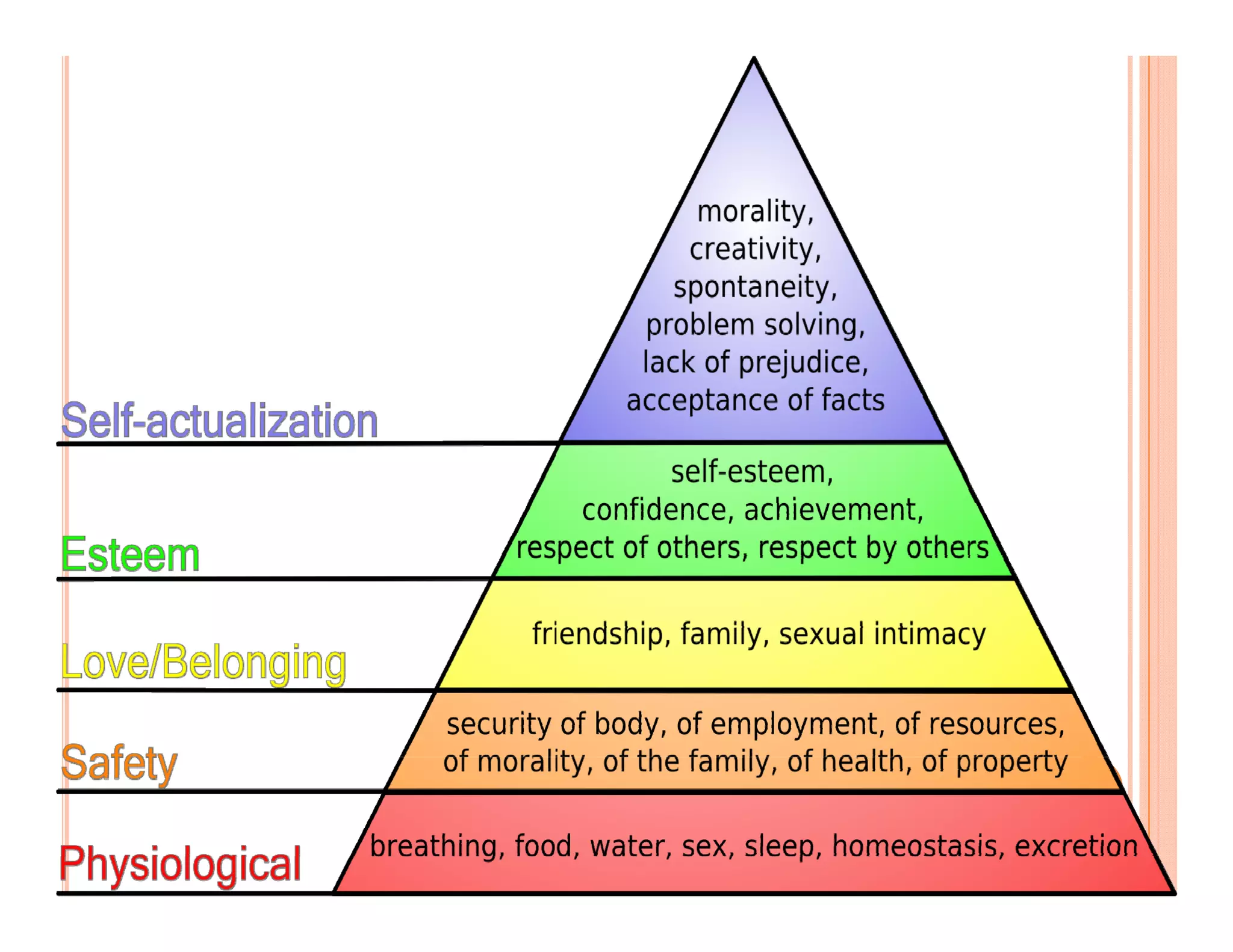
Maslow believed that human motivation is hierarchical, with self-actualization at the top of the hierarchy. Skinner thought that behavior is shaped by consequences in the environment - reinforcement increases the likelihood of a behavior repeating. Erikson's psychosocial theory describes eight stages of development from infancy to old age, with a psycho-social task to be resolved at each stage to promote healthy development.