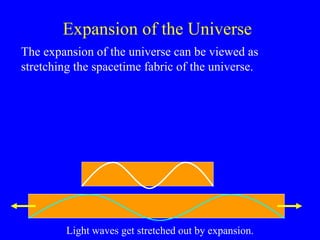
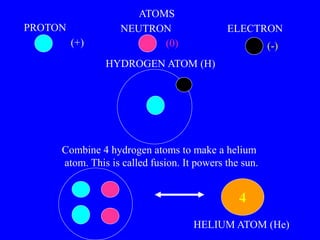
The document discusses the origin and expansion of the universe according to the Big Bang theory. It provides evidence that the universe began in an enormous explosion known as the Big Bang around 13.8 billion years ago. The universe has been expanding ever since, as evidenced by the observation that galaxies are moving away from us in all directions. The document also notes the discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation, which provides further evidence of the Big Bang.