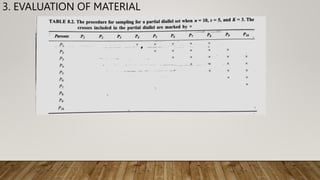
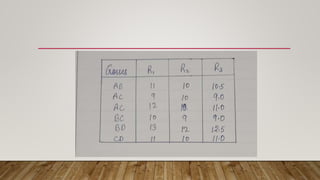
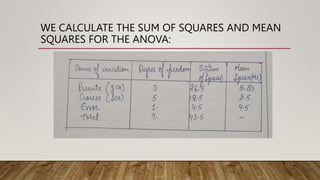
This document describes a partial diallel mating design used in plant breeding. A partial diallel design involves crossing a subset of genotypes from a group of parental lines, rather than making all possible crosses in a complete diallel. The document provides an example using four parental lines each crossed with two other lines, resulting in six crosses that are evaluated. This allows estimation of genetic parameters like general combining ability (GCA) and specific combining ability (SCa). Partial diallel designs reduce costs compared to complete diallels while still enabling selection of best parents and study of gene-environment interactions.