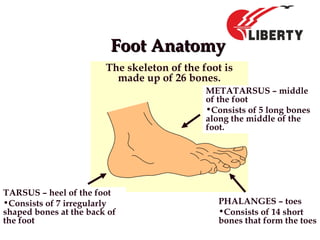
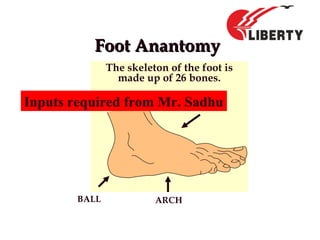
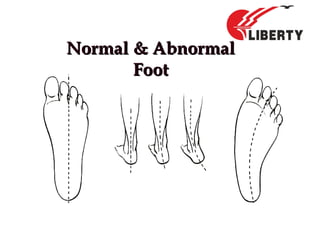
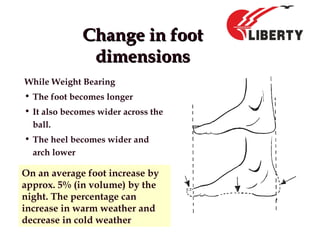
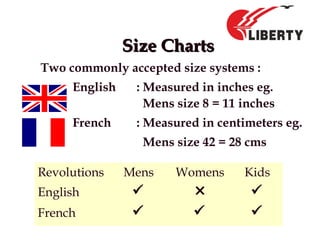
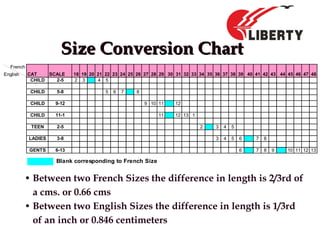
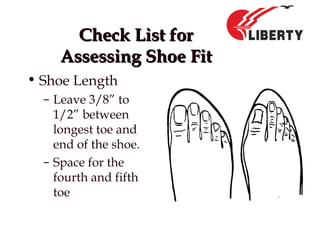
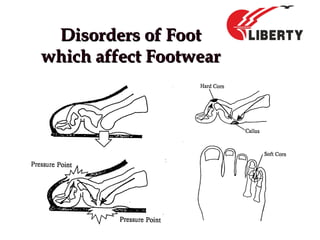
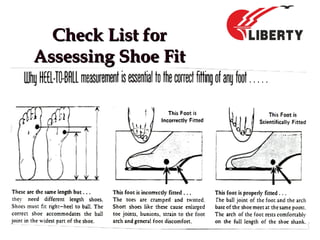
The document provides a comprehensive overview of foot anatomy, mechanics, foot size measurement techniques, and shoe fitting procedures. It emphasizes the importance of proper shoe fitting to prevent foot ailments and discusses different foot types and their characteristics. The content includes guidelines for assessing shoe fit and evaluating worn shoes to recommend appropriate footwear.