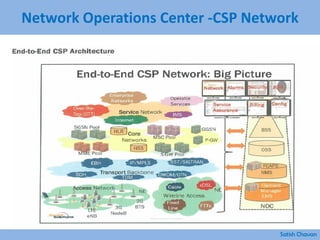
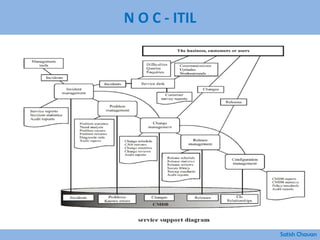
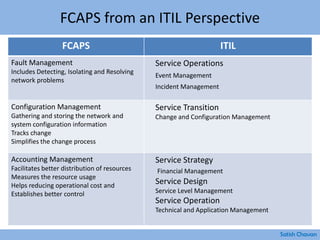
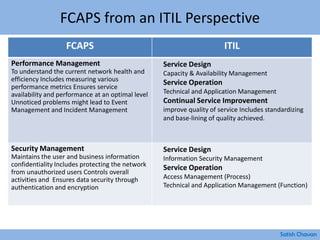
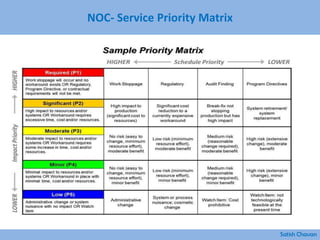
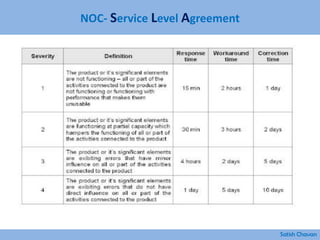
The document discusses best practices for building a network operations center (NOC). Some key points:
- A NOC monitors and controls network activity from one or more locations. Early versions date back to the 1960s when AT&T opened centers to monitor switches and routes.
- Modern NOCs use network monitoring software and sophisticated systems to detect issues across multiple layers of the network before they impact the business.
- Maintaining skilled staff, efficient processes, integrated tools, automation, and a focus on performance, security and being proactive are characteristics of an effective NOC.