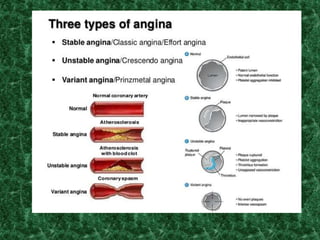
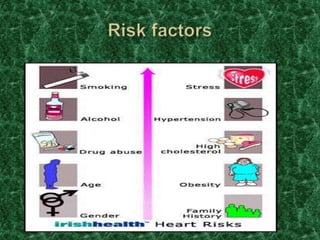
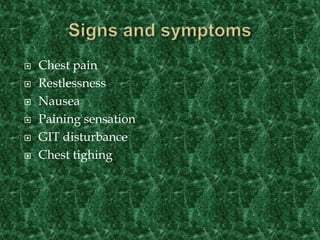
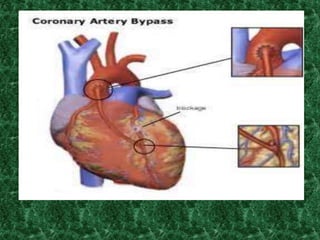
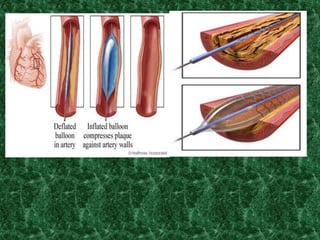
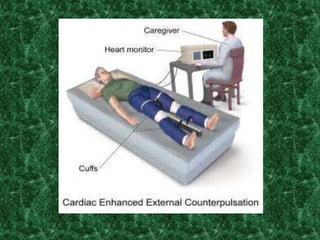
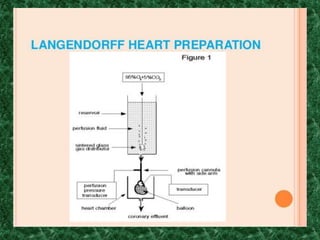
Screening methods for anti-anginal agents include in vivo and in vitro models. In vivo models involve inducing ventricular failure in animals through repeated injections of plastic microspheres into the left ventricular artery. In vitro models screen agents using isolated tissues like heart muscle to assess effects on coronary blood flow, oxygen consumption, and mechanical activity. Common classifications of anti-anginal agents are nitrates, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, potassium channel openers, and others like dipyridamole and trimetazidine.