Embed presentation
Download to read offline




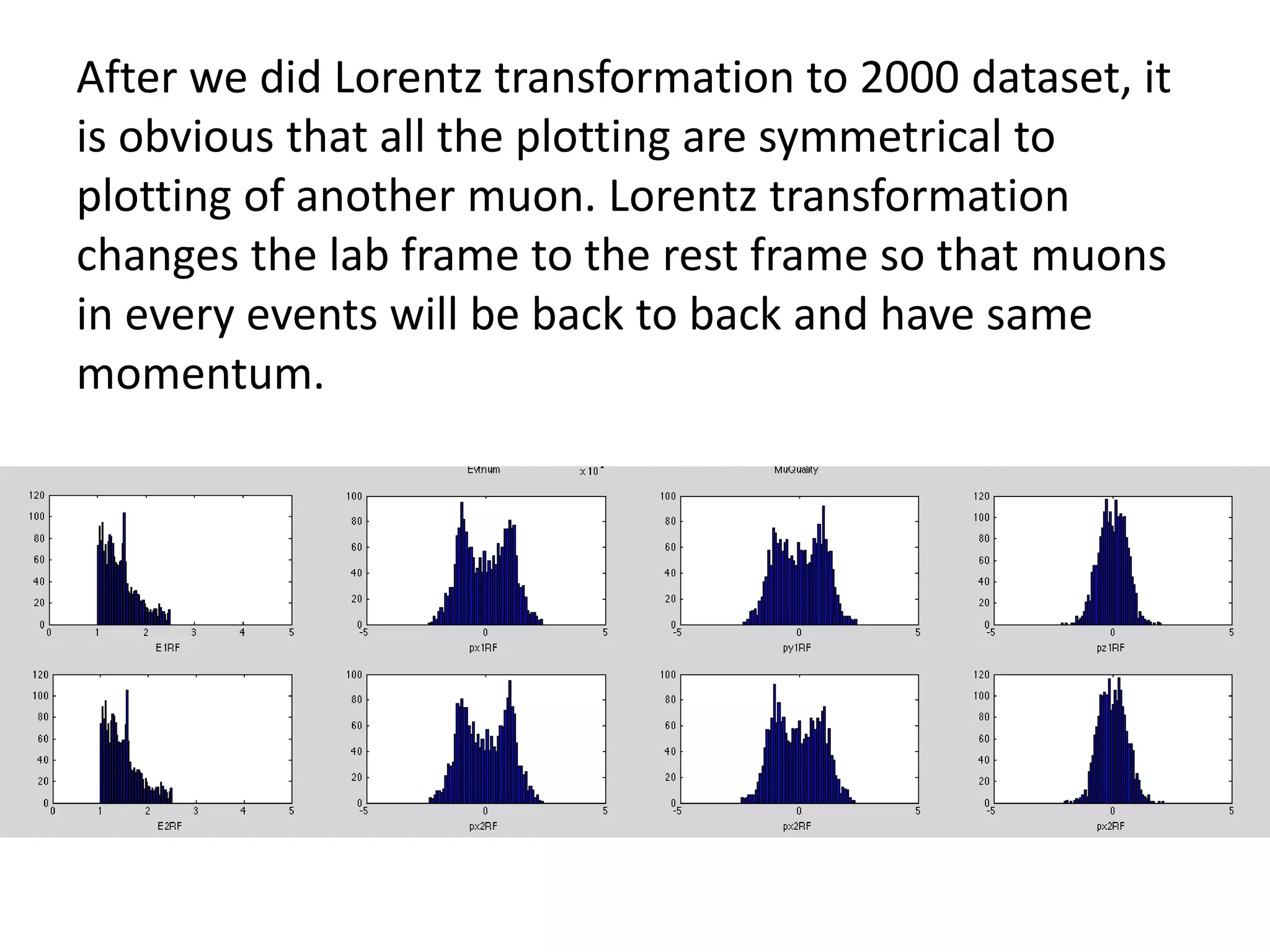
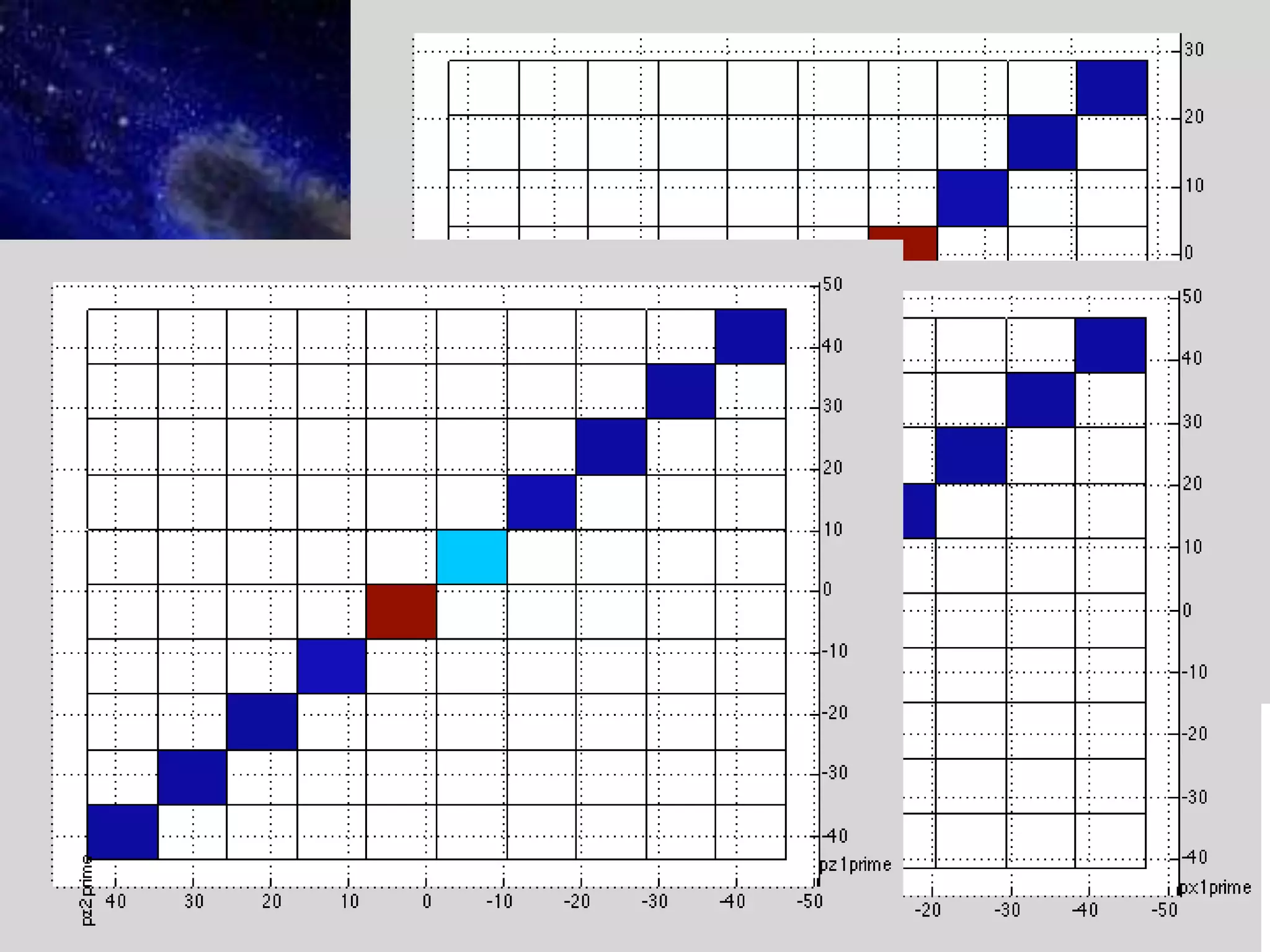
Lorentz transformations are used in particle physics because they describe how measurements of space and time are related between observers moving at constant velocities, which is important when particles move near the speed of light. Galilean transformations do not account for the speed of light and are therefore not accurate enough for particle physics where velocities approach light speed. Applying Lorentz transformations to experimental data sets of particles brings their measurements into a common rest frame and allows for symmetrical analysis that reveals insights about particle behavior.






