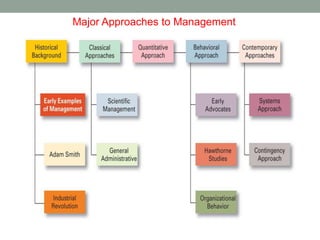
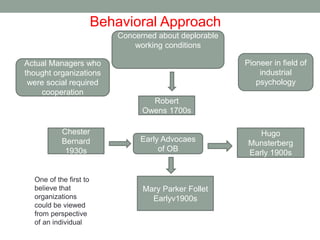
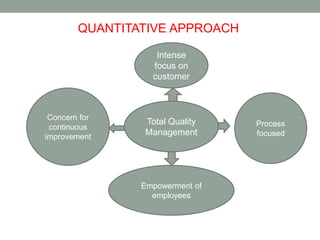
This document discusses four major approaches to management: classical, behavioral, quantitative, and contingency. The classical approach includes scientific management theorists like Taylor and general administrative theorists like Fayol and Weber. The behavioral approach focuses on individuals and organizational behavior, influenced by researchers like Mary Parker Follett. The quantitative approach applies statistics and other analytical tools to management problems and decisions, exemplified by total quality management. Finally, the contingency approach believes the best management approach depends on the specific circumstances of an organization.