Recommended
PPTX
activity 1 power point presentations in geometry
PPT
Geometry Power Point 5th grade
PDF
Introduction to Basic Geometry
PPTX
Introduction-to-Geometry (1)Building Blocks of Geometry .pptx
PPTX
introductiontobasicgeometricterms-210316005542 (1).pptx
PPTX
Application of geometry in real life
PPTX
PPT
PDF
basics of geometry with practical images
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Geometry basics things to understand geometry.pptx
PDF
presentationofmaths-160226144340.pdf
PPTX
bcfse ewew/120455 Geometry 01 Basics of Geometry.pptx
PPT
Geometry and measurement review
PPT
PPTX
Geometry: Chapters 1-3 Vocabulary
PPTX
PDF
PDF
Geometry 1 basic definitions
PPT
CABT Math 8 - Basics of Geometry
PPT
Geometry sizes and shapes
PDF
PPTX
Instructional Materials in Mathematics
PPTX
ilovepdf_merged.pptx bjmnc. Jb jtcbkknncchkk
PPTX
Geometric deisgns_new.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Emily Treacy Geometry In The Real World Project Block 5 December 2009 Compressed
PPTX
Pokus sa layon tagaganap grade 10 filipino
PPTX
mitolohiya Power point presentation in filipino
More Related Content
PPTX
activity 1 power point presentations in geometry
PPT
Geometry Power Point 5th grade
PDF
Introduction to Basic Geometry
PPTX
Introduction-to-Geometry (1)Building Blocks of Geometry .pptx
PPTX
introductiontobasicgeometricterms-210316005542 (1).pptx
PPTX
Application of geometry in real life
PPTX
PPT
Similar to geometry presentation power point presentation
PDF
basics of geometry with practical images
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Geometry basics things to understand geometry.pptx
PDF
presentationofmaths-160226144340.pdf
PPTX
bcfse ewew/120455 Geometry 01 Basics of Geometry.pptx
PPT
Geometry and measurement review
PPT
PPTX
Geometry: Chapters 1-3 Vocabulary
PPTX
PDF
PDF
Geometry 1 basic definitions
PPT
CABT Math 8 - Basics of Geometry
PPT
Geometry sizes and shapes
PDF
PPTX
Instructional Materials in Mathematics
PPTX
ilovepdf_merged.pptx bjmnc. Jb jtcbkknncchkk
PPTX
Geometric deisgns_new.pptx
PPT
PPTX
Emily Treacy Geometry In The Real World Project Block 5 December 2009 Compressed
More from MarielaAlapapCamba1
PPTX
Pokus sa layon tagaganap grade 10 filipino
PPTX
mitolohiya Power point presentation in filipino
PPTX
plane and solid geometry power point presentation
PPTX
consumer behavior analysis and marketing strategy
PPTX
ANEKDOTA power point presentation filipino 10
PPT
math 208 report fundamental theorem of arithmetic
PPTX
in the set z on integers mathematics 208.pptx
PPTX
gregor mendel's principles of inheritance
PPTX
GROUPS-QOUTIENT, PRODUCT OF SUBGROUP, COMPOSITION SERIES.pptx
PPTX
the set of natural numbers in mathematics
PPTX
Prime Numbers.power point presentations
DOCX
class activity in grade 10 mathematics JHS
PPTX
relation and operations power point presentation
PPTX
Ang matanda at ang dagat power point presentation
PPTX
relation and operations power point presentation
PPTX
relation and operations 204 presentation
PPTX
The Real Numbers power point presentations
DOCX
Week-2-August-30-September-2-2022-RAISEplusweek-1-f2f.docx
PPTX
in the set z on integers, we define addition and multiplicatio
PPTX
Rational Numbers_MATH 204_Ethelyn Alvarez (2).pptx
Recently uploaded
PDF
Shining a Light on Collections: Cyanotype Printing as Public Engagement Mona...
PDF
Visualising Library Insights: Power BI Dashboard for Data-Driven Decision Mak...
PDF
Application of ICT Lecture 7 Ethical Considerations in Use of ICT Platforms a...
PDF
Sentence Comprehension The Integration of Habits and Rules (Language, Speech,...
PDF
BỘ 20 ĐỀ THI GIẢ LẬP MỨC ĐỘ 9+ KỲ THI TỐT NGHIỆP TRUNG HỌC PHỔ THÔNG NĂM 2026...
PDF
A predictive coding framework for rapid neural dynamics during sentence-level...
PPTX
LEARNING PART 2.SHILPA HOTAKAR PSYCHOLOGY NOTES pptx
PPTX
LEARNING PART 1. SHILPA HOTAKAR PSYCHOLOGY NOTES pptx
PPTX
GRADE-1-Q3-MATH-WEEK-6.pptx_202633333333
PDF
Homebound (2025): A Critical Analysis of Social Realism, Systemic Apathy, and...
PPTX
Prenatal Development of Cranium, Jaw and Face
PPTX
CARDIOTONIC CHAPTER NO. 5 PHARMACOGNOSY DIGITALIS AND ARJUNA BARK
PPTX
AI Literacy at UCD Library. Dr Marta Bustillo & Sandra Dunkin, University Col...
PPTX
Spectrofluorometery one of the analytical technique
PPTX
Caring for Collections – New directions at UCC Library. Louise O’Connor, Uni...
PPTX
Conduction System of the Heart, The Cardiac Cycle, The Cardiac Output, ECG.pptx
PPTX
Auto Plan Feature in Odoo 18 Planning Module
PPTX
PixelX : Think Design Experience powerpoint presentation
PPTX
Set online status in Odoo 19_Do not distrurb
PDF
Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry Unit 5 Cycloalkanes
geometry presentation power point presentation 1. 2. - the branch of mathematics that is concerned with the
properties and relationships of:
- points, lines, angles, curves, surfaces, and solids.
- The visual study of shapes, sizes, patterns, and positions.
What is
Geometry?
3. 4. 5. Line
Has no beginning or end.
Continues indefinitely in both directions.
Can be illustrated by drawing arrows at each end.
6. Line Segment
Has a beginning point and an end point.
Line segments on a shape are called sides.
Can be found in many shapes.
7. 8. Lines in the same
plane that do not
intersect or cross
each other.
Parallel
9. Two or more lines that meet at a point.
Intersecting
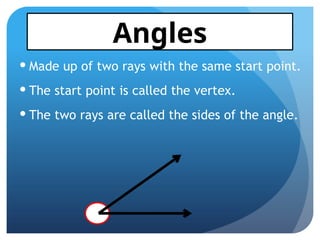
10. 11. Made up of two rays with the same start point.
The start point is called the vertex.
The two rays are called the sides of the angle.
Angles
12. 13. Zero Angles
Right Angles
Acute Angles
Obtuse Angles
Straight Angles
Supplementary Angles
Complimentary Angles
Different Angles
14. 15. Plane Figure:
A two-dimensional
shape (2D).
A shape on a plane.
Includes points,
lines, polygons,
circles, triangles,
hexagon,
pentagons, etc.
A plane figure is any
set of points on a
plane.
16. Quadrilateral - a plane figure having four
sides and four angles.
Parallelograms - a quadrilateral having both
pairs of opposite sides parallel to each other.
17. 18. Space figures are three dimensional figures.
Faces: Side of the space figure
Edges: Where two faces meet
Vertex or Vertices: the corners of the space figures
EDGE
FACE
VERTEX
Space Figures!