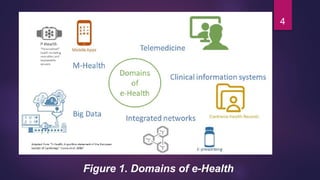
The document discusses the rise of e-health technologies and their impact on healthcare management, particularly focusing on older adults' experiences with e-health uptake. It outlines various ICT-driven health platforms in India, such as telemedicine services and health information systems, which aim to enhance healthcare accessibility and efficiency. Additionally, it highlights the challenges associated with e-health, including technological disparities and interoperability issues, alongside the vital role of public health informatics in promoting health and preventing disease.