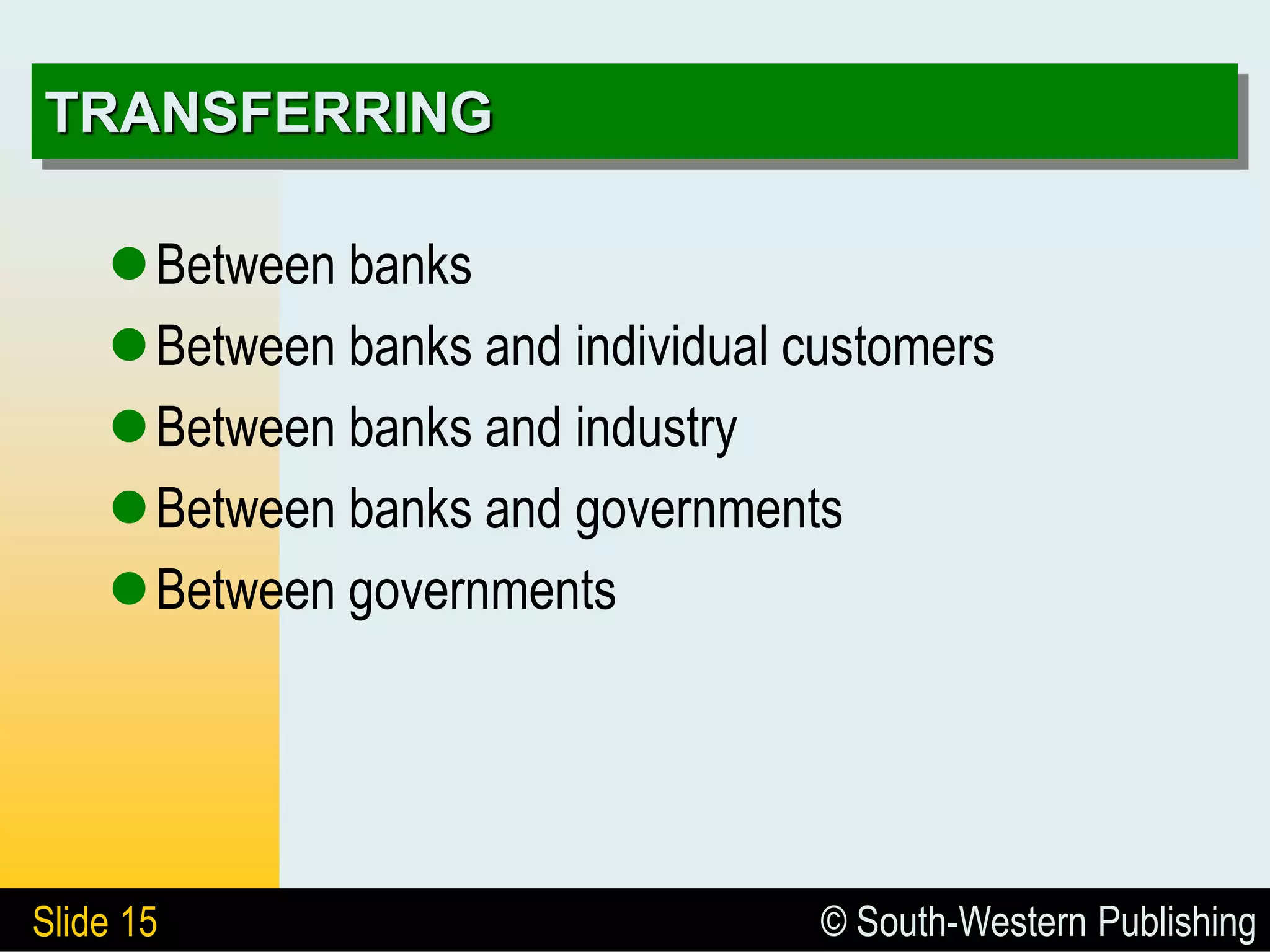
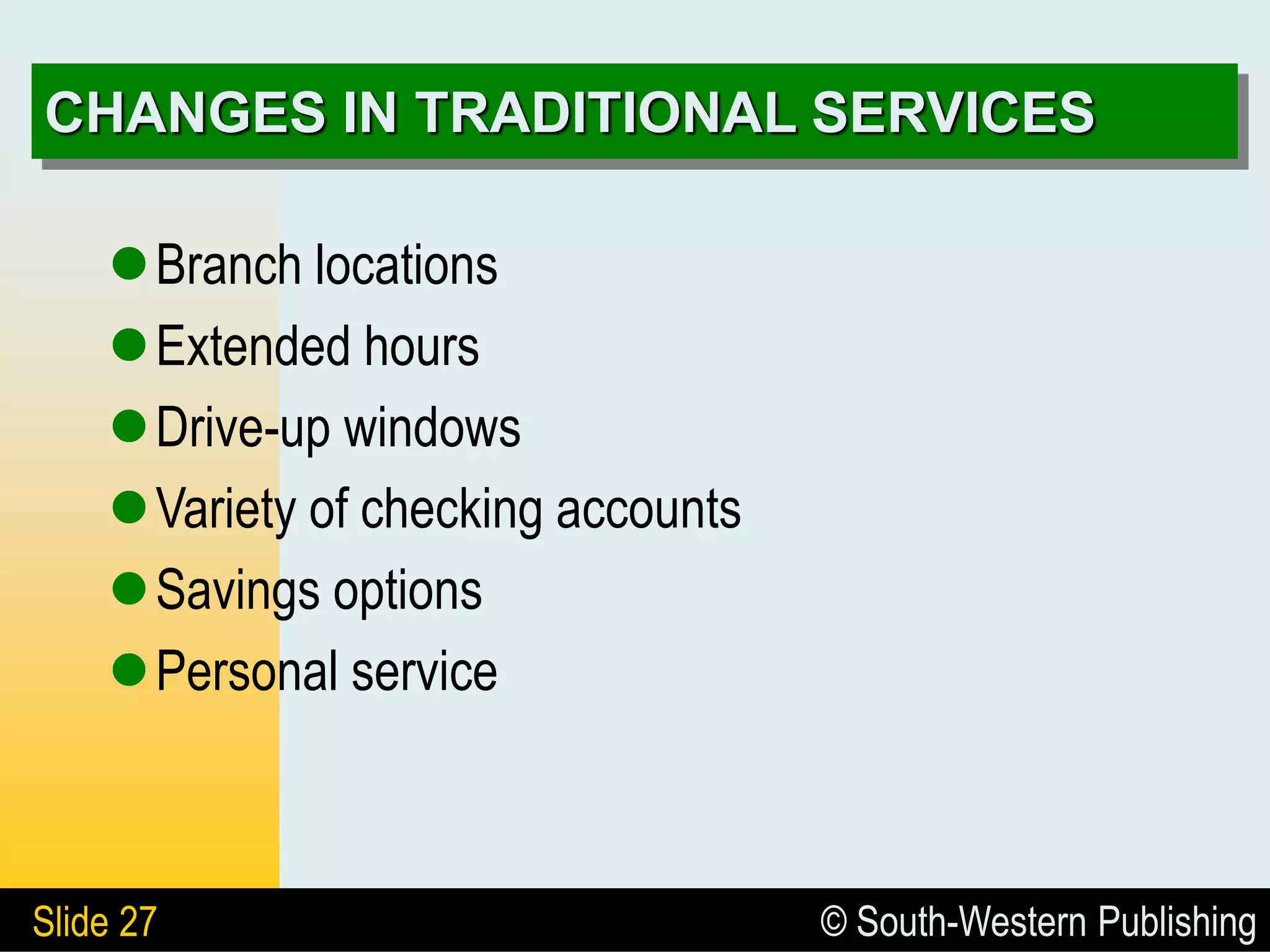
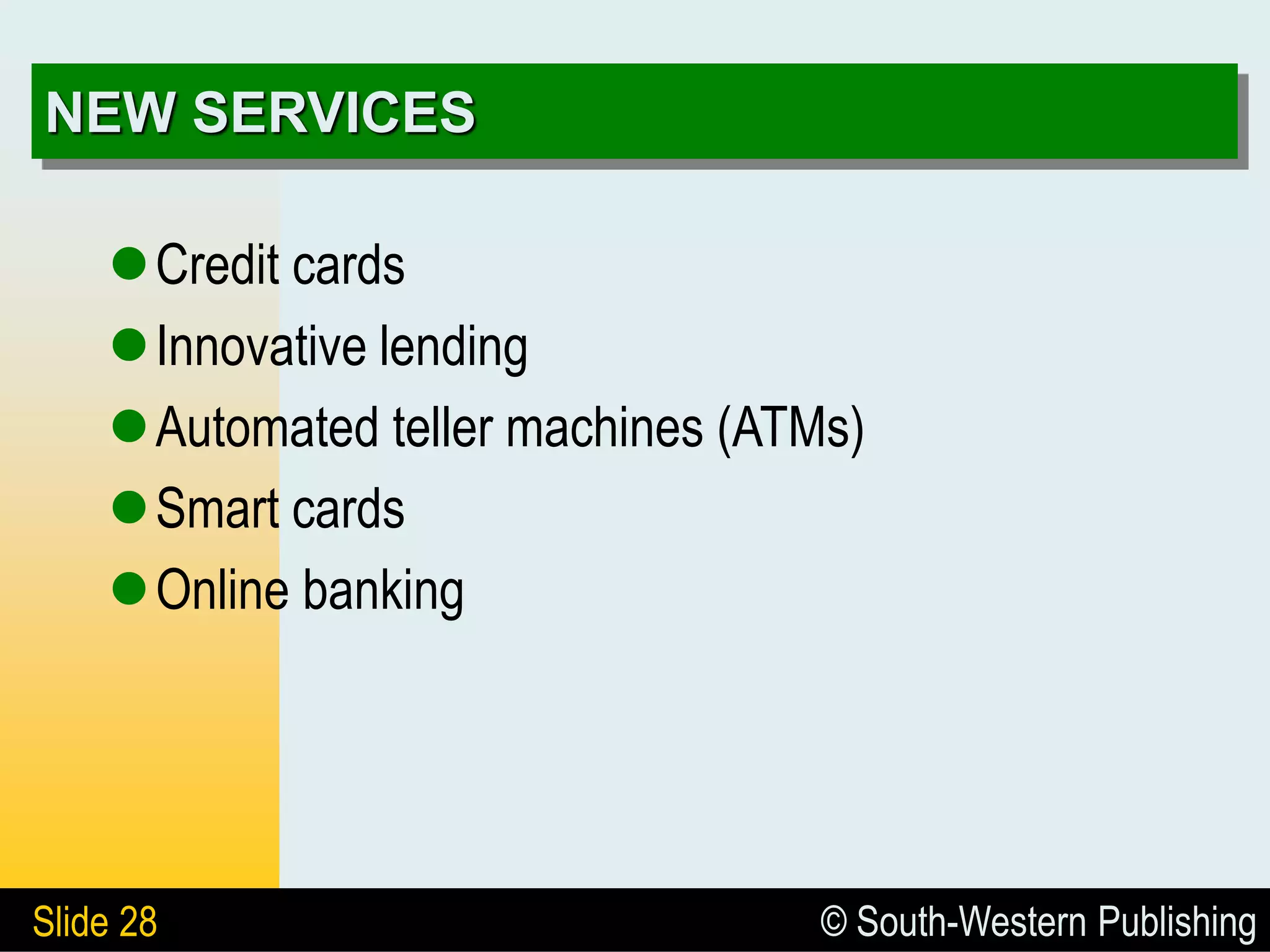
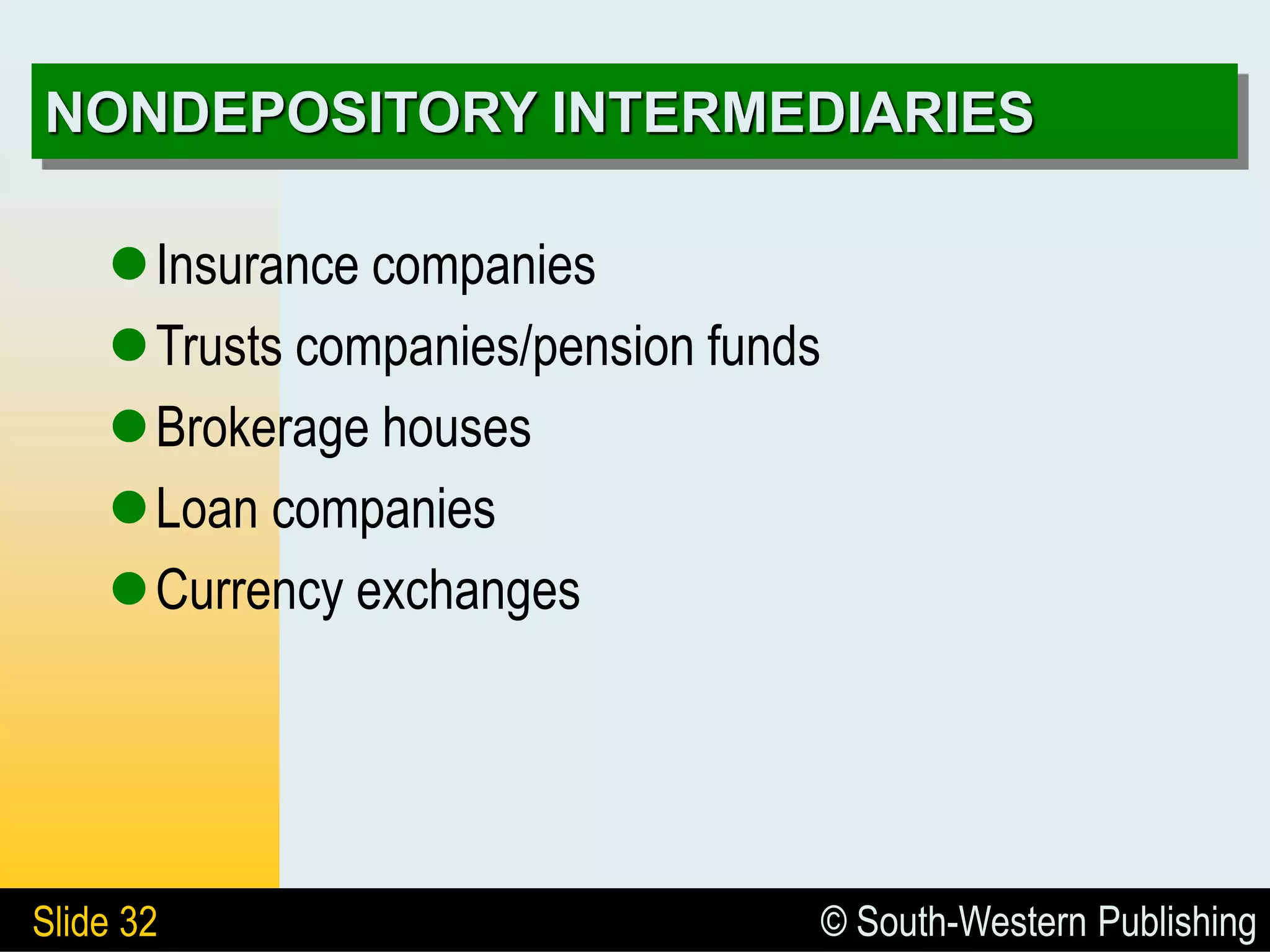
The document provides an overview of the business of banking, highlighting the role banks play in the economy and their functions as financial intermediaries. It discusses the evolution of banking, types of banks, the impact of technology, and the importance of creditworthiness in lending practices. Additionally, it differentiates between depository and nondepository financial institutions and outlines various services banks offer to remain competitive.