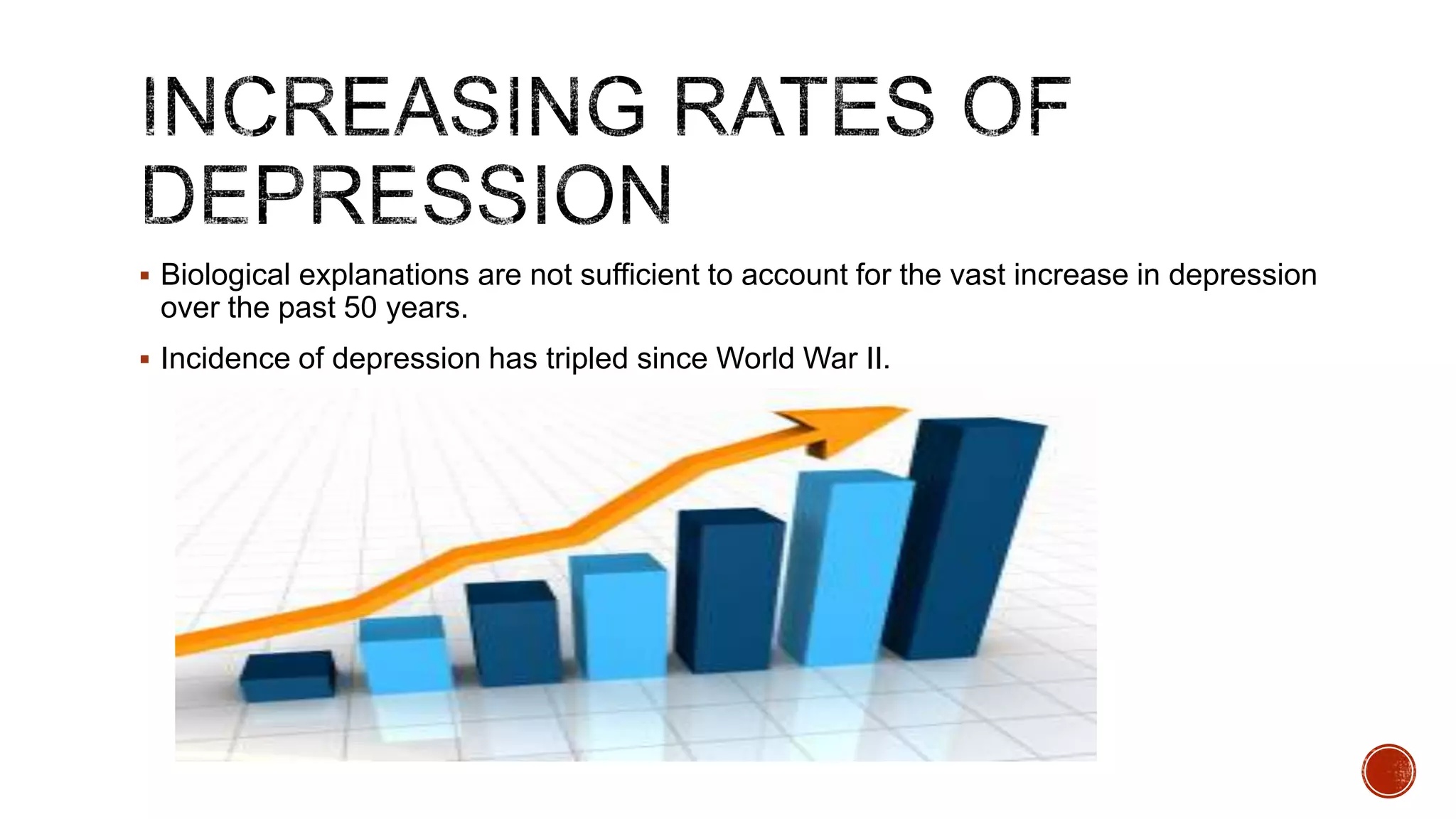
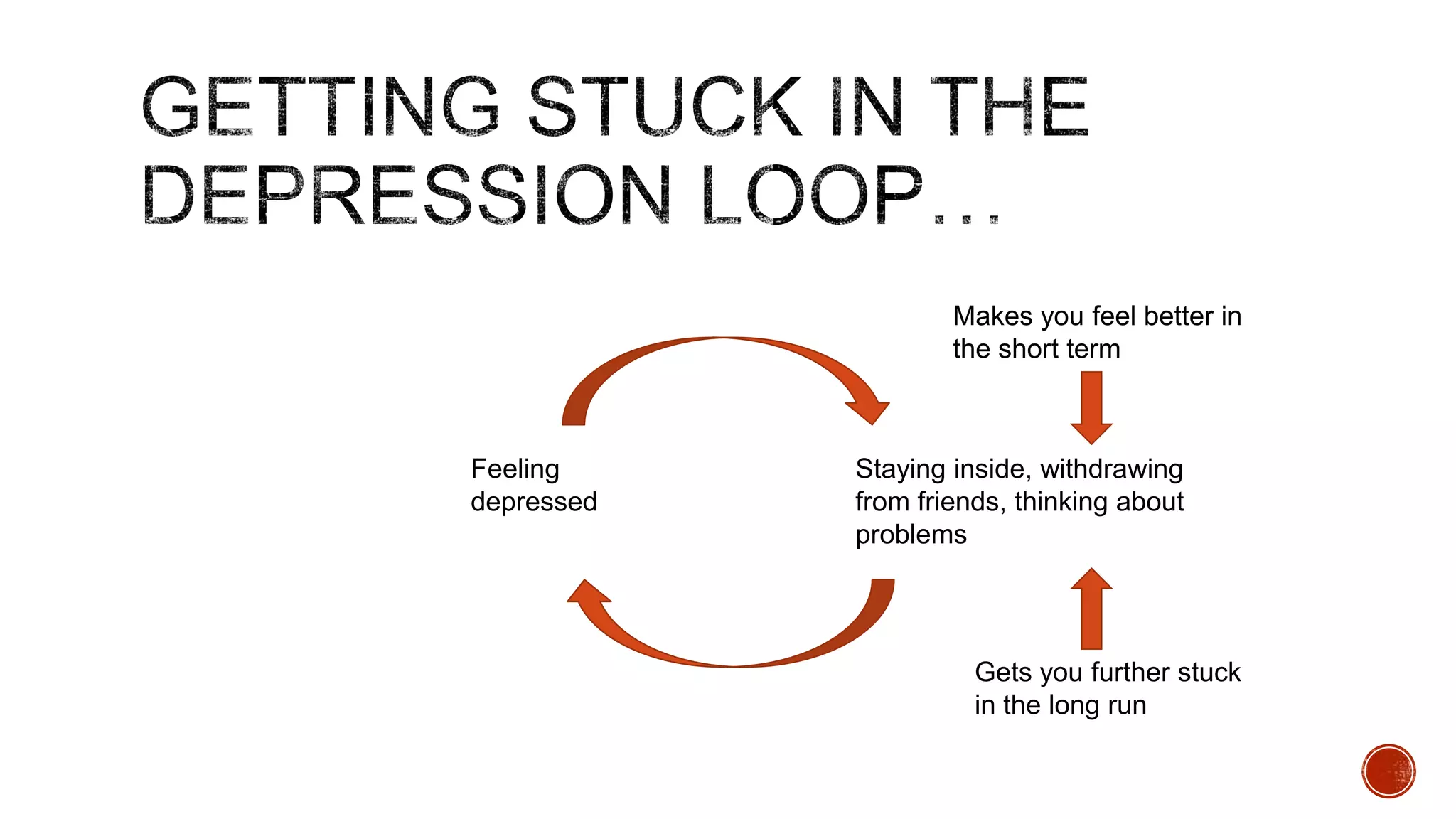
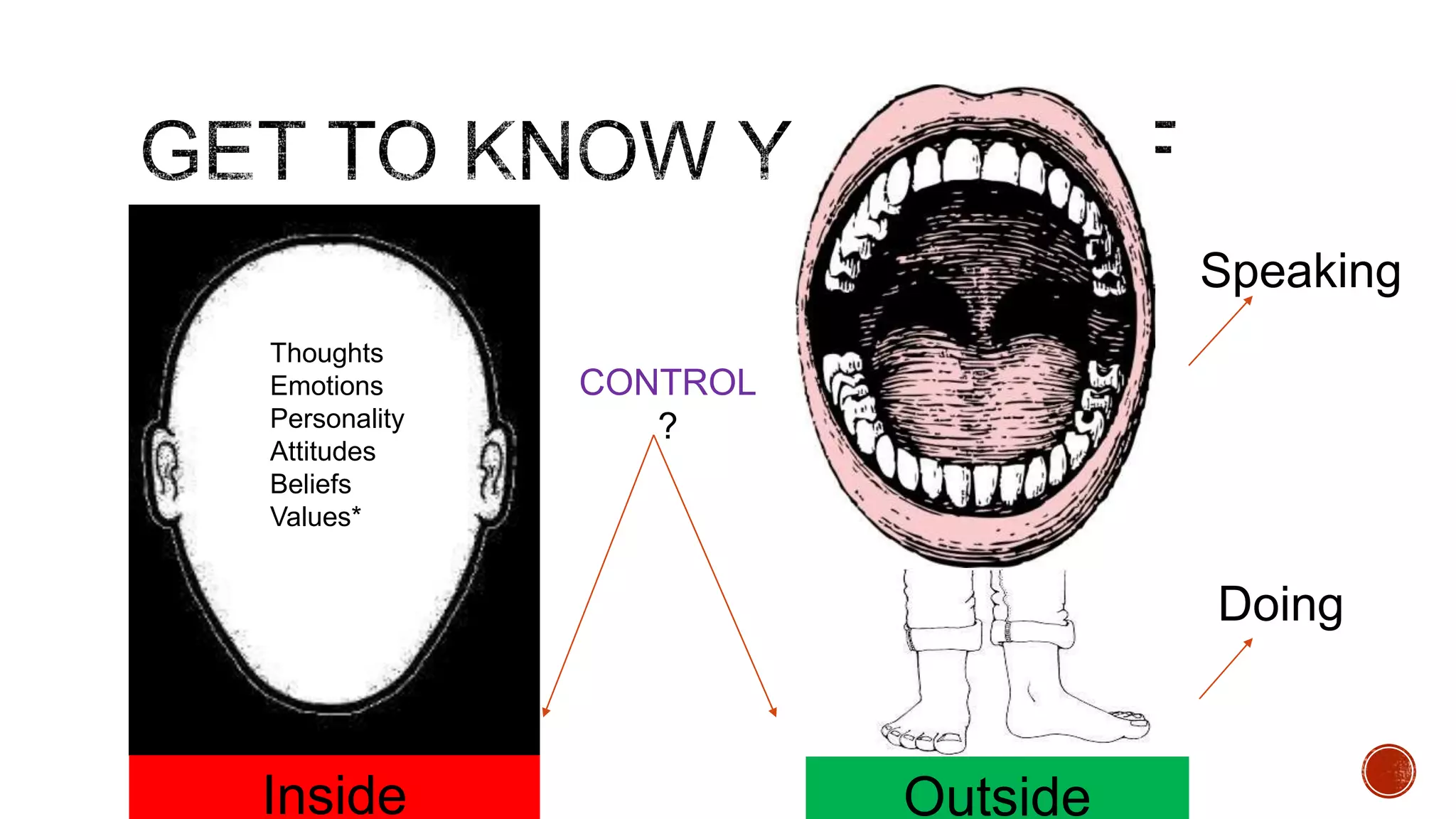
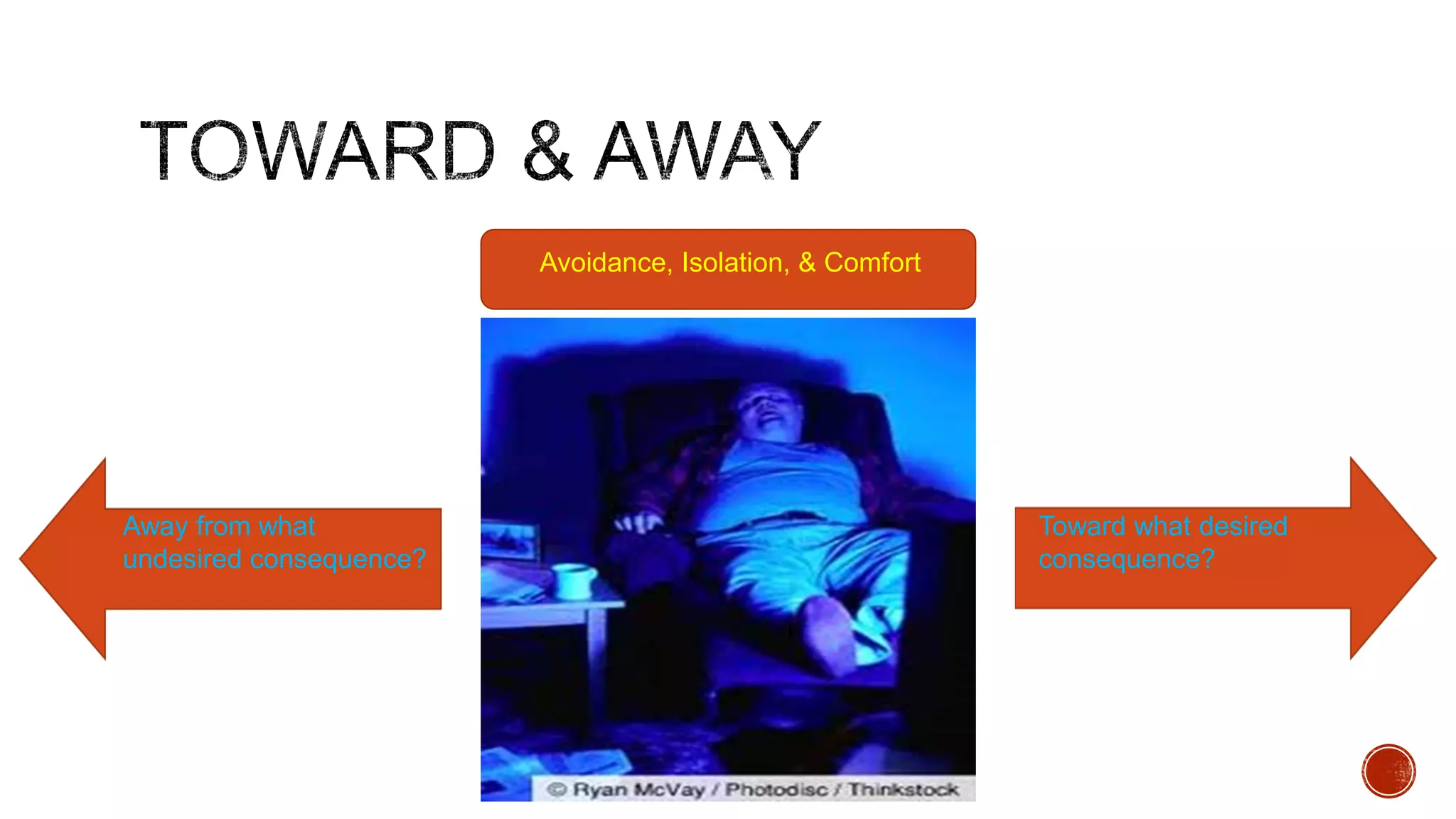
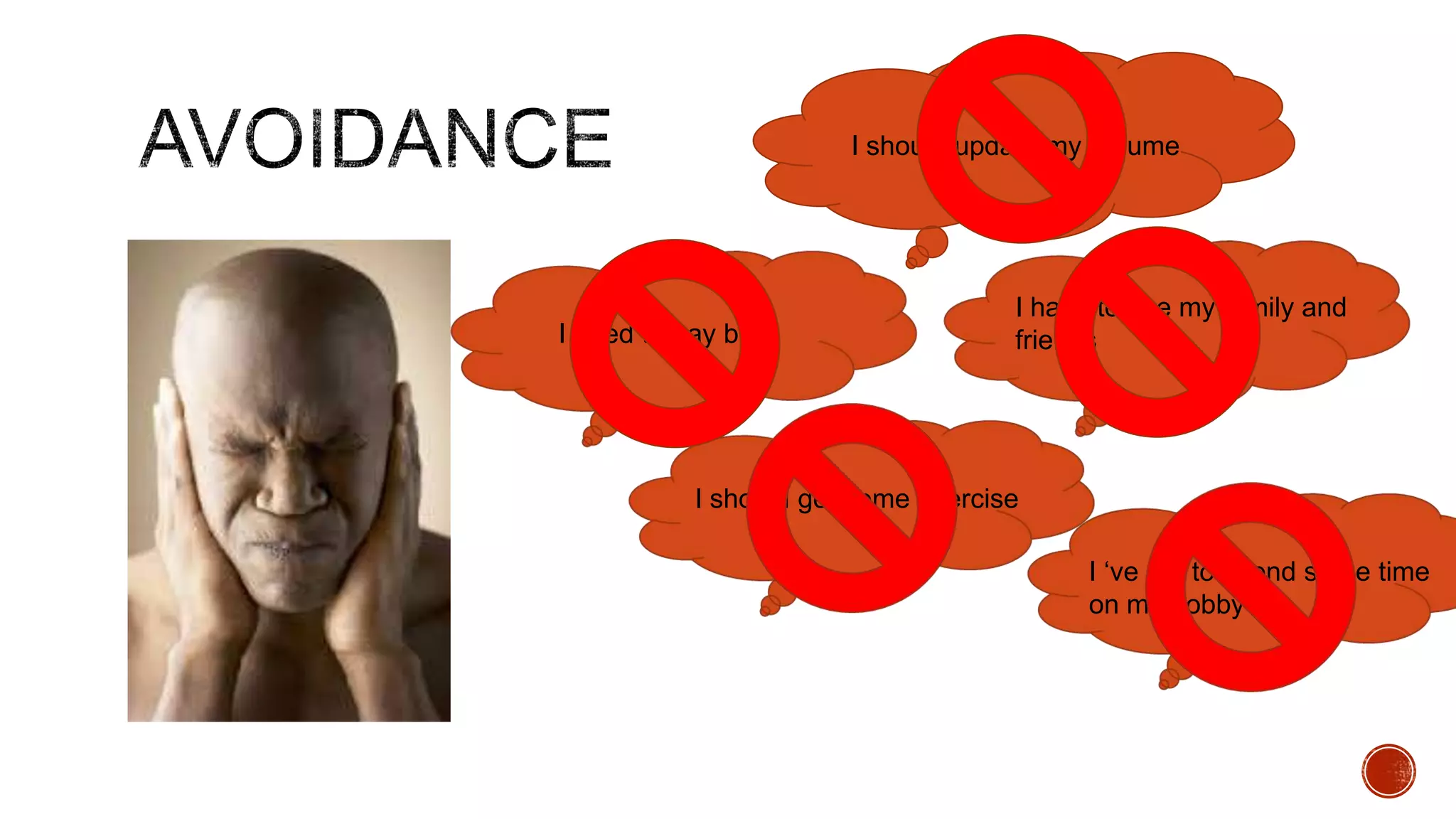
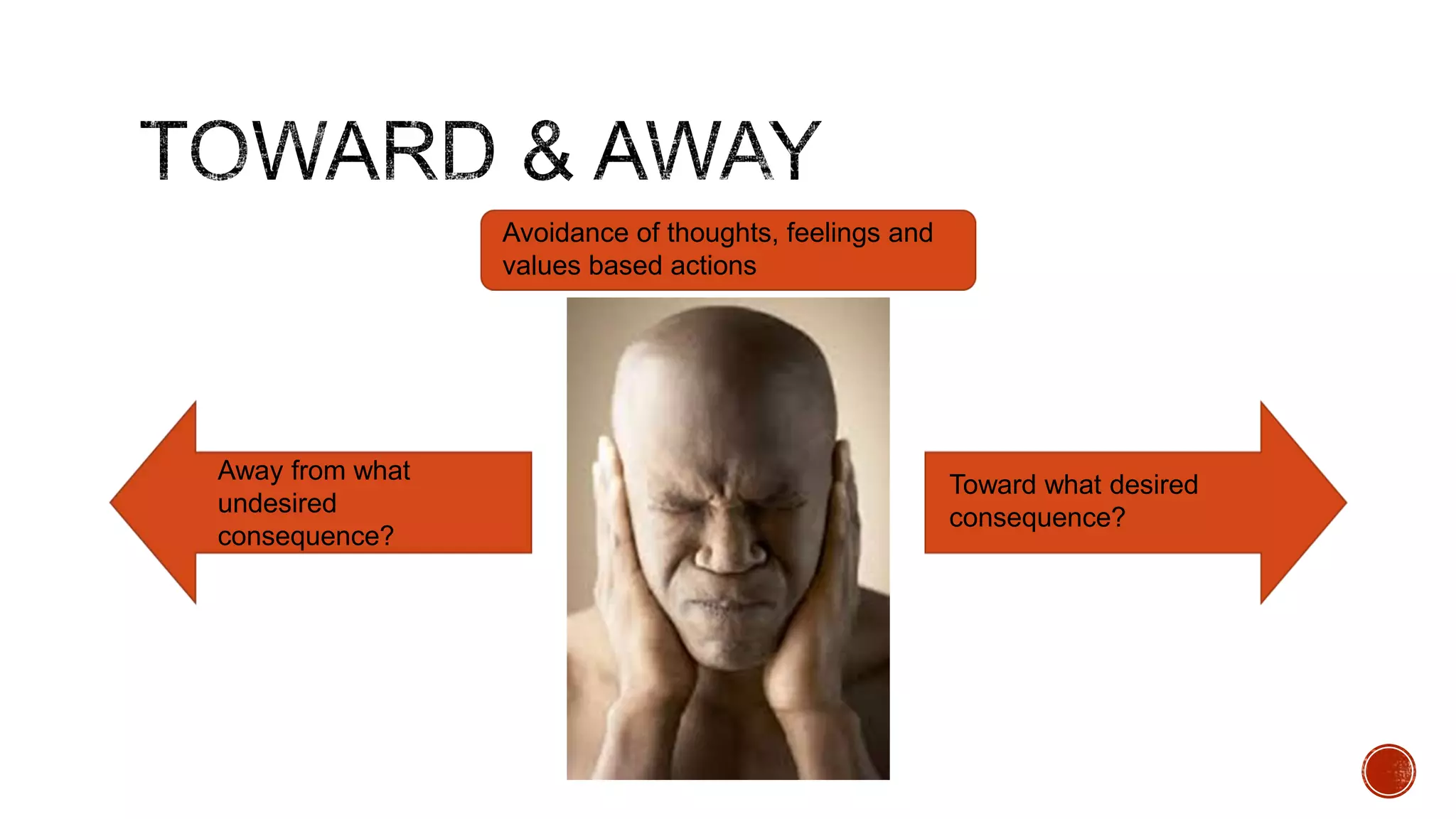
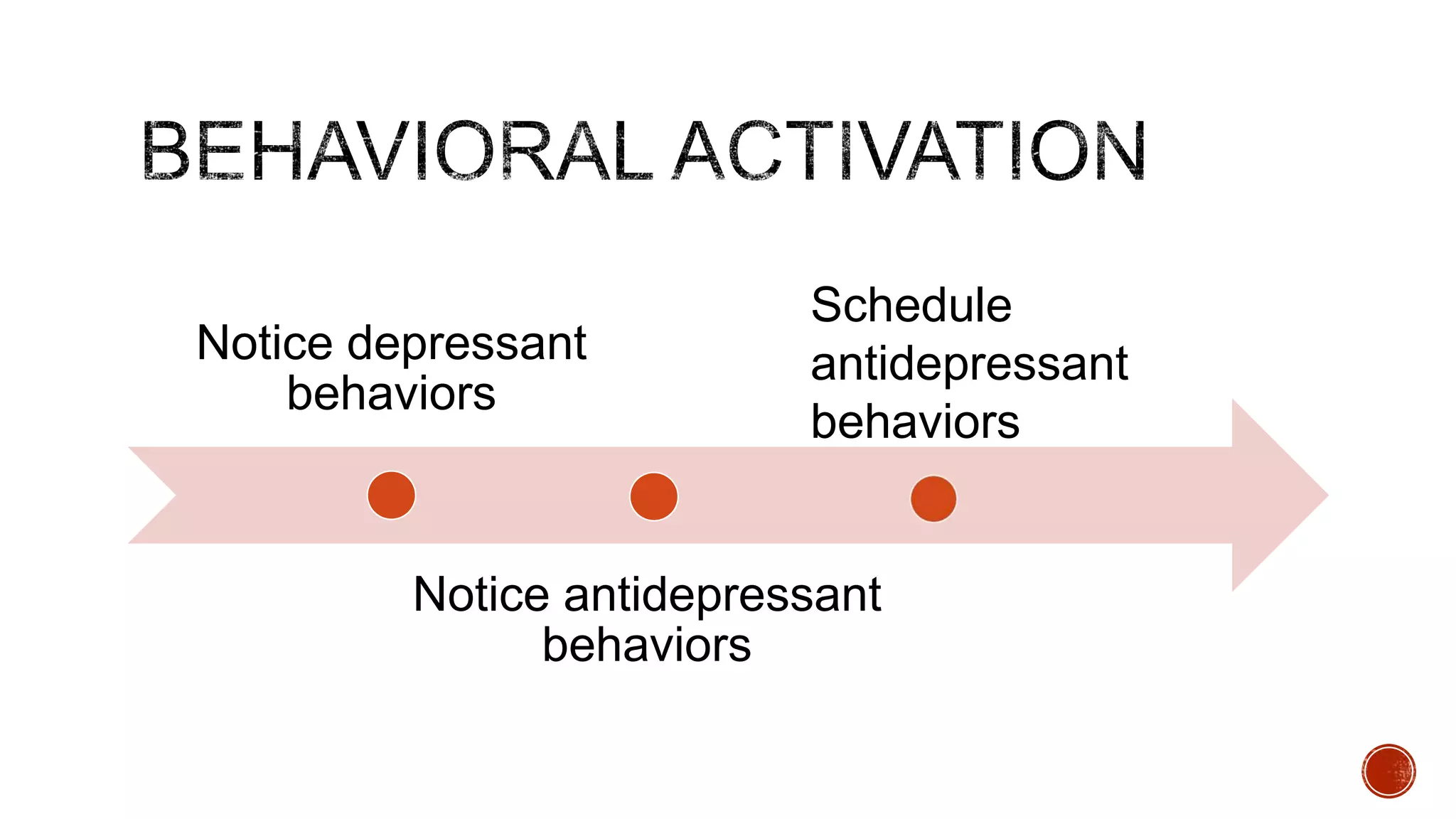
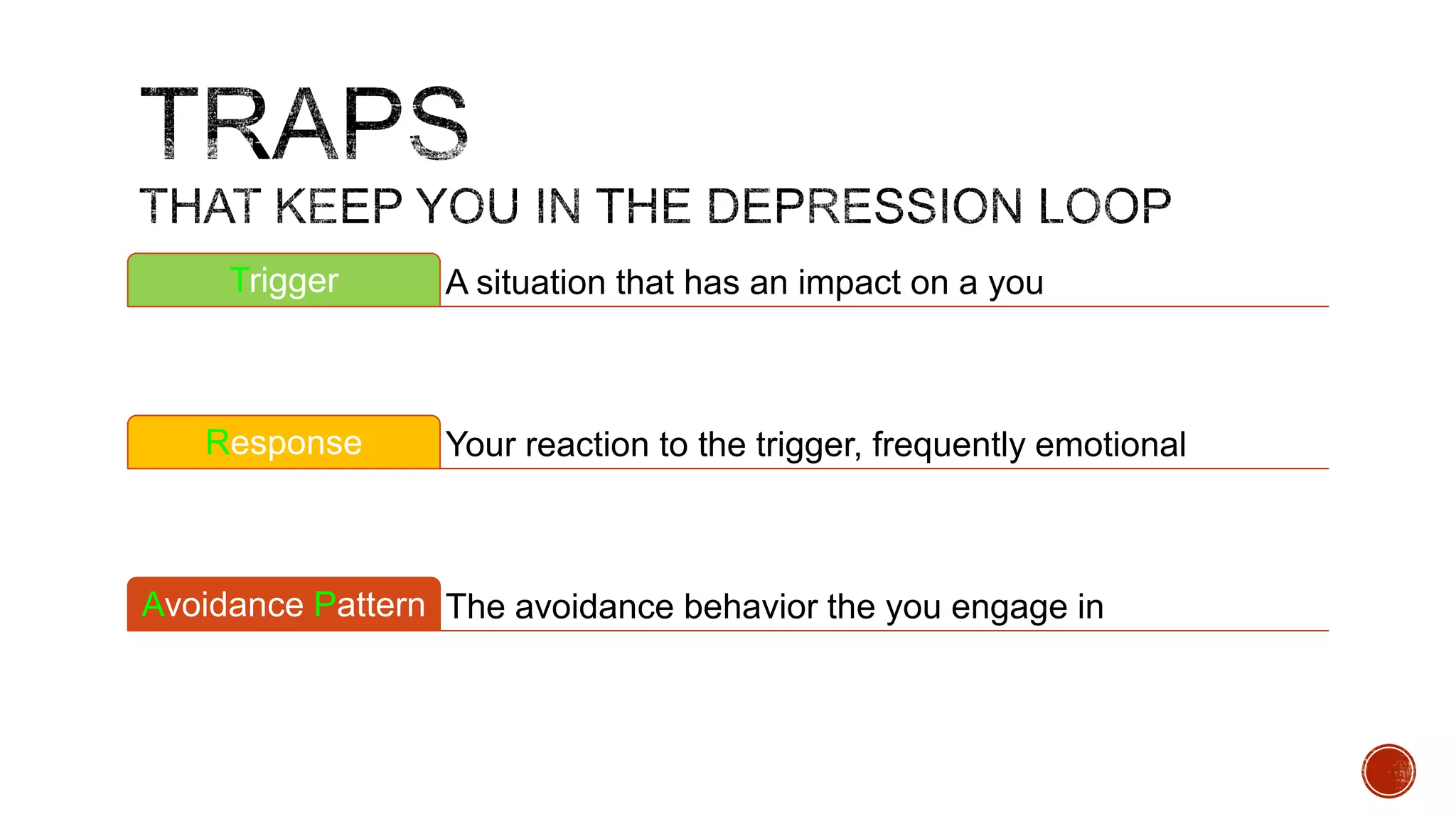
The document discusses theories about why rates of depression have increased dramatically in recent decades. While biological factors are involved, they are insufficient to explain such a large rise. Theories discussed include that depression results from biological, behavioral, cognitive, and interpersonal factors interacting. Rates of depression also differ across cultures and time periods. Rumination, avoidance, isolation, and withdrawal from social support are behaviors associated with depression that paradoxically maintain the condition long-term rather than providing short-term relief.