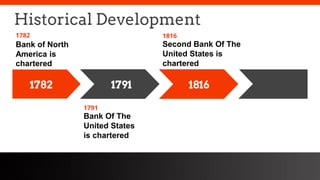
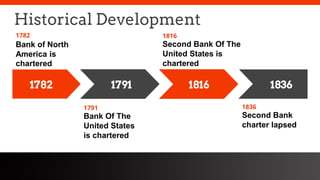
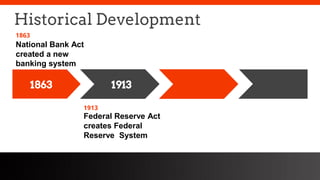
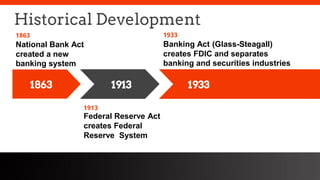
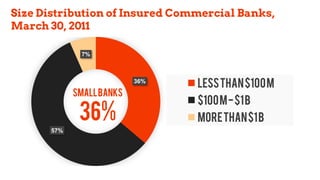
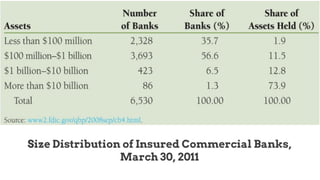
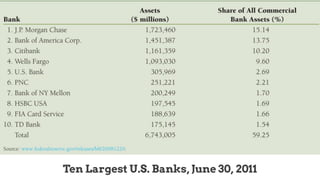
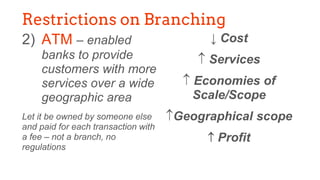
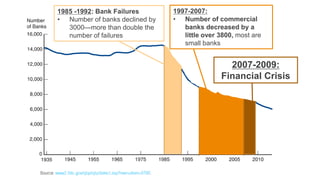
This document provides an overview of the historical development of the US banking system from 1782 to the present. It discusses the chartering of early banks, the creation of the Federal Reserve System in 1913, and the Glass-Steagall Act of 1933 which separated commercial and investment banking. It also describes how financial innovation eroded traditional banking by creating new shadow banking system activities and products, and led to industry consolidation and nationwide banking following the repeal of interstate banking laws.