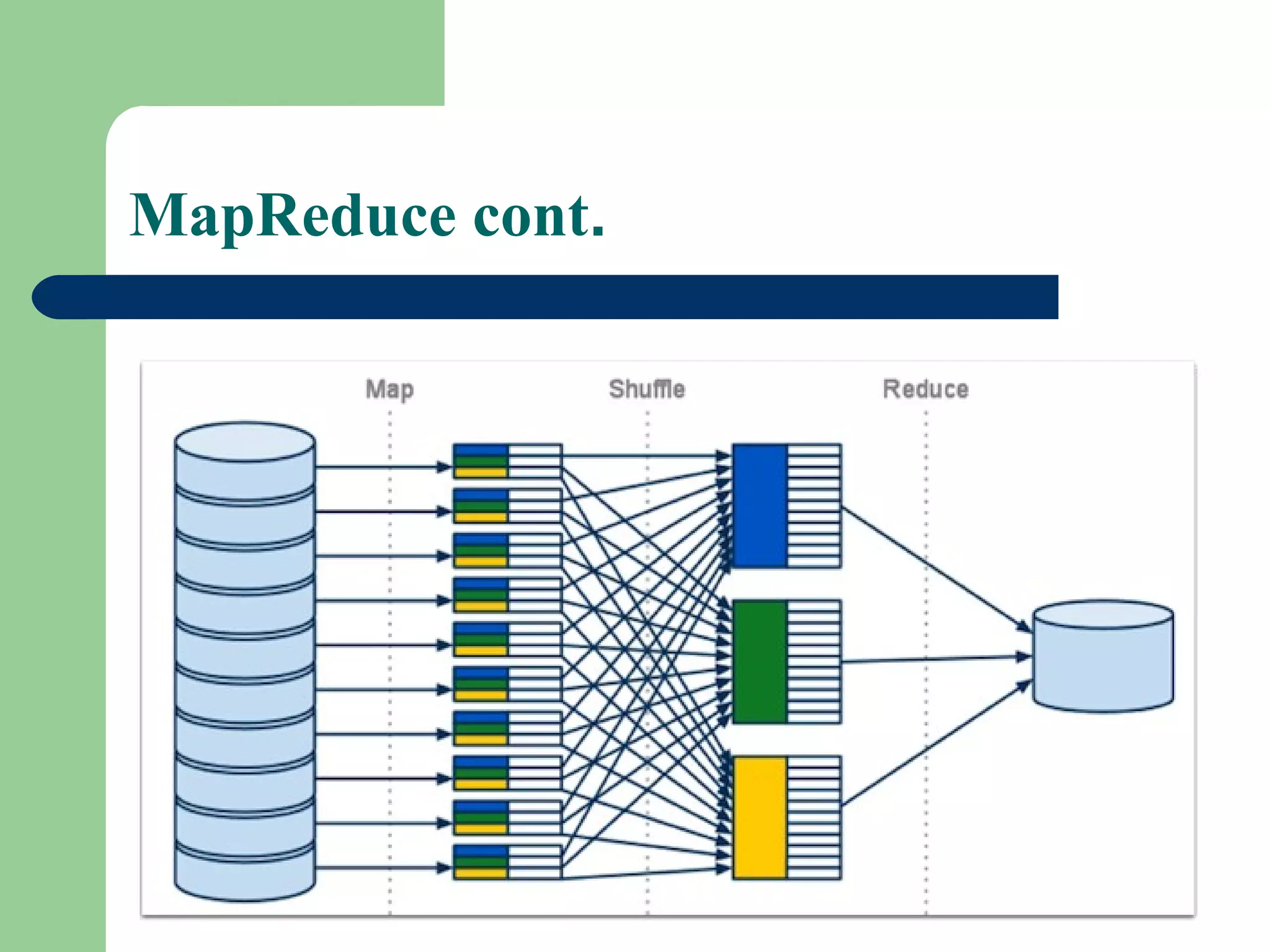
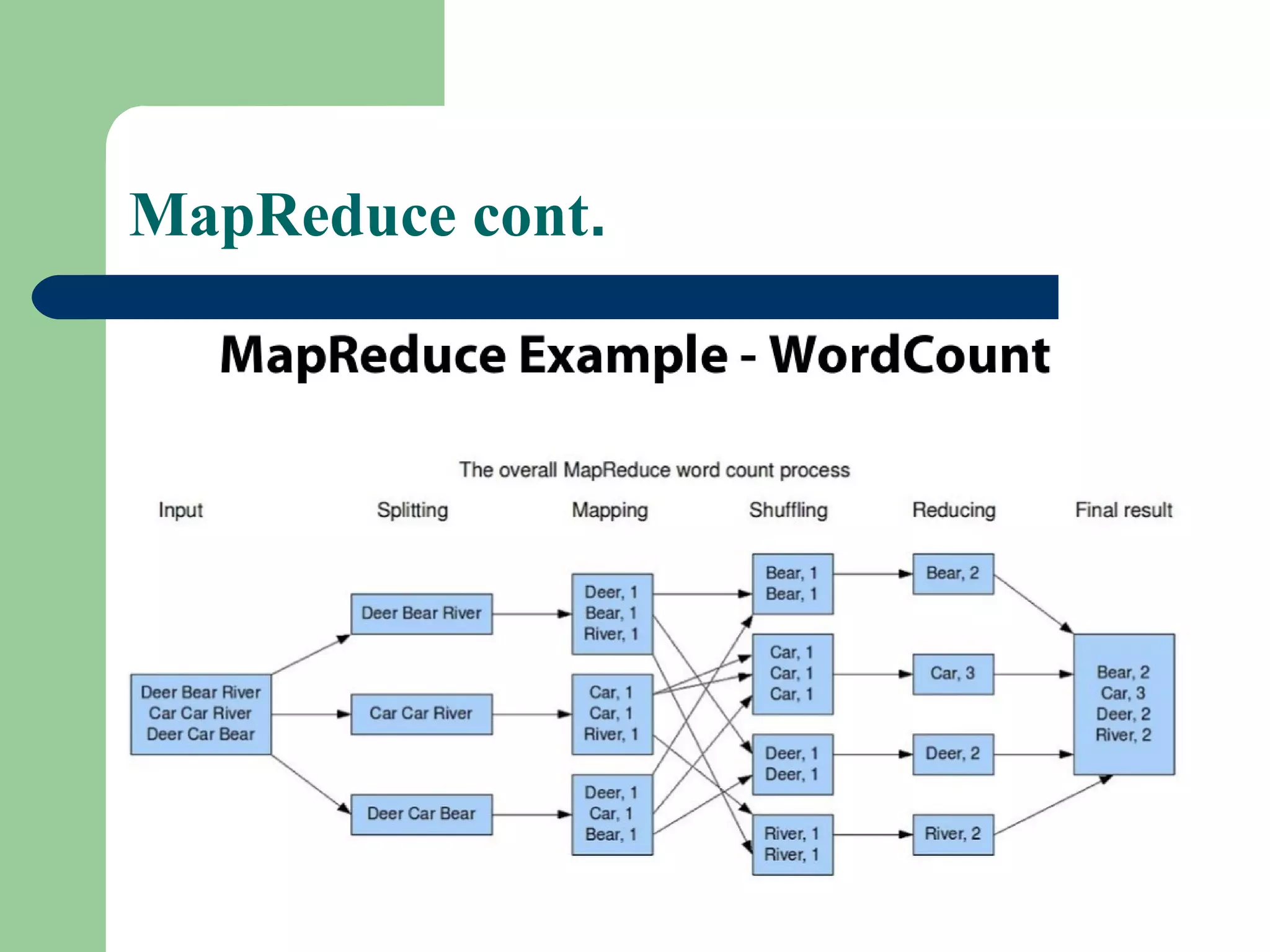
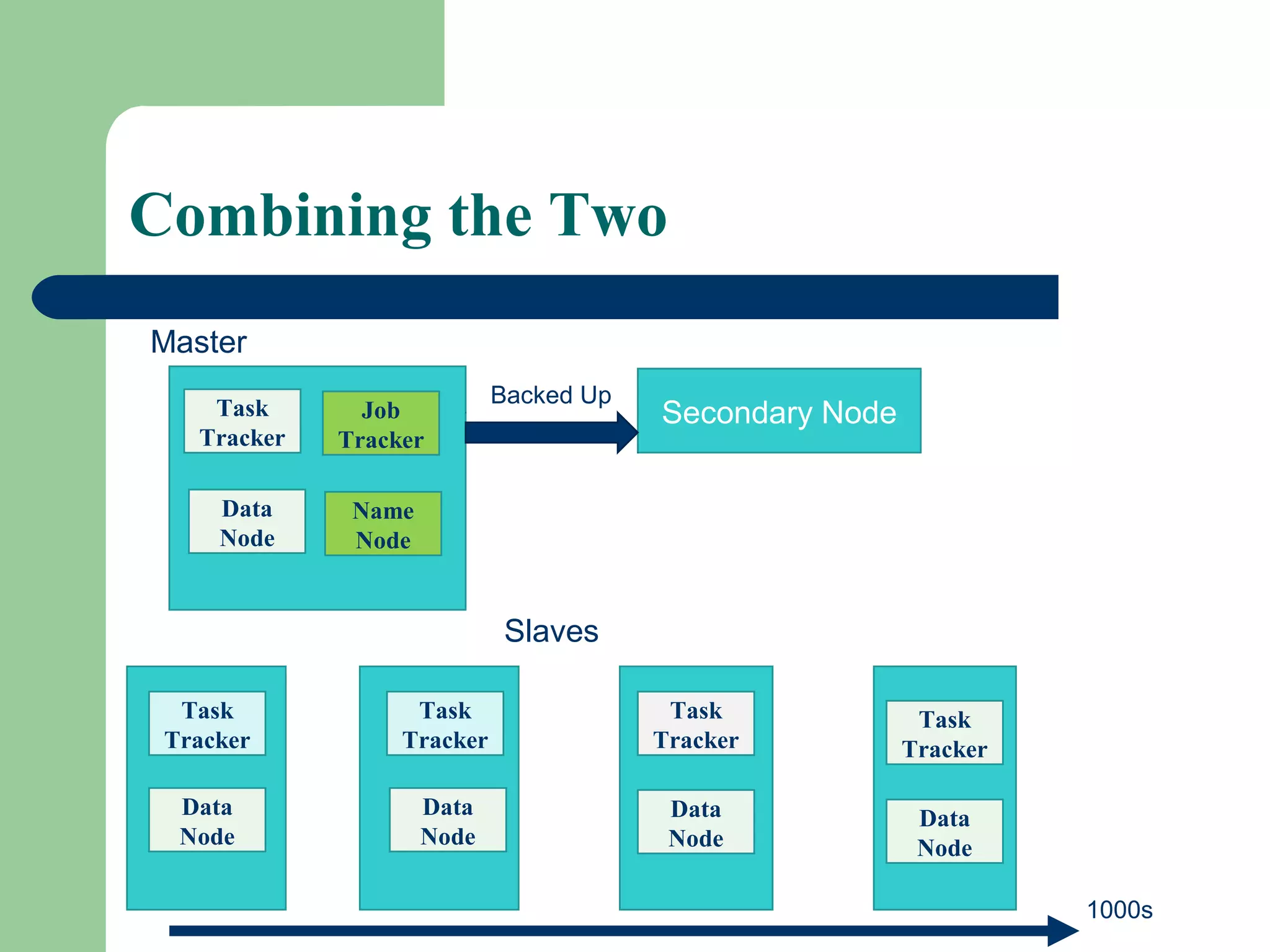
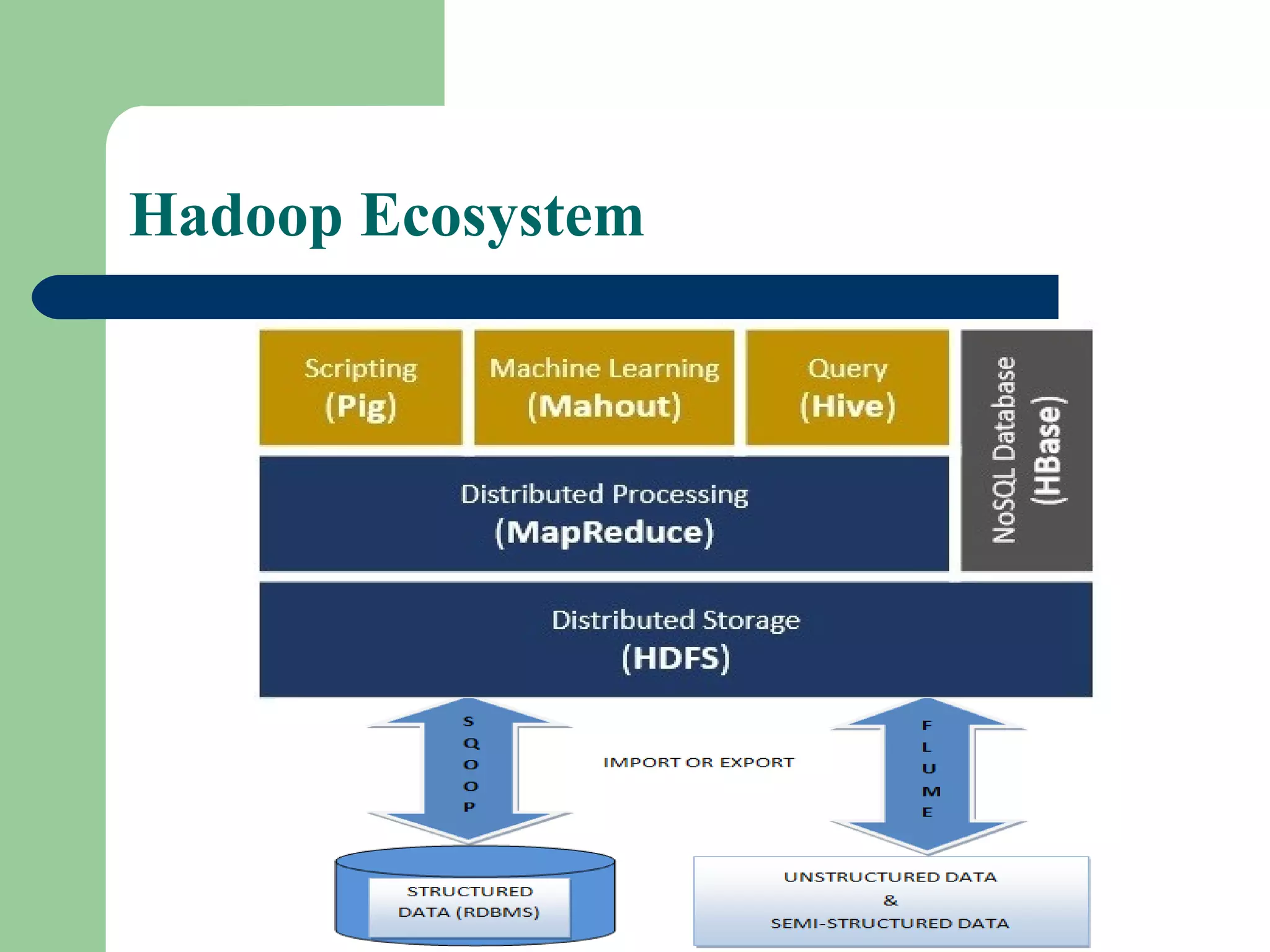
This document provides an overview of big data and Hadoop. It defines big data as large volumes of unstructured data that are too costly and time-consuming to load into traditional databases. It notes that big data comes from various sources like web data, social networks, and sensor data. The challenges of big data include slow disk speeds and the need for parallel processing. Hadoop is introduced as an open-source framework that uses HDFS for storage across clusters and MapReduce for parallel processing of large datasets. Key aspects of HDFS and MapReduce are summarized.