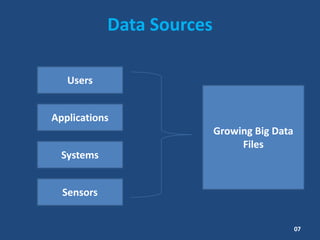
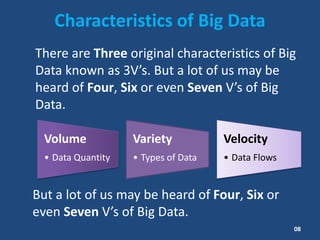
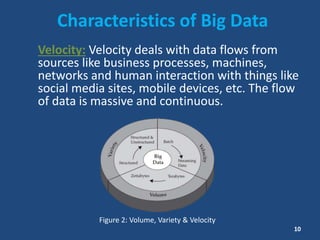
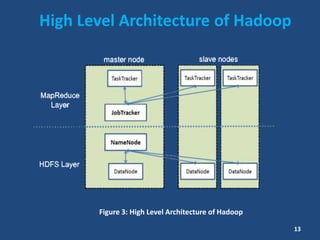
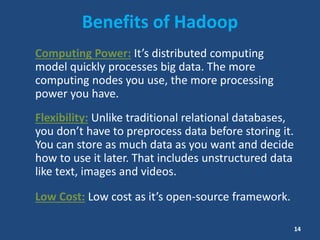
This document contains information about a group project on big data. It lists the group members and their student IDs. It then provides a table of contents and summaries various topics related to big data, including what big data is, data sources, characteristics of big data like volume, variety and velocity, storing and processing big data using Hadoop, where big data is used, risks and benefits of big data, and the future of big data.