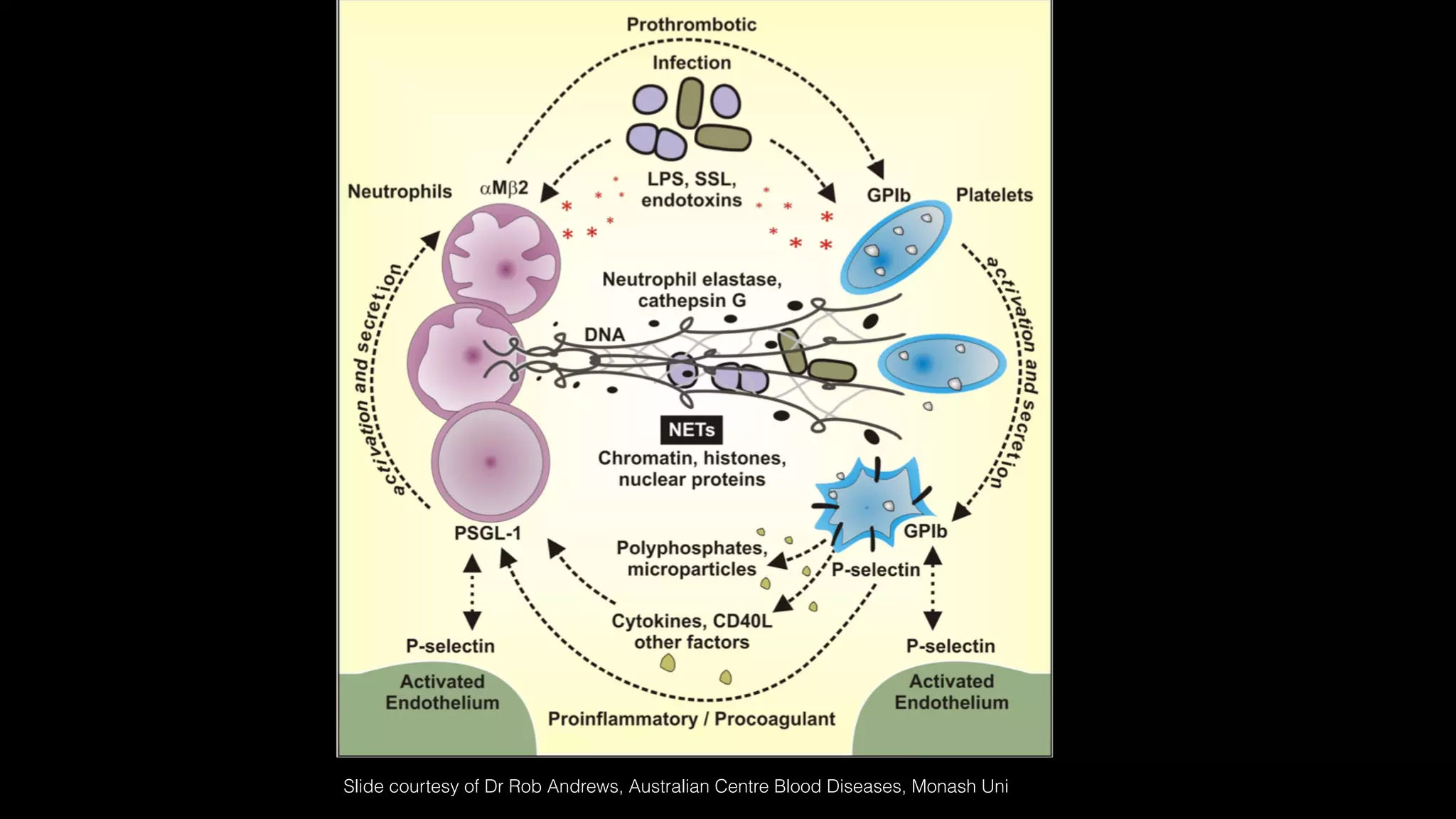
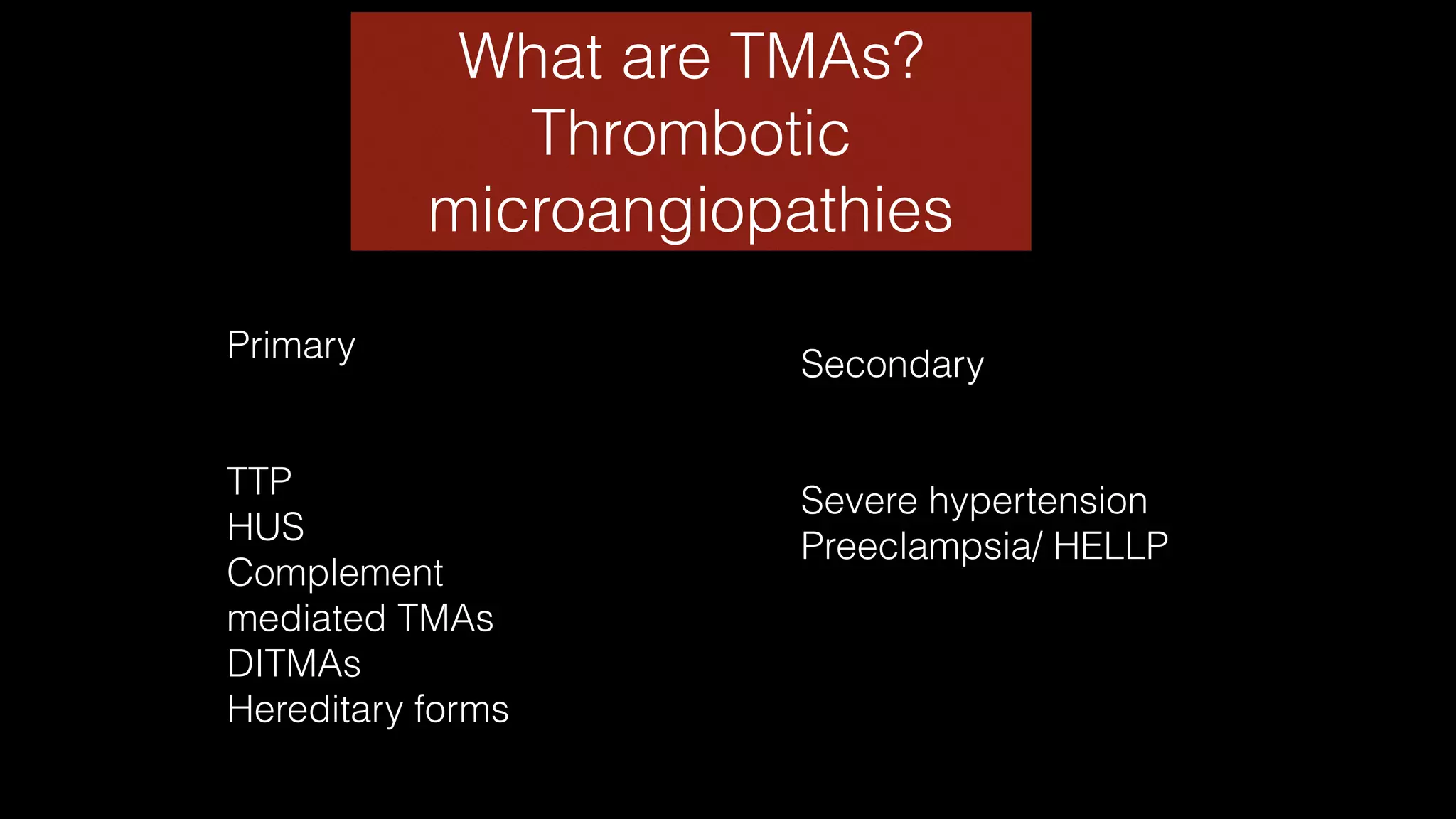
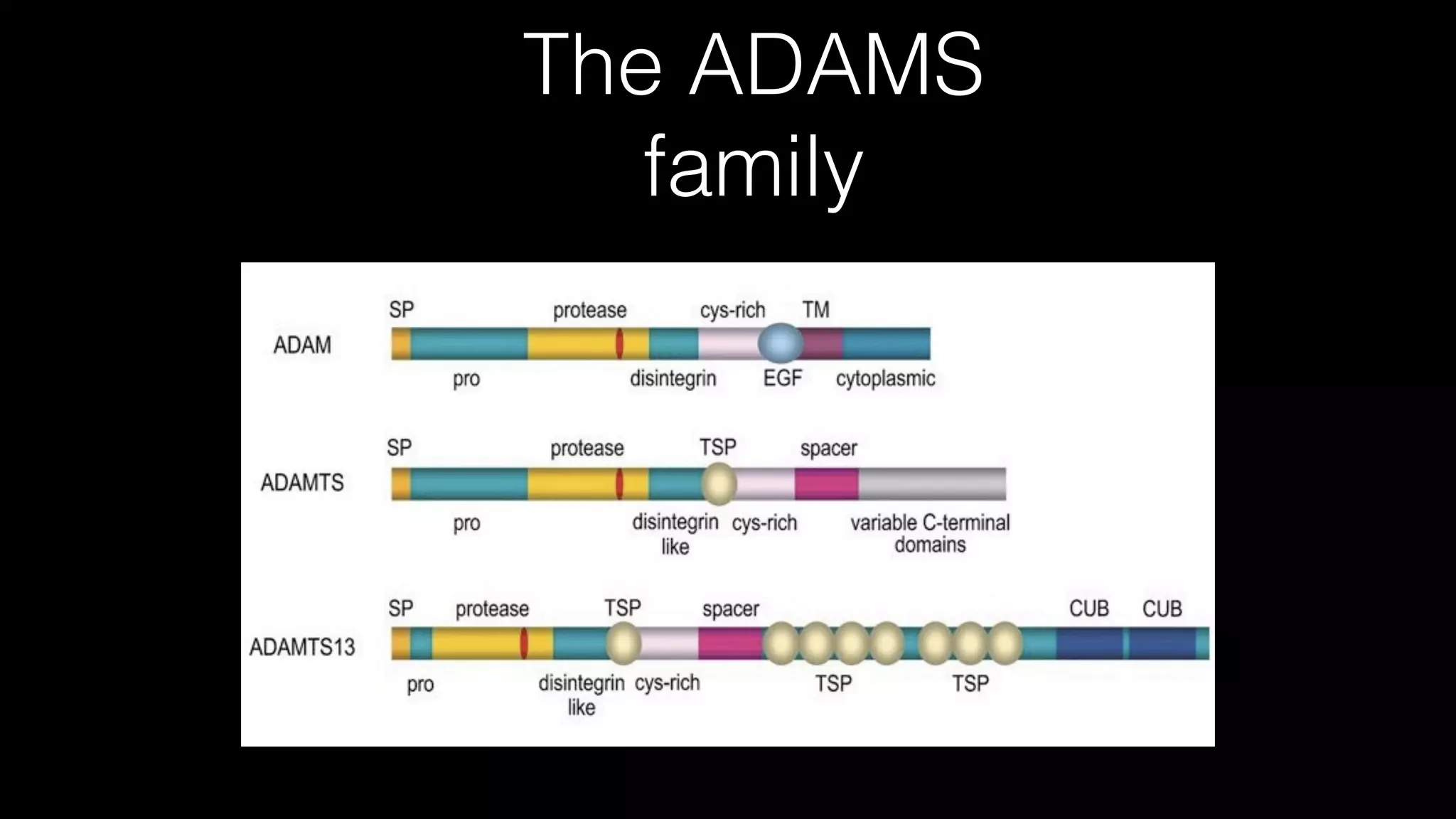
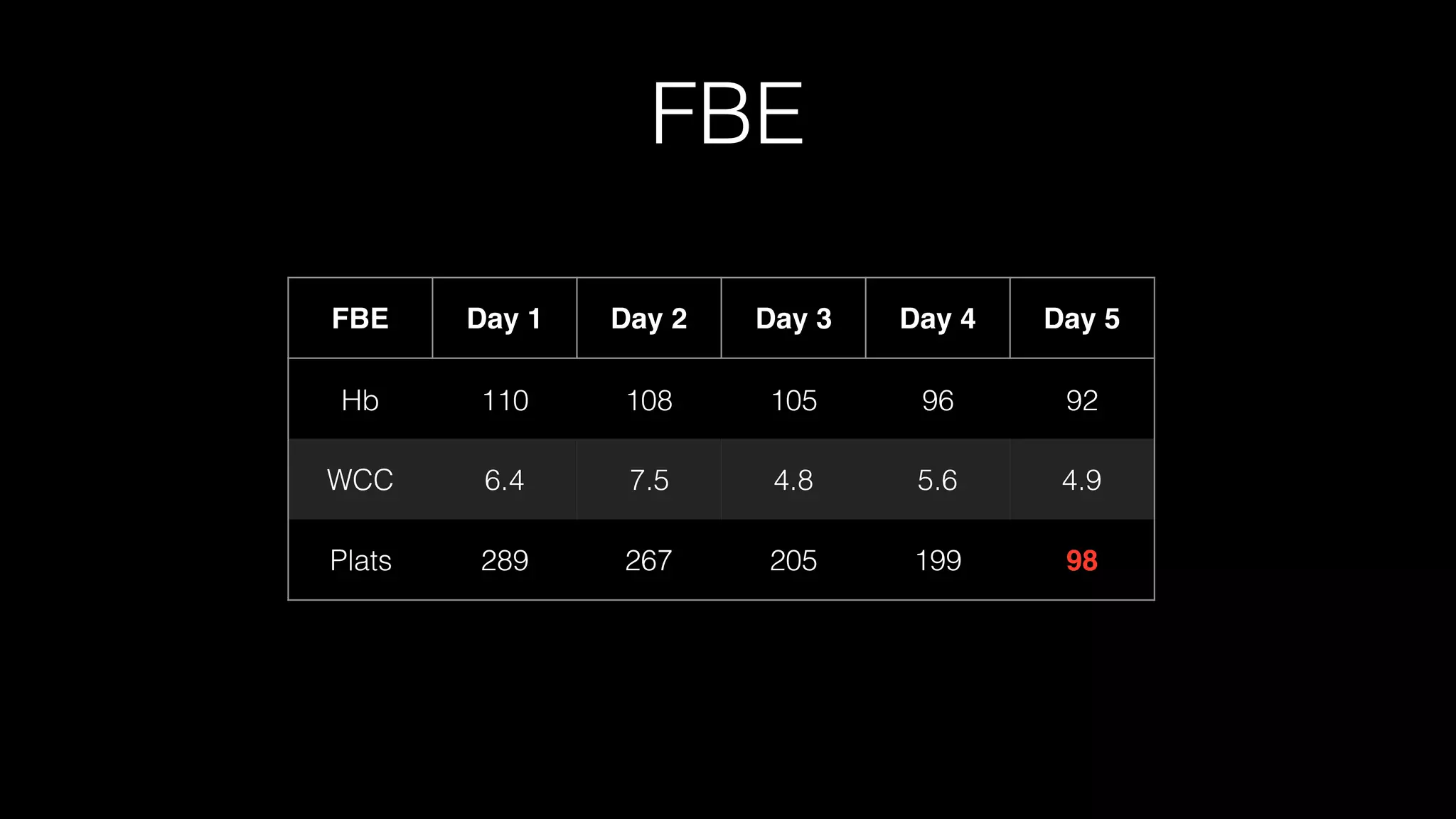
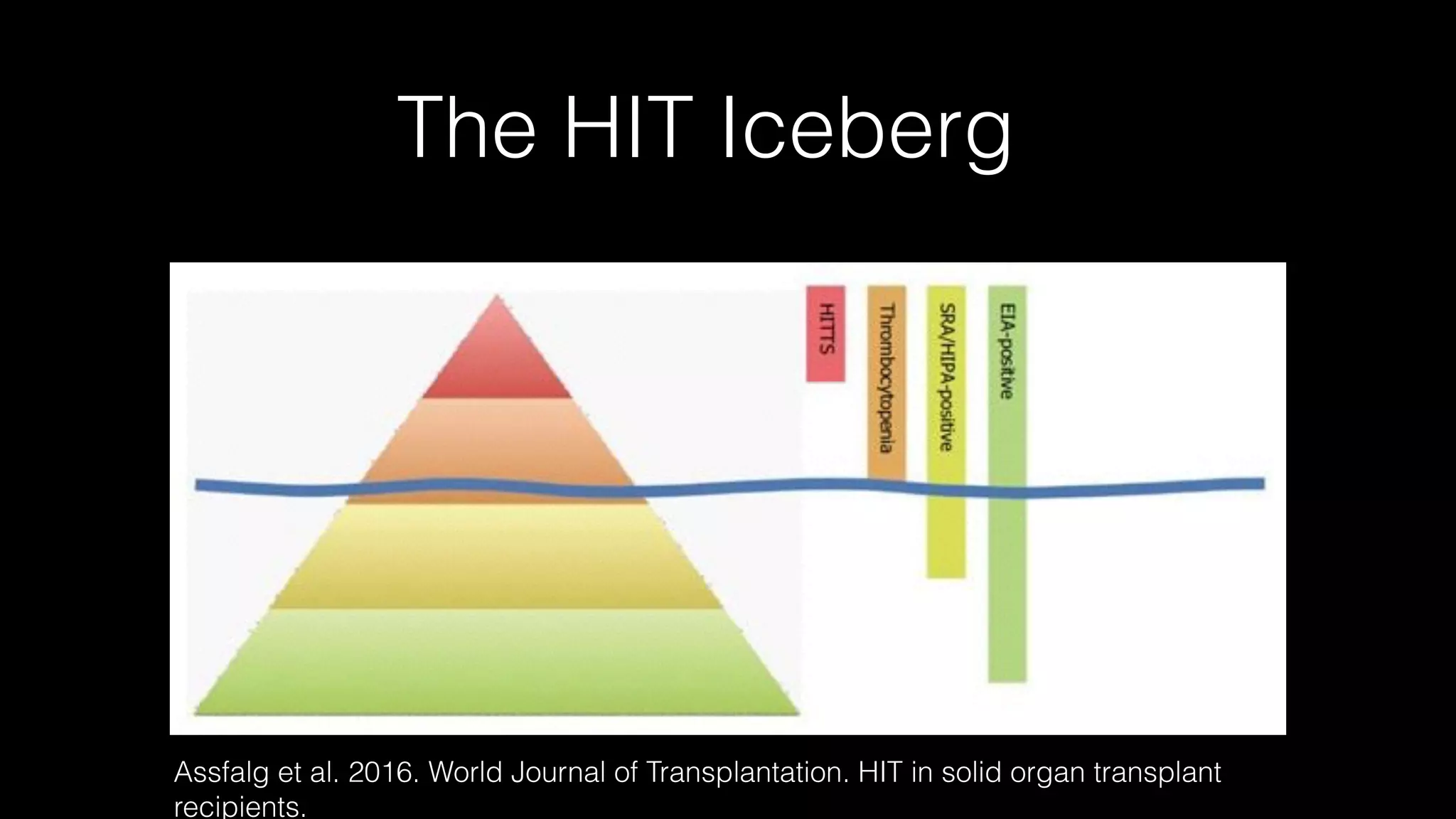
The document discusses complex clinical cases involving coagulopathy, specifically DIC, thrombotic microangiopathies, and their associations with severe illness in ICU patients. It emphasizes the multifactorial nature of thrombocytopenia and the importance of proper diagnosis and management of conditions like TTP and HIT. Key laboratory findings and treatment strategies are highlighted, addressing the urgency of intervention in these life-threatening scenarios.