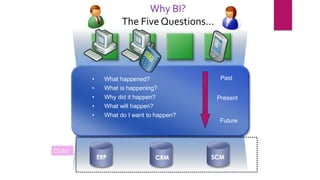
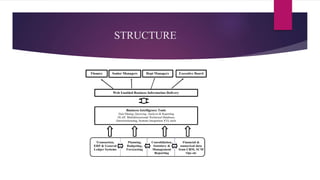
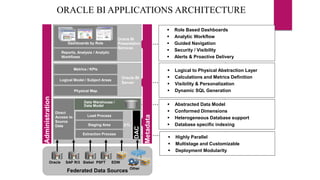
Business intelligence (BI) is software and solutions that collect, analyze, and provide access to data to help users make better decisions. It includes tools like data warehousing, reporting, data mining, and dashboards. BI has grown significantly in recent years and is applied across industries like customer relationship management, supply chain management, and enterprise resource planning. It provides faster and more accessible reports to answer questions about past, present, and future business performance and goals.