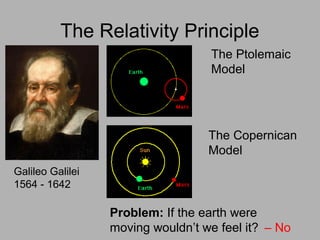
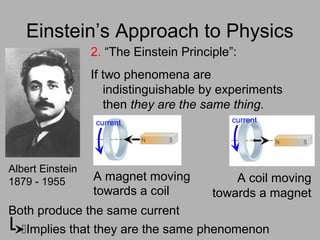
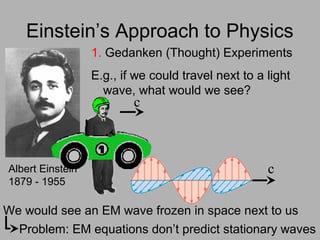
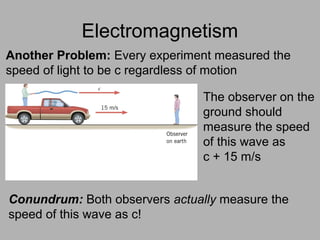
1. Einstein used thought experiments and his principle that indistinguishable phenomena are the same to formulate the theory of special relativity.
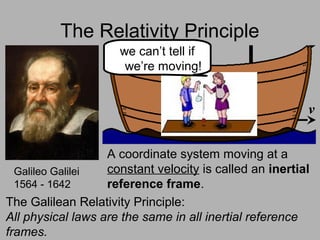
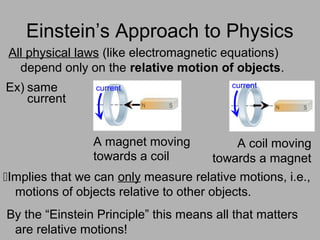
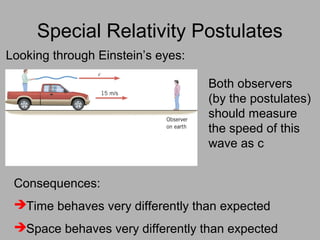
2. The two postulates of special relativity are that all physical laws are the same in any inertial reference frame and that the speed of light is constant.
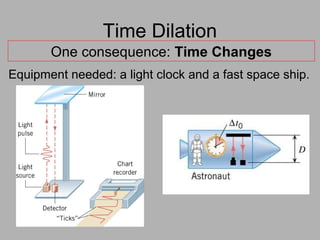
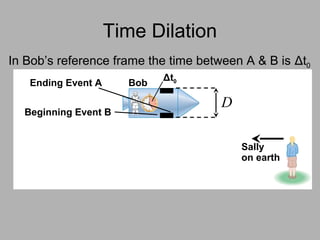
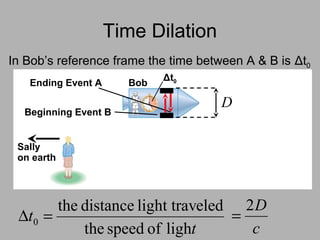
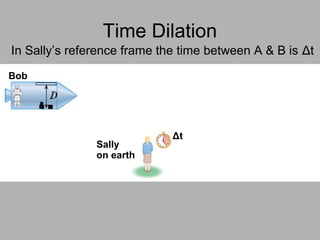
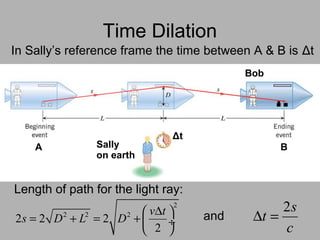
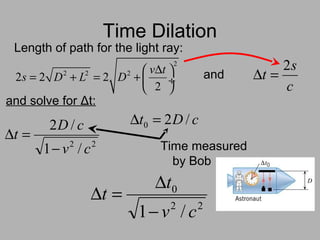
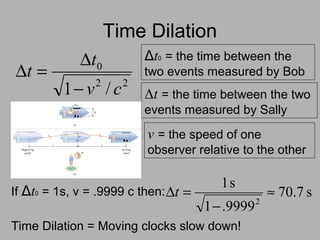
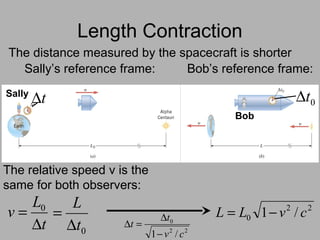
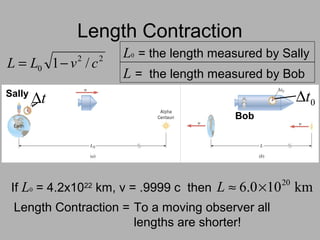
3. Key consequences of special relativity include time dilation, where moving clocks run slow, and length contraction, where lengths appear shorter to observers in motion.