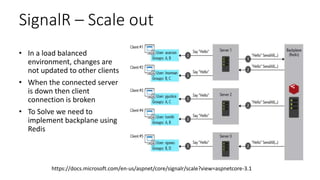
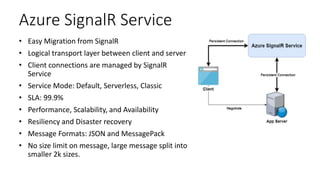
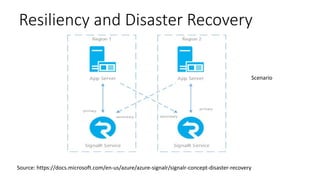
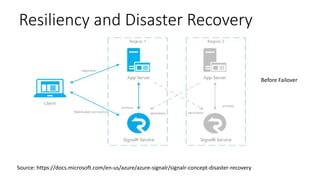
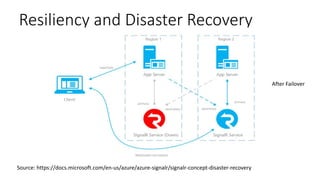
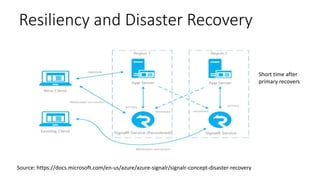
The document provides an overview of real-time web technologies including polling, long polling, server-sent events, websockets, and Azure SignalR Service, detailing their functionalities and use cases. It discusses the efficient communication protocols supported by SignalR and the challenges of scaling in load-balanced environments, recommending a Redis backplane for resilience. Additionally, it outlines the advantages of the Azure SignalR Service, such as performance, scalability, and disaster recovery capabilities.