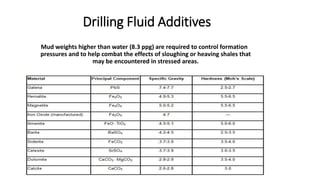
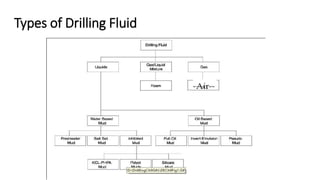
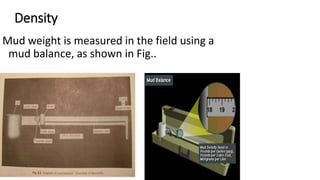
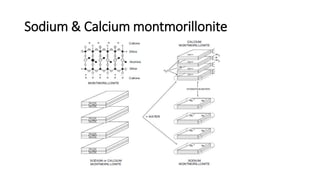
This document discusses the functions and types of drilling fluids. It describes how drilling fluids transport cuttings to the surface, clean drill bits, provide downhole pressure control, prevent fluid loss into formations, and power downhole tools. The key types of drilling fluids are water-based mud, oil-based mud, and gas-based fluids. Water-based mud is the most common and uses additives to control density, viscosity, and clay chemistry. Oil-based mud is used in reactive shale formations and has advantages in high temperatures but also environmental and health disadvantages.