This document defines and describes basic geometry terms including:
- Geometry is the branch of mathematics concerned with shapes, their properties, and spatial relationships.
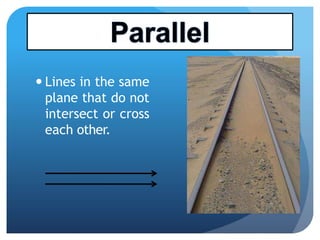
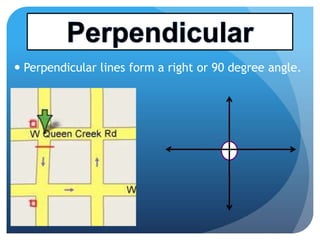
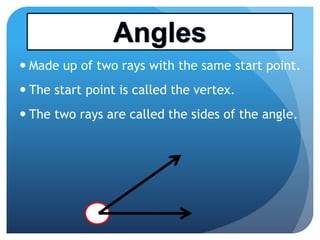
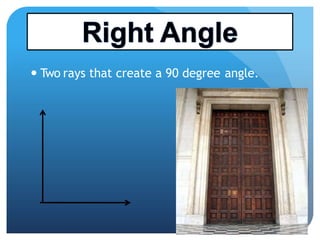
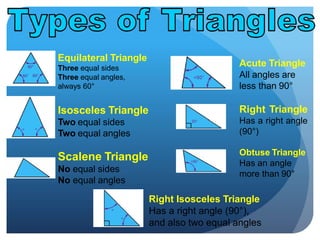
- It defines types of lines, angles, and their properties. Common line types include rays, segments, and parallel/perpendicular lines. Common angle types include acute, obtuse, right, and straight angles.
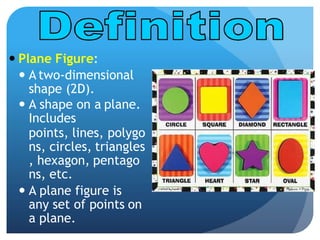
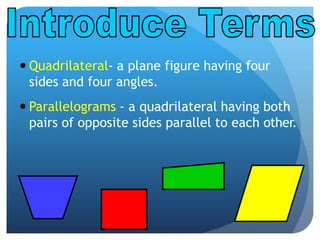
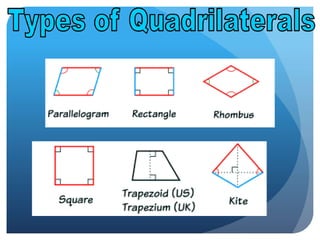
- Plane figures are two-dimensional shapes defined by points and lines on a flat surface. Common plane figures include polygons, circles, and quadrilaterals.
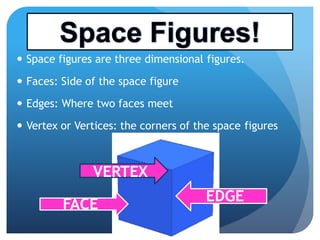
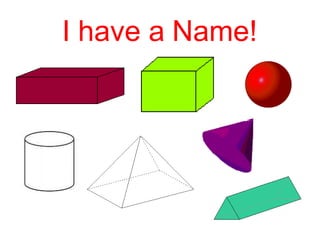
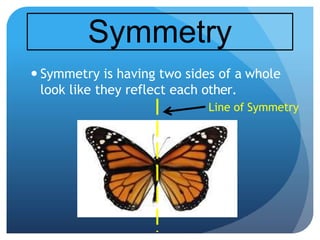
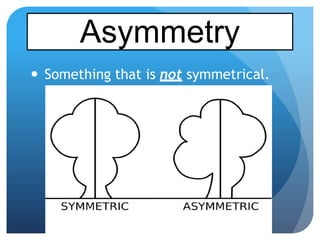
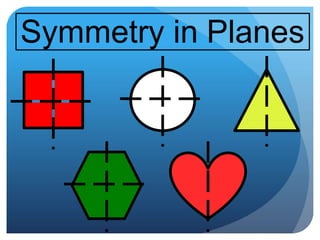
- Space figures are three-dimensional shapes with faces, edges, and vertices. Examples given are tessellations and symmetry in planes and space.