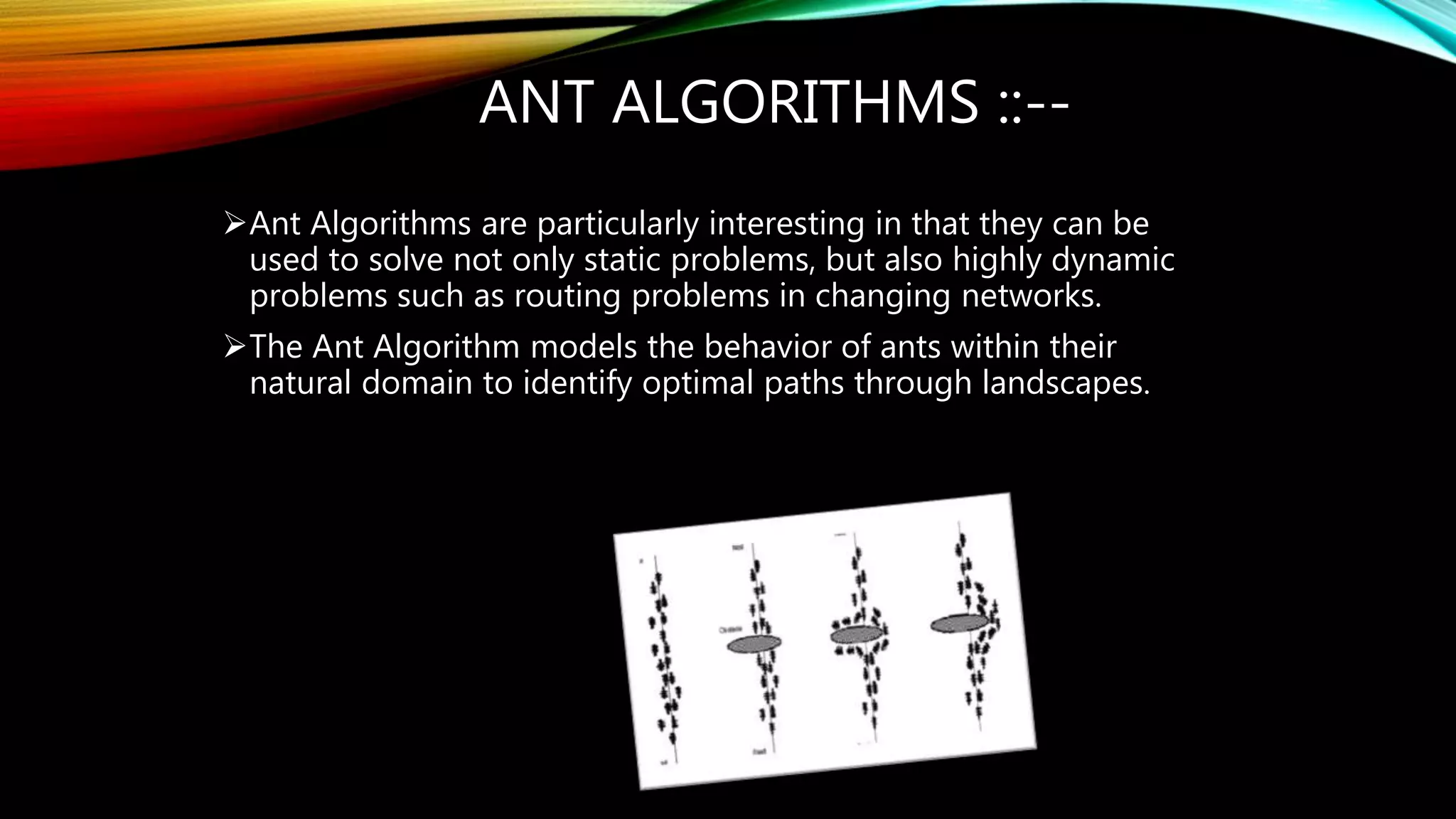
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence including definitions, history, and common techniques. It discusses genetic algorithms, ant algorithms, neural networks, fuzzy logic, and branches of AI such as machine learning. The history of AI is explored from the 1940s to today. Methods for achieving AI are described as top-down (symbolic) and bottom-up (connectionist). In conclusion, AI is presented as both an initially solvable but ultimately thorny technology, with early promises not fully realized but work continuing today.