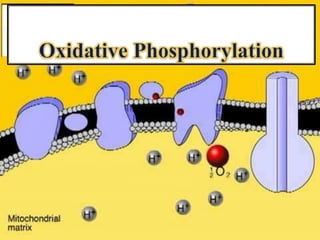
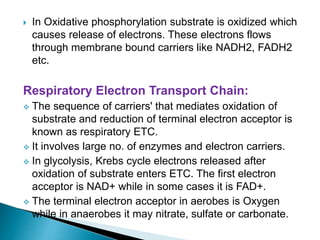
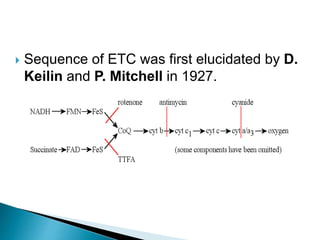
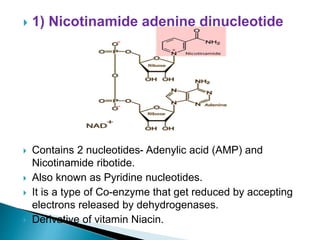
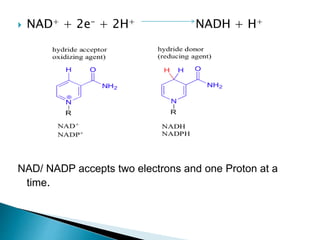
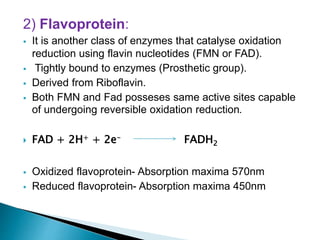
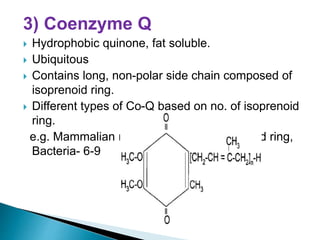
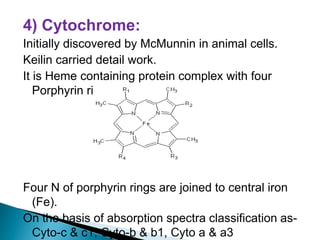
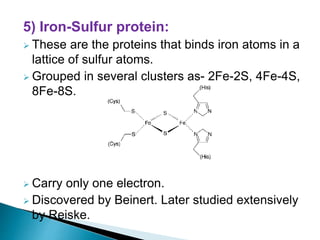
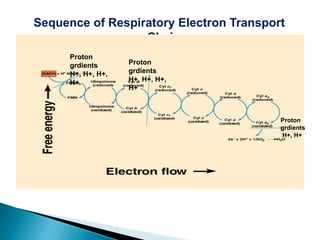
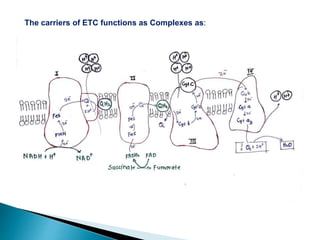
The document explains the process of oxidative phosphorylation and the respiratory electron transport chain (ETC) in aerobic organisms, detailing how ATP is generated when electrons flow from substrates to terminal electron acceptors like oxygen or other inorganic substances in anaerobes. Various components of the ETC, such as NAD+, flavoproteins, cytochromes, and iron-sulfur proteins, are described along with their roles in electron transport and ATP synthesis. It also discusses the chemiosmotic hypothesis, which describes how proton motive force is generated and utilized for ATP production.