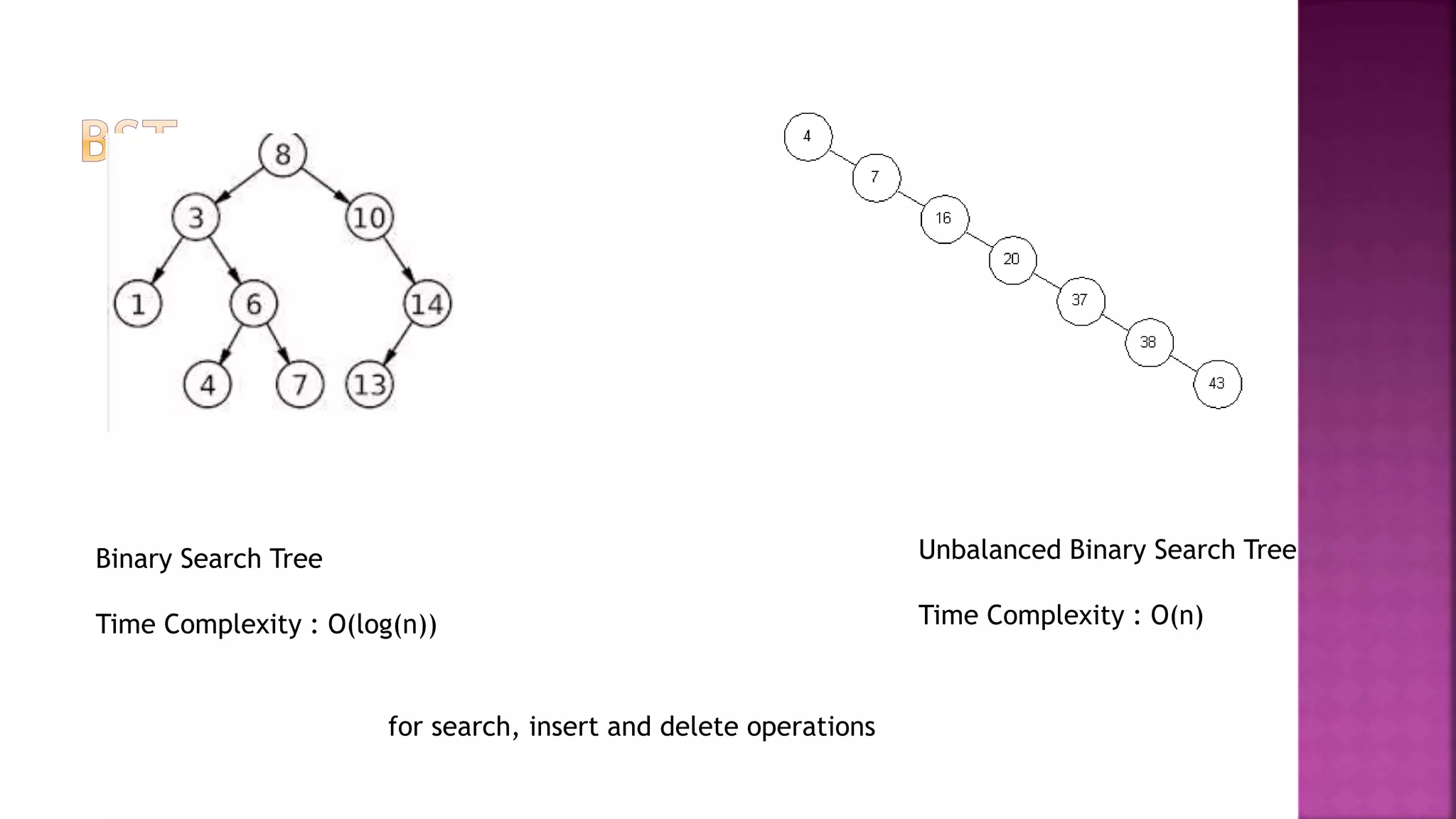
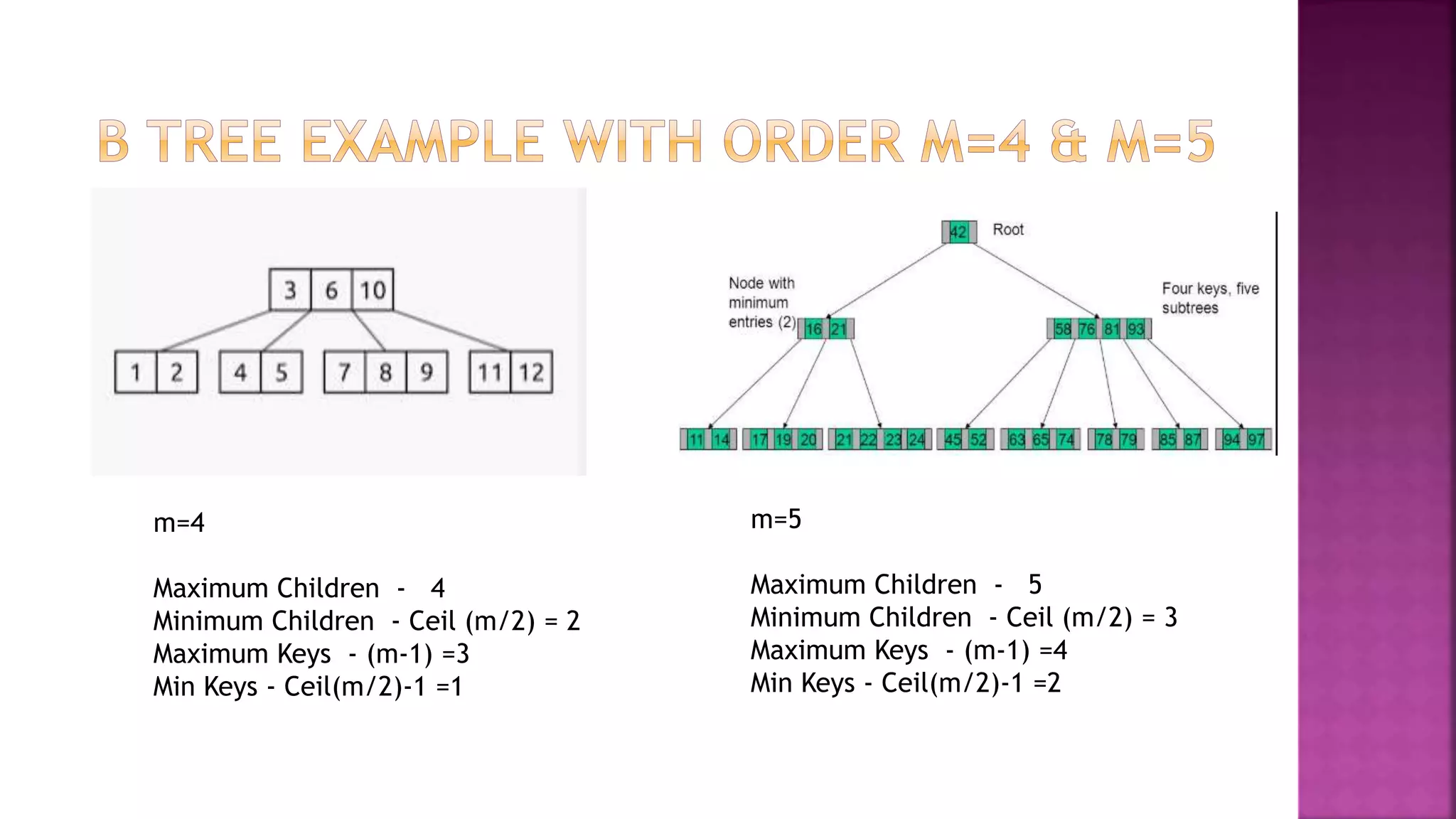
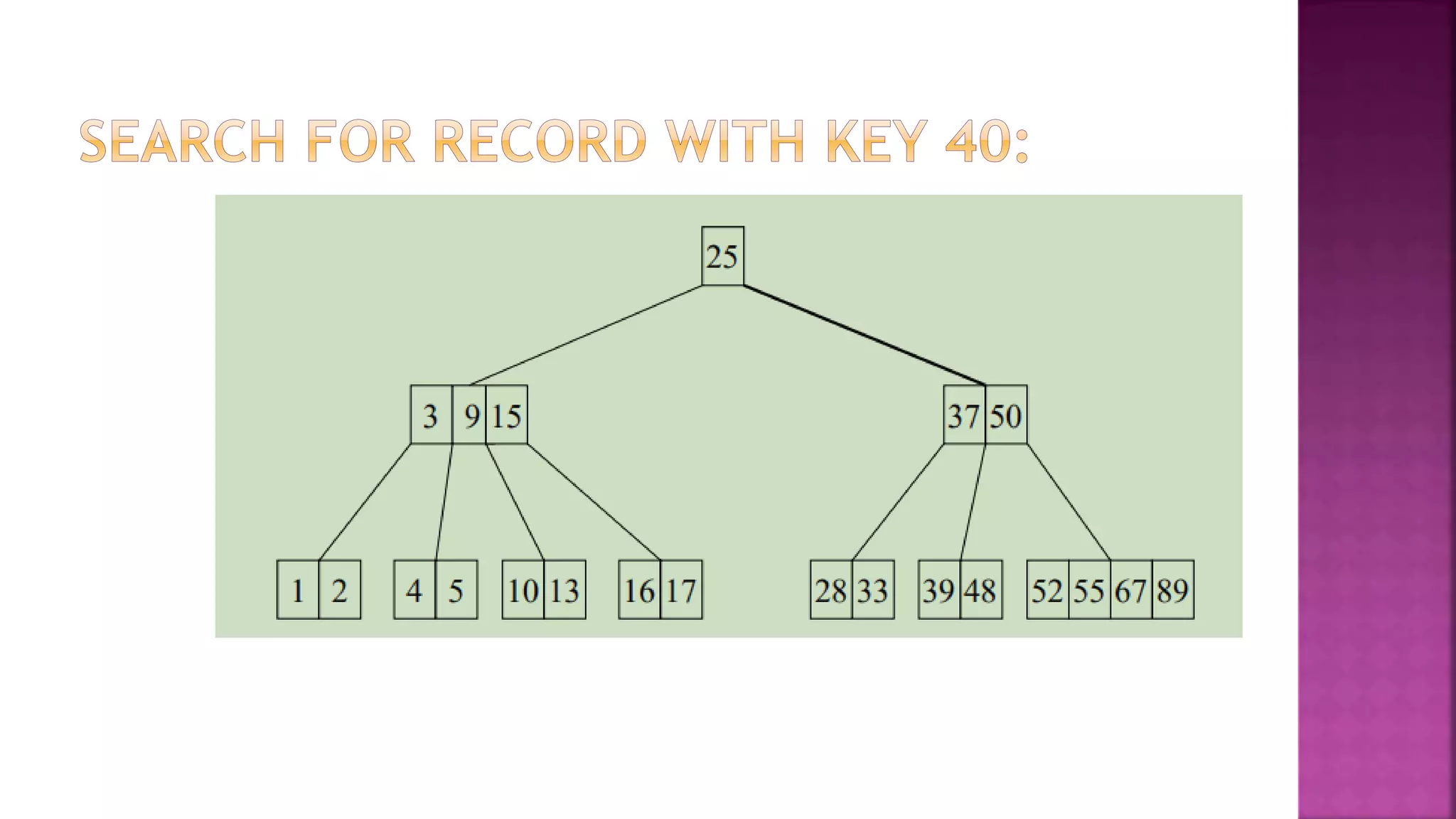
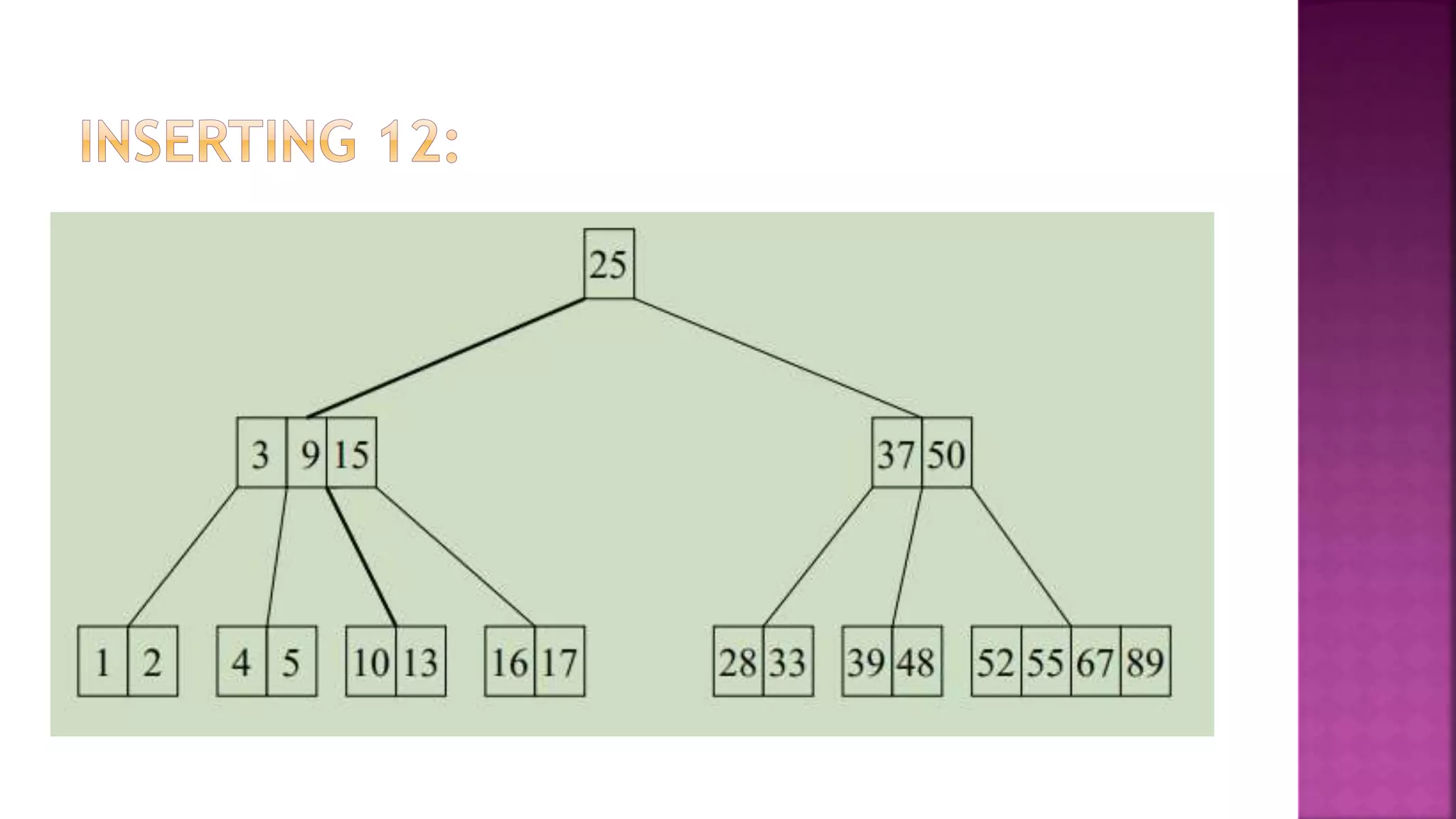
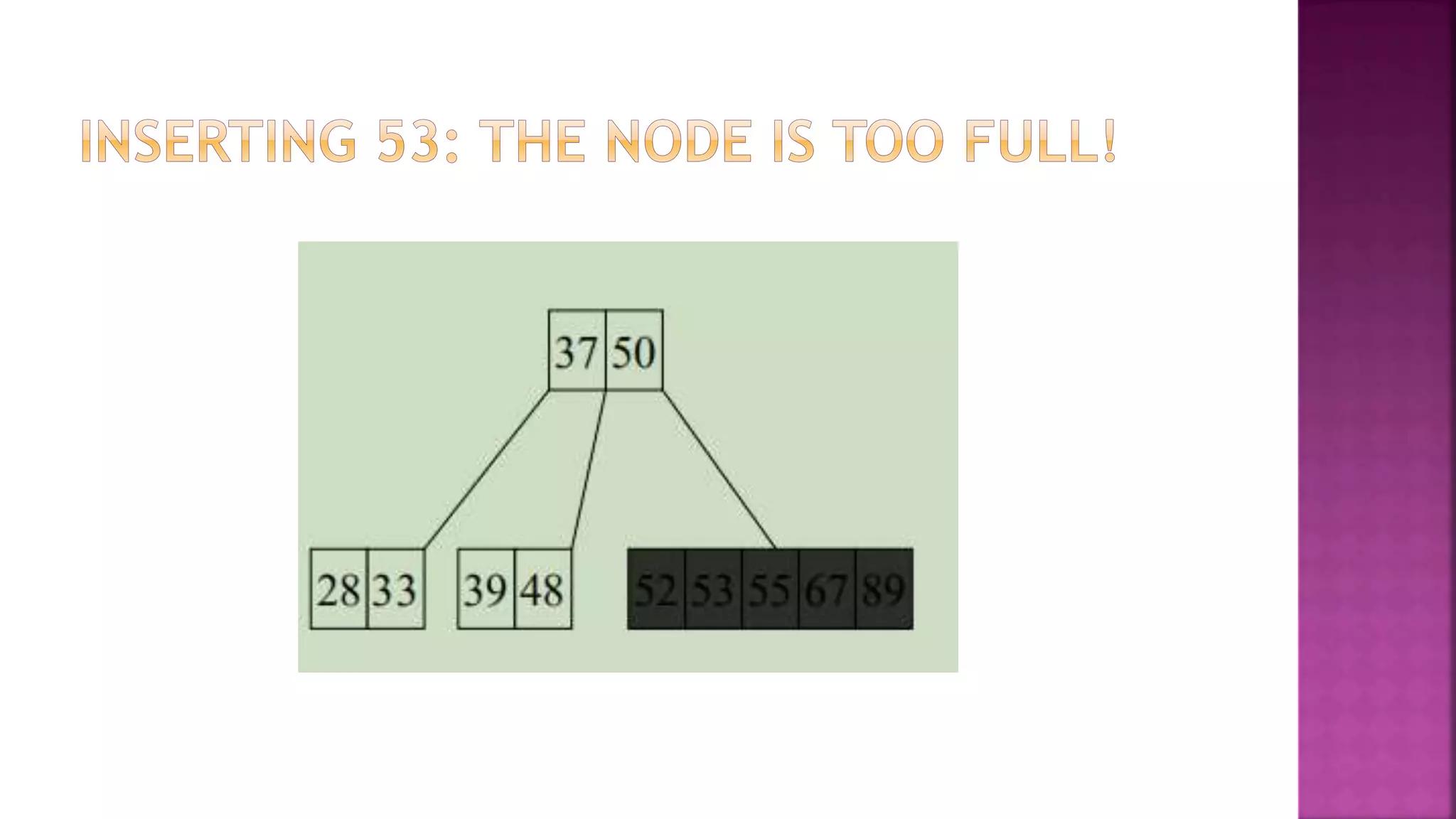
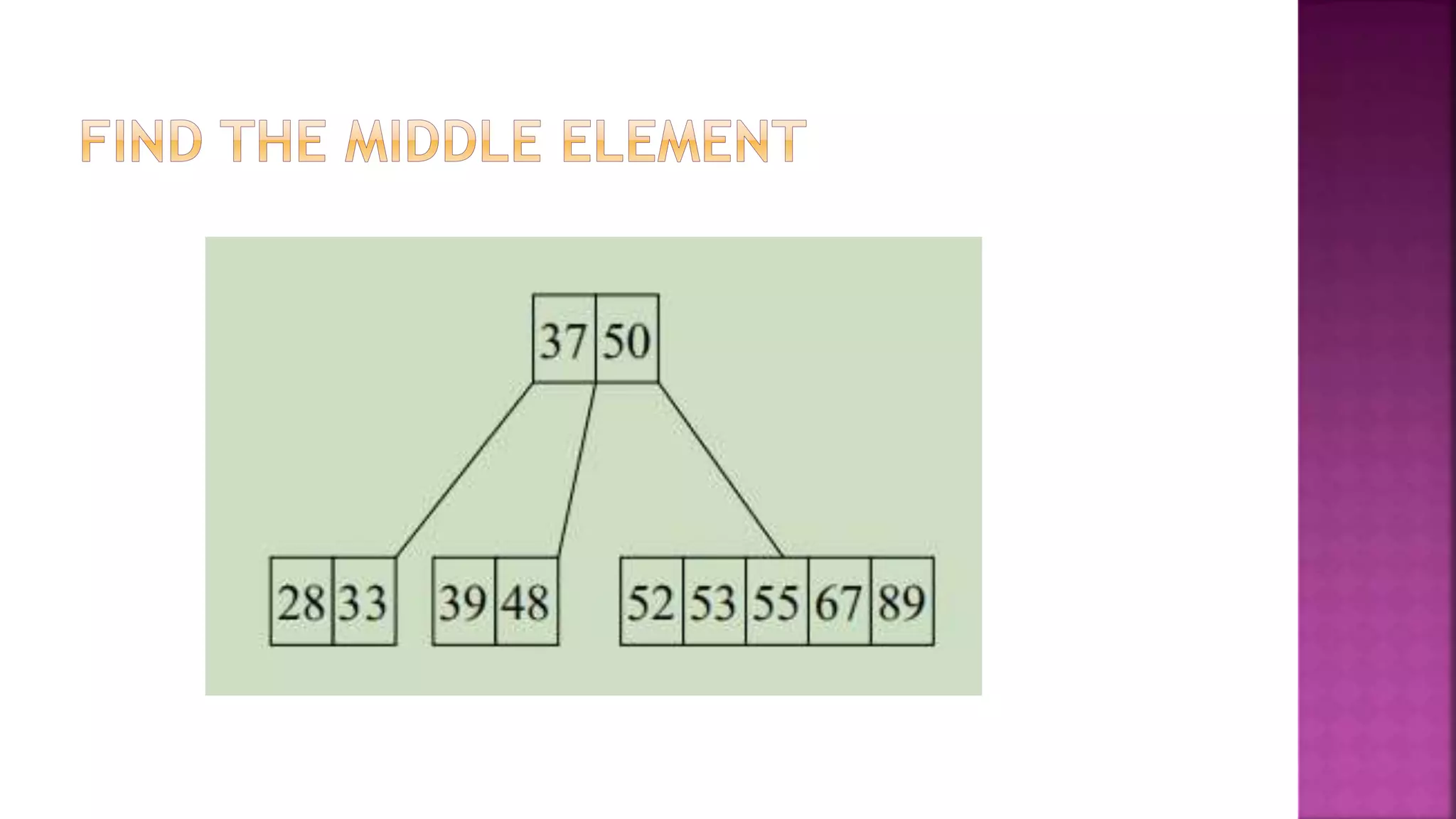
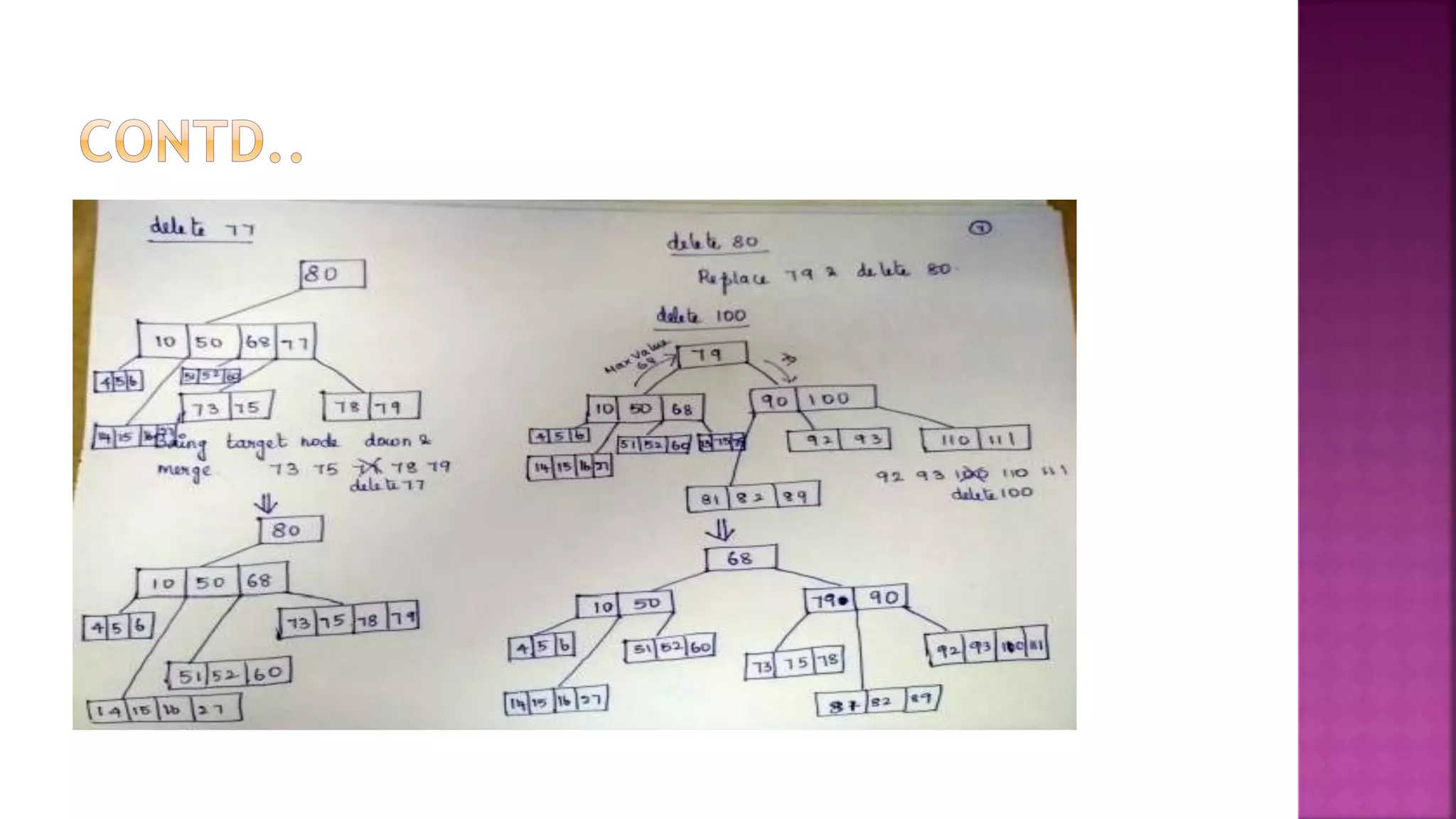
The document discusses trees and B-trees, which are data structures used to store and retrieve data efficiently. It notes that B-trees are well-suited for external memory as each node can hold multiple data items and child pointers. The key properties of B-trees are that each node has between m/2 and m child pointers and m-1 or fewer keys, ensuring the tree remains balanced during search, insertion, and deletion operations. An example of constructing a B-tree of order 4 from a sample data set is also provided.