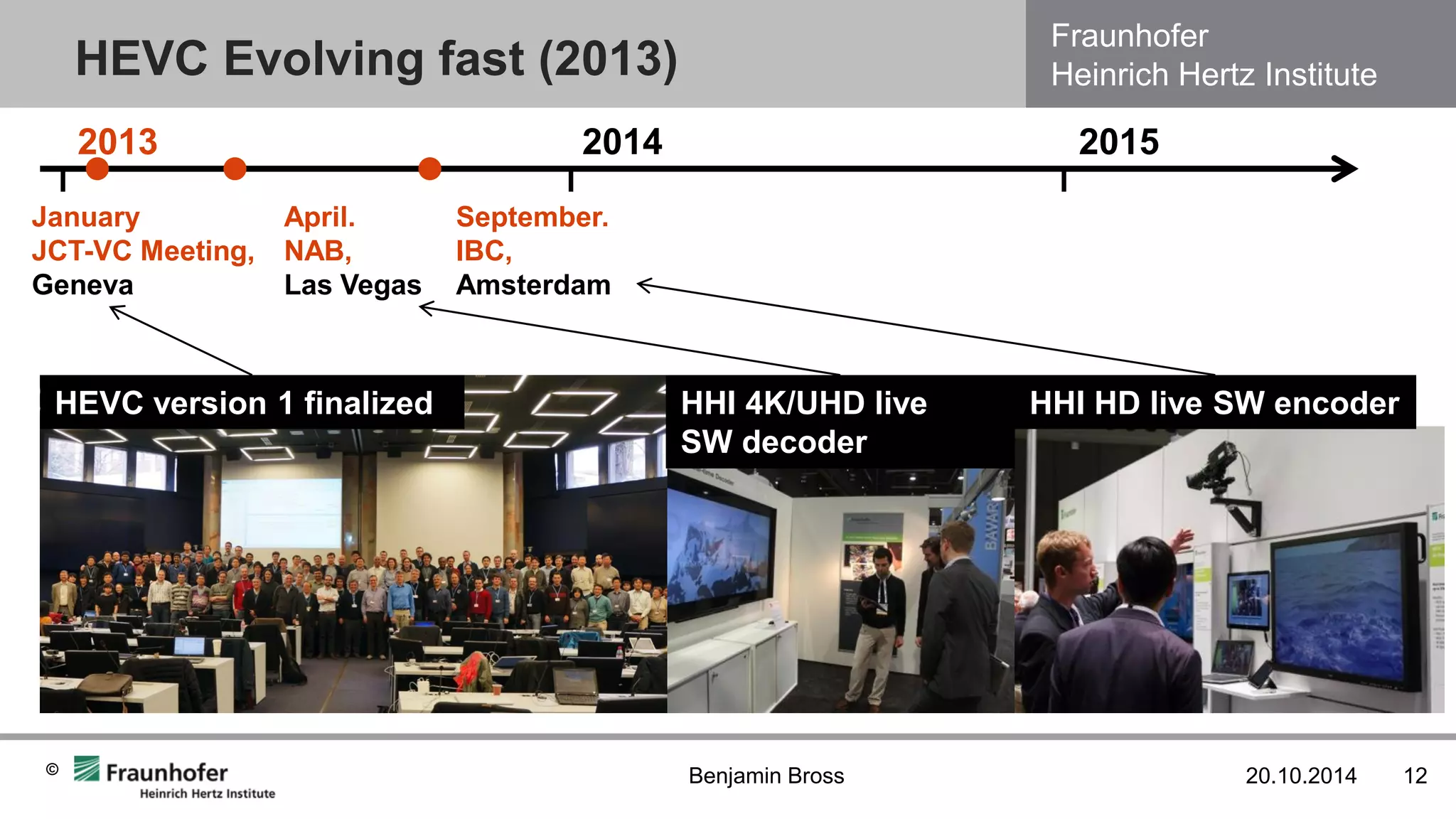
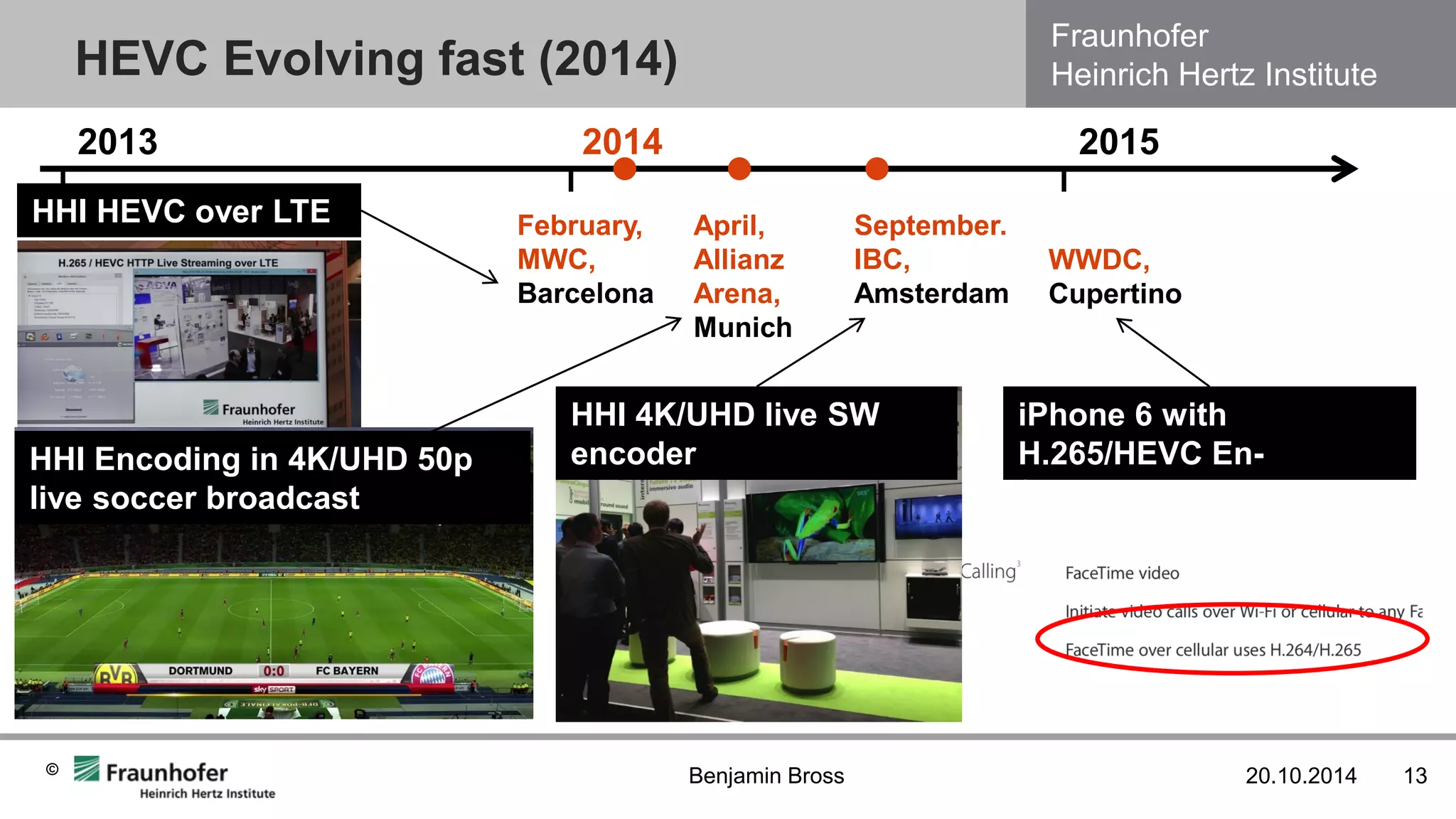
The document discusses the H.265/HEVC video coding standard. It provides an overview of HEVC version 1.0 and its extensions, including its coding efficiency compared to prior standards. Studies show HEVC achieves 50% bitrate reduction over H.264/AVC for the same subjective quality. For low delay applications, HEVC requires 48-73% fewer bits than VP9 or H.264/AVC encoders. While reference encoders are slow, real-time encoders have approached the coding efficiency of the reference within 1.5 years. Future extensions include higher color depths, multiview, and scalable coding.

![Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute
©
Several studies reporting bitrate savings of H.265/HEVC HM Reference Encoder for the same objective/subjective quality:
HEVC 1.0 – Performance
20.10.2014
5
Benjamin Bross
AVC HP
VP9
AVC HP
VP9
Encoder
Sequences
Objective [PSNR]
Subjective [MOS]
Objective [PSNR]
Subjective [MOS]
Objective [PSNR]
Objective [PSNR]
AVC
VP9
[1] Ohm2012
35%
49%
40%
JSVM
JCT-VC
[2] Grois2013
39%
43%
x264
WebM
JCT-VC
(Class A,B,E, F)
[3] Rerabek2014
39%
53%
36%
49%
JM
WebM
4K
[4] Grois2014
41%
33%
x264
WebM
JCT-VC
(Class E)
Entertainment (Random Access)
Interactive (Low Delay)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benjaminbrossfraunhoferhhih-141106060651-conversion-gate01/75/The-H-265-MPEG-HEVC-Standard-5-2048.jpg)
![Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute
©
Several studies reporting bitrate savings of H.265/HEVC HM Reference Encoder for the same objective/subjective quality:
HEVC 1.0 – Performance
20.10.2014
6
Benjamin Bross
AVC HP
VP9
AVC HP
VP9
Encoder
Sequences
Objective [PSNR]
Subjective [MOS]
Objective [PSNR]
Subjective [MOS]
Objective [PSNR]
Objective [PSNR]
AVC
VP9
[1] Ohm2012
35%
49%
40%
JSVM
JCT-VC
[2] Grois2013
39%
43%
x264
WebM
JCT-VC
(Class A,B,E, F)
[3] Rerabek2014
39%
53%
36%
49%
JM
WebM
4K
[4] Grois2014
41%
33%
x264
WebM
JCT-VC
(Class E)
Entertainment (Random Access)
Interactive (Low Delay)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benjaminbrossfraunhoferhhih-141106060651-conversion-gate01/75/The-H-265-MPEG-HEVC-Standard-6-2048.jpg)
![Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute
©
HEVC 1.0 – Low Delay Performance
20.10.2014
7
Benjamin Bross
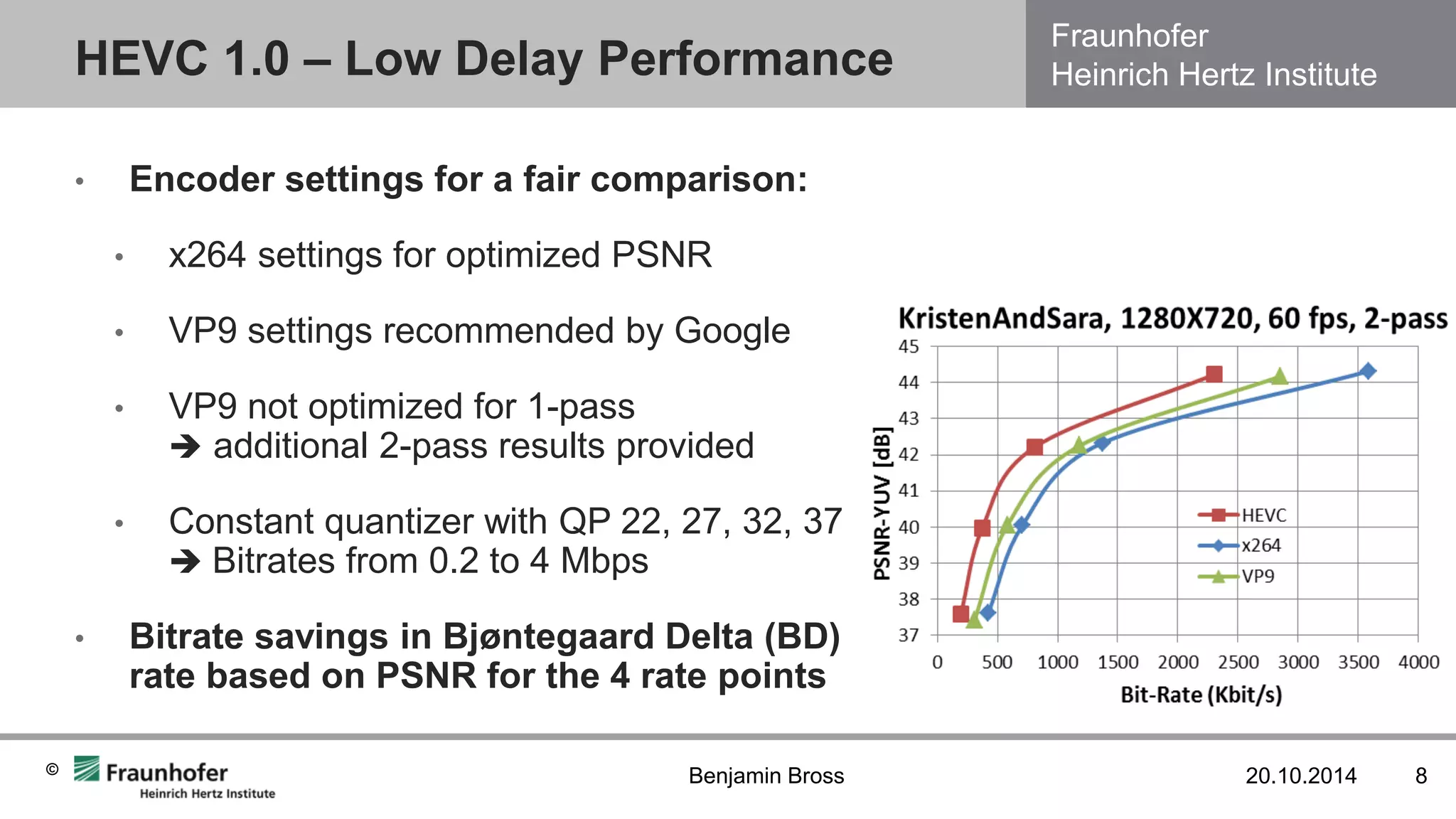
Low Delay performance study from Grois et al [4]:
•Tested publicly available encoders:
•H.265/HEVC HM reference encoder
•H.264/AVC x264 r2334
•VP9 WebM v1.2.0-3088-ga81bd12
•IPPP coding structure (I-picture followed by P-pictures)
•Three JCT-VC 720p60 class E test sequences](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benjaminbrossfraunhoferhhih-141106060651-conversion-gate01/75/The-H-265-MPEG-HEVC-Standard-7-2048.jpg)
![Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute
©
HEVC 1.0 – Low Delay Performance
20.10.2014
9
Benjamin Bross
•For same objective quality (PSNR), VP9 and x264 have significant bitrate overhead:
•VP9 48% more than HM
•x264 73% more than HM
•2nd pass encoding does not gain much for low delay
•Runtime differences by factor ~103 between x264 and reference encoders (HM and VP9)
1
10
100
1000
10000
0
20
40
60
80
Encoding Speedup
Bitrate overhead to HEVC HM in BD-rate [%]
VP9 (1-pass)
VP9 (2-pass)
x264 (1-pass)
x264 (2-pass)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benjaminbrossfraunhoferhhih-141106060651-conversion-gate01/75/The-H-265-MPEG-HEVC-Standard-9-2048.jpg)
![Fraunhofer Heinrich Hertz Institute
©
[1] Ohm et al, “Comparison of the Coding Efficiency of Video Coding Standards – Including High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC) ”, IEEE Trans. CSVT, Dec. 2012
[2] Grois et al, “Performance comparison of H.265/MPEG-HEVC, VP9, and H.264/MPEG-AVC encoders”, PCS 2013
[3] Rerabek et al, “Comparison of compression efficiency between HEVC/H.265 and VP9 based on subjective assessments”, SPIE Proc. 9217, 2014
[4] Grois et al, “Comparative Assessment of H.265/MPEG-HEVC, VP9, and H.264/MPEG-AVC Encoders for Low-Delay Video Applications”, SPIE Proc. 9217, 2014
The H.265/MPEG-HEVC Standard
20.10.2014
15
Benjamin Bross](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/benjaminbrossfraunhoferhhih-141106060651-conversion-gate01/75/The-H-265-MPEG-HEVC-Standard-15-2048.jpg)
