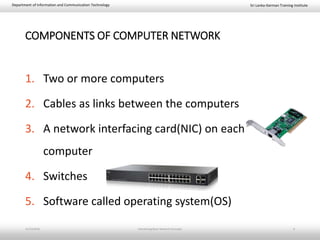
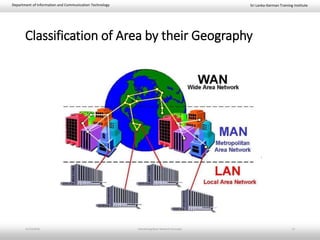
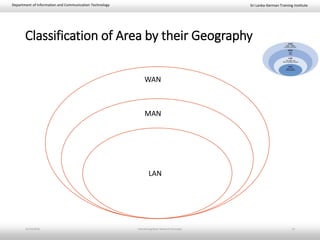
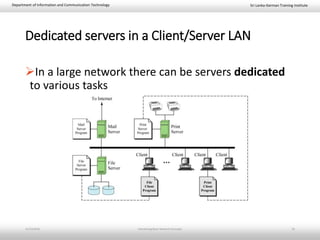
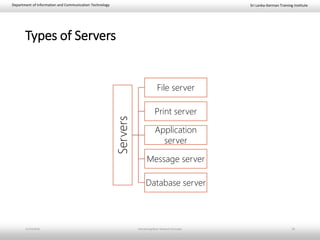
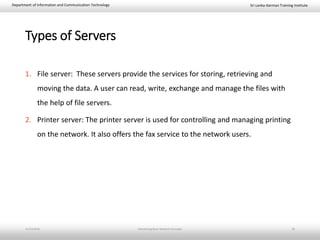
This document provides an introduction to basic network concepts. It defines a computer network and its components, which include two or more interconnected computers, cables, network interface cards, switches, and operating systems. It describes the applications and benefits of networks, such as sharing resources and communicating over long distances, as well as some disadvantages like high installation costs. It also classifies networks based on their geographical area into personal, local, metropolitan and wide area networks. Finally, it discusses peer-to-peer and client-server network models.
![Sri Lanka-German Training InstituteDepartment of Information and Communication Technology
National Diploma in Information and Communication Technology – Bridging
[BIT-FON] Fundamentals of Networking
Task 01: Introducing Basic Network Concepts
11/23/2018 Introducing Basic Network Concepts 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/01basicnetworkconcepts-181123164240/85/basic-network-concepts-1-320.jpg)