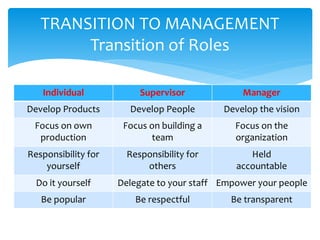
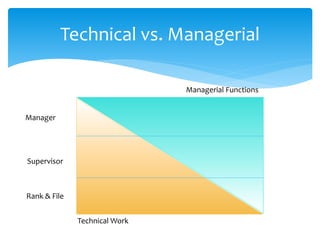
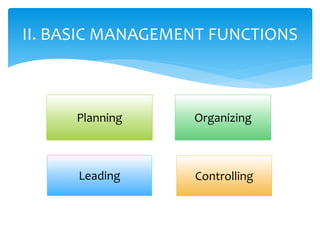
This document outlines the key functions of management. It discusses the transition from an individual contributor role to a management role, which involves developing people rather than just products. The four basic management functions are then explained in further detail: planning involves predetermining actions and goals, organizing is arranging work and relationships, leading is influencing others' actions, and controlling assesses progress and results. Effective supervision is achieved through getting results via people, maintaining morale in their presence or absence, and earning respect.