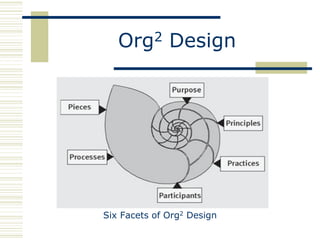
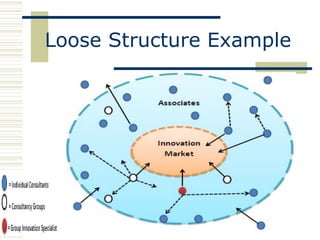
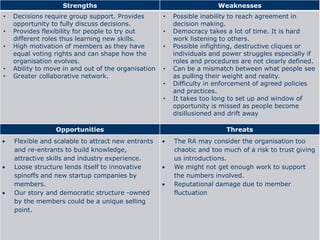
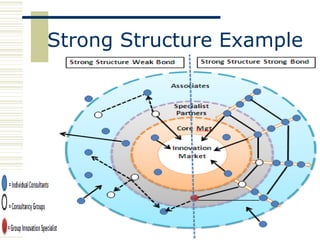
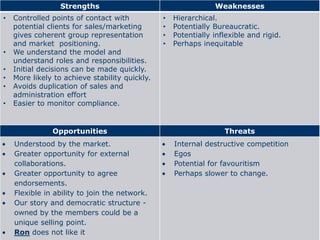
The document discusses organizational design approaches and loose versus strong organizational structures. It presents the six facets of Org2 design - purpose, principles, practices, participants, processes, and pieces. Examples are given for how a loose and strong structure could work in practice for an innovation organization. Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats are listed for each structure type. The document aims to analyze different organizational design models and considerations for structure.