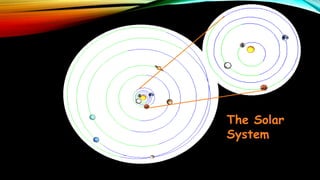
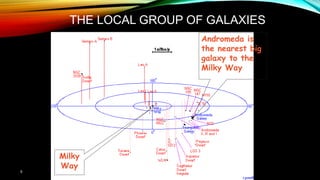
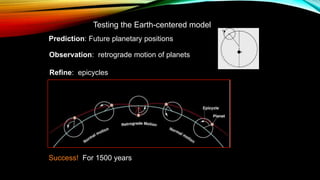
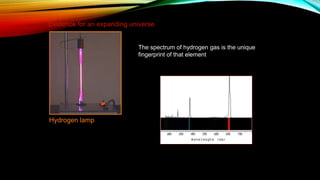
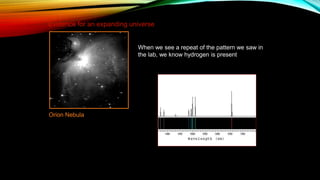
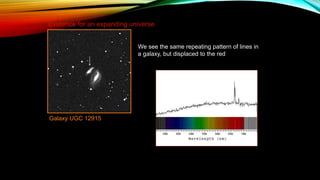
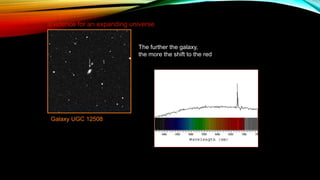
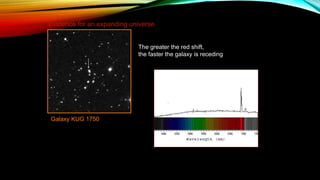
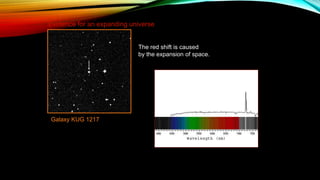
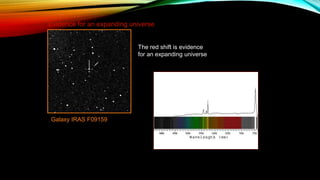
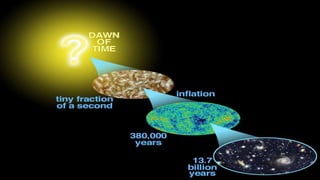
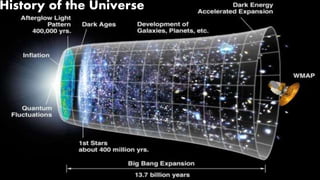
This document provides an overview of the size and evolution of the universe from the perspective of Earth. It begins with a description of the solar system and Milky Way galaxy before expanding out to discuss the immense size of the observable universe. The remainder of the document discusses the history of cosmological theories about the origin and structure of the universe from ancient cultures through modern times. It outlines the progression from geocentric to heliocentric to modern Big Bang models, highlighting evidence like galaxy redshifts that support an expanding universe evolving over billions of years.