This document outlines key concepts in motivation theory, including:
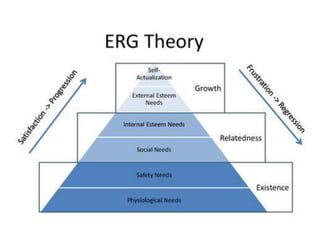
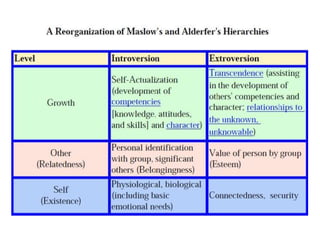
- Maslow's hierarchy of needs which arranges human needs in a pyramid from basic physiological needs to growth needs.
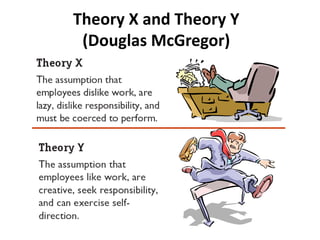
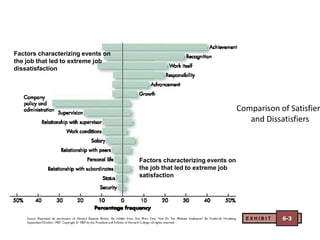
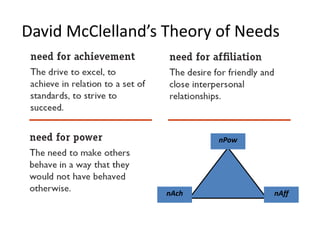
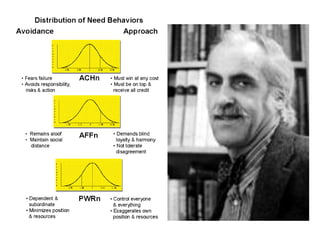
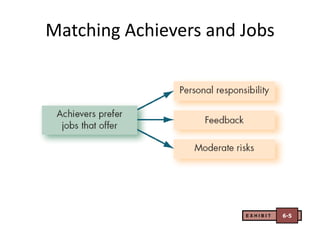
- Herzberg's two-factor theory which distinguishes between motivators like achievement that drive job satisfaction and hygiene factors whose absence can cause dissatisfaction.
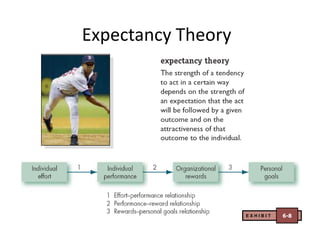
- Expectancy theory which proposes that motivation depends on the expectation that effort will lead to good performance and performance will be rewarded.
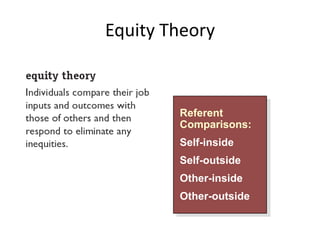
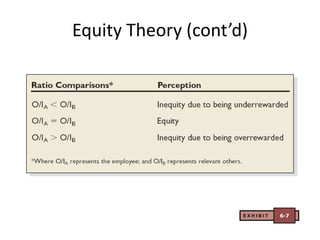
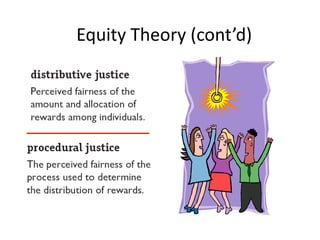
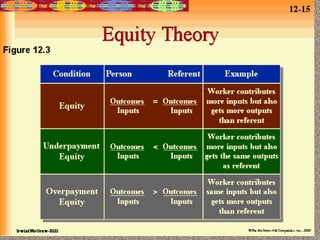
- Equity theory which suggests people are motivated to maintain fair relationships and balances of inputs and outcomes compared to others.