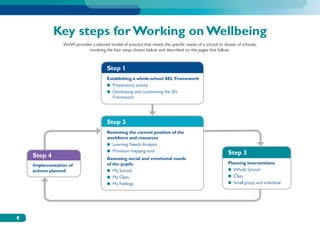
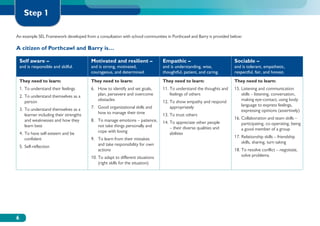
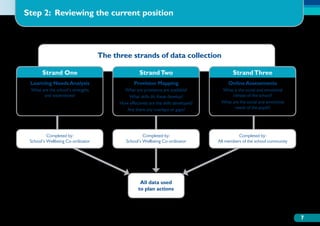
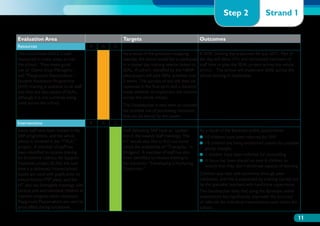
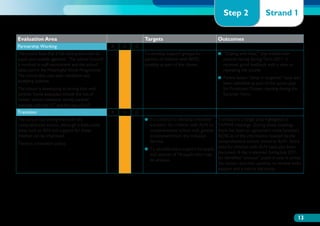
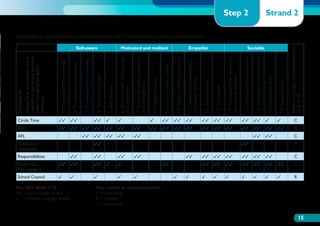
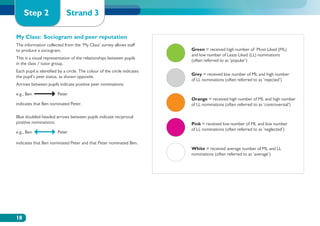
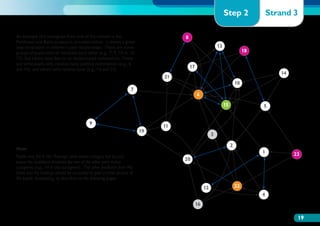
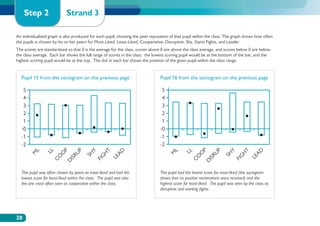
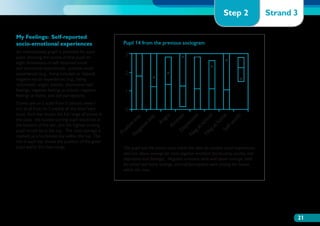
The document discusses the Working on Wellbeing project, which aims to help schools develop comprehensive approaches to social and emotional learning. This includes identifying and meeting students' social and emotional needs. The project recognizes that behavior is influenced by students' social and emotional development and environment both in and out of school. As such, the project helps schools create a positive climate that promotes wellbeing and social/emotional skills. It outlines four key steps: 1) Establishing a whole-school social/emotional framework 2) Reviewing the current position 3) Planning interventions 4) Implementing planned actions. The appendices provide examples from related projects.