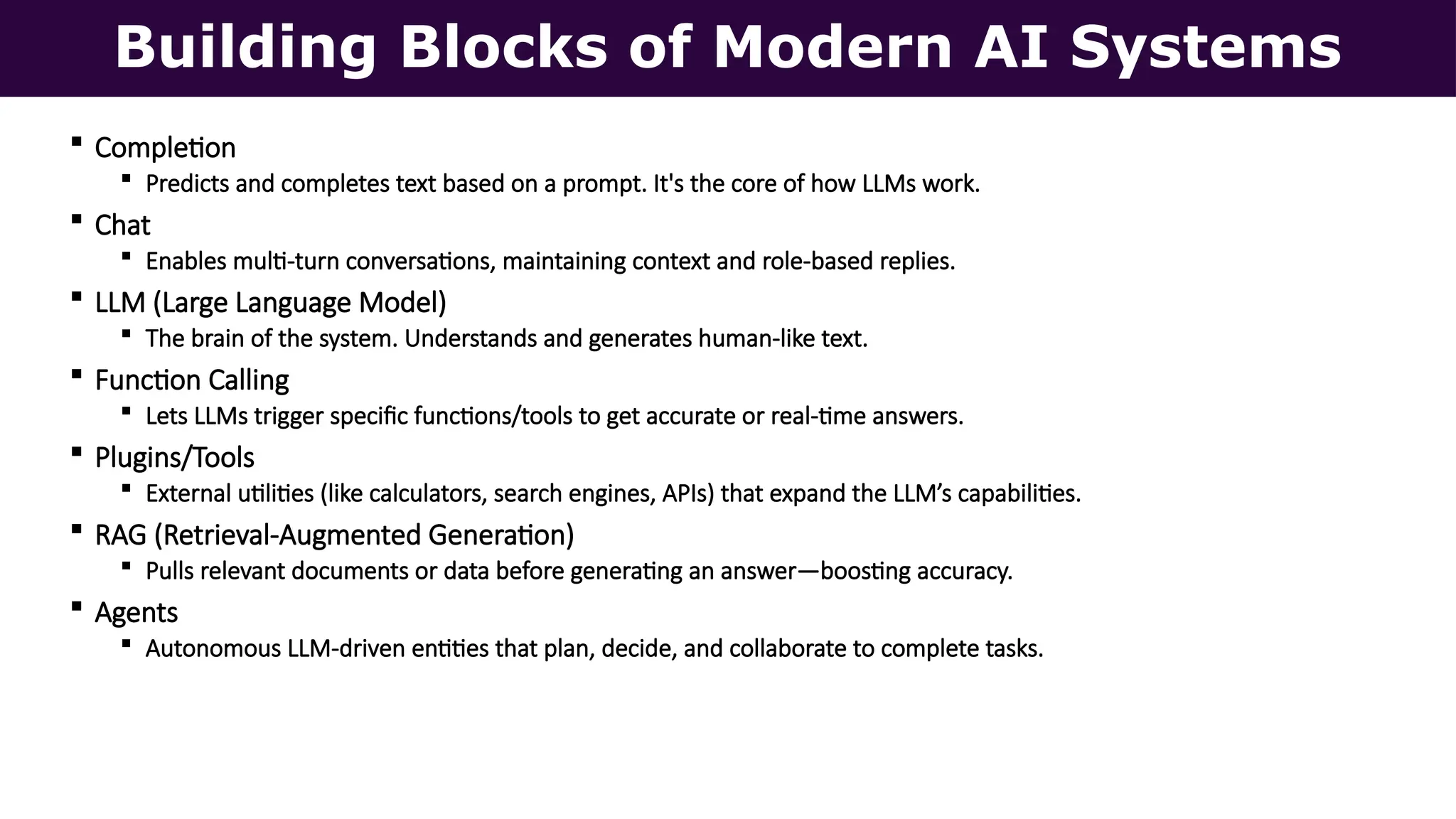
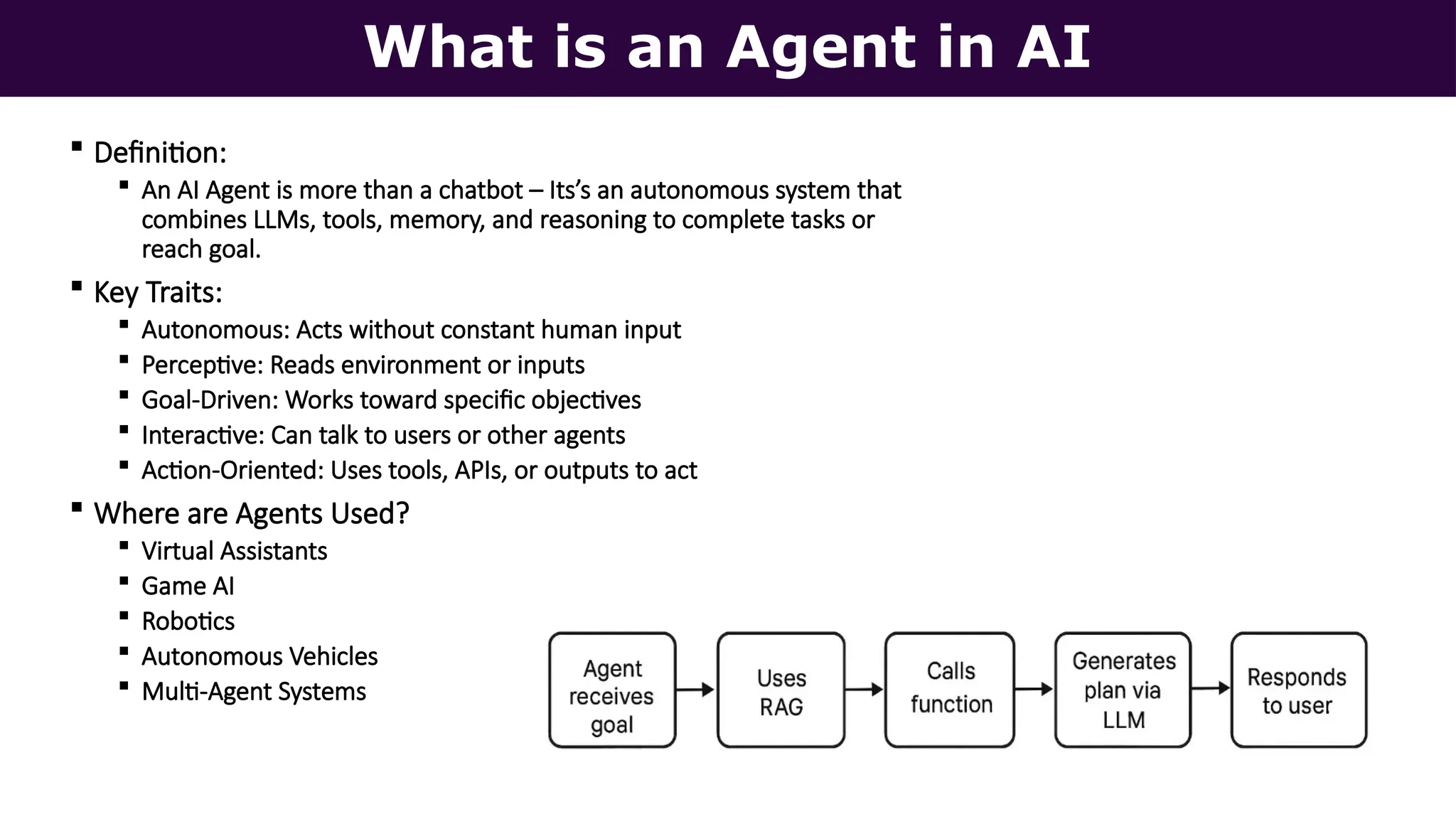
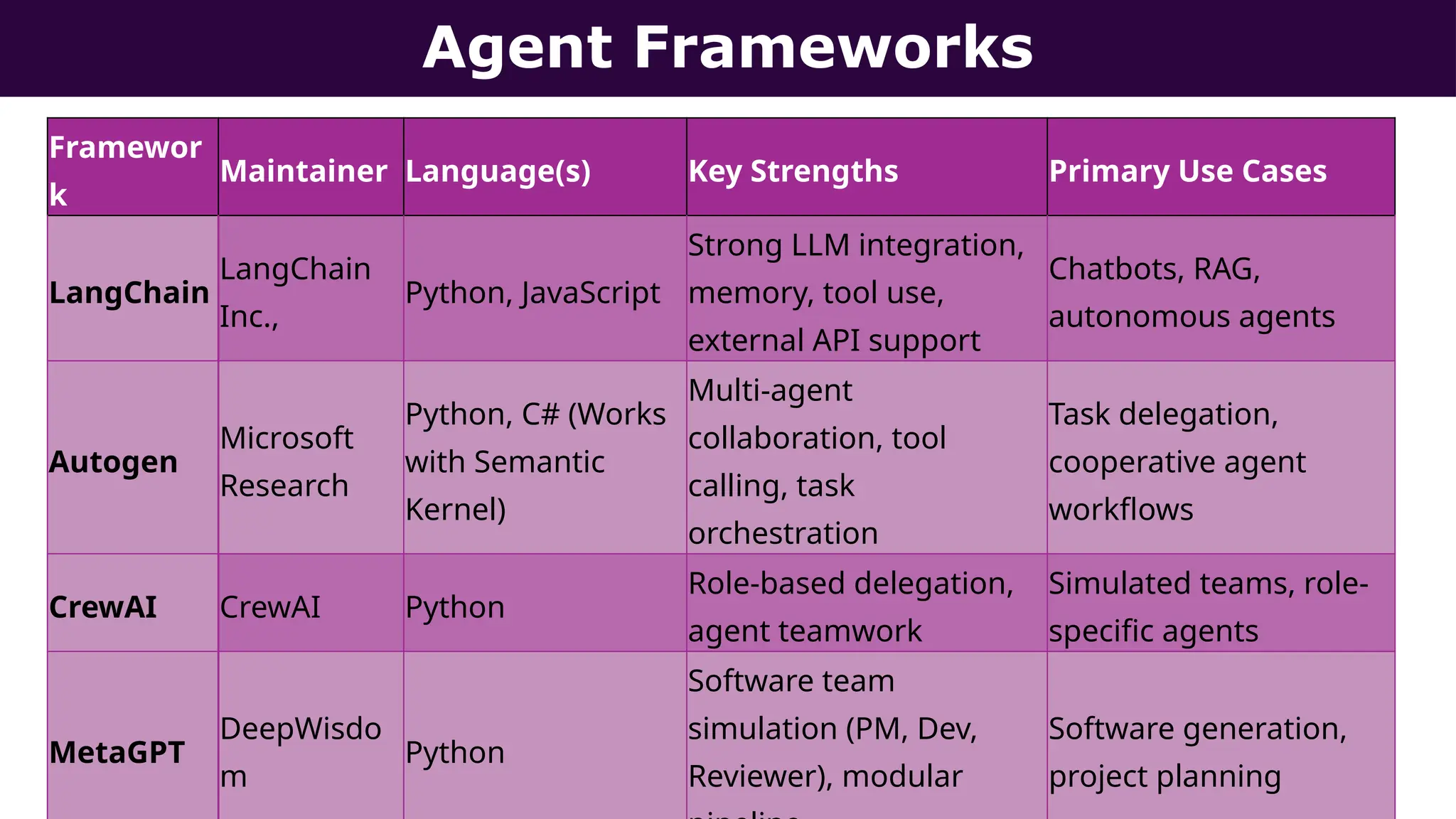
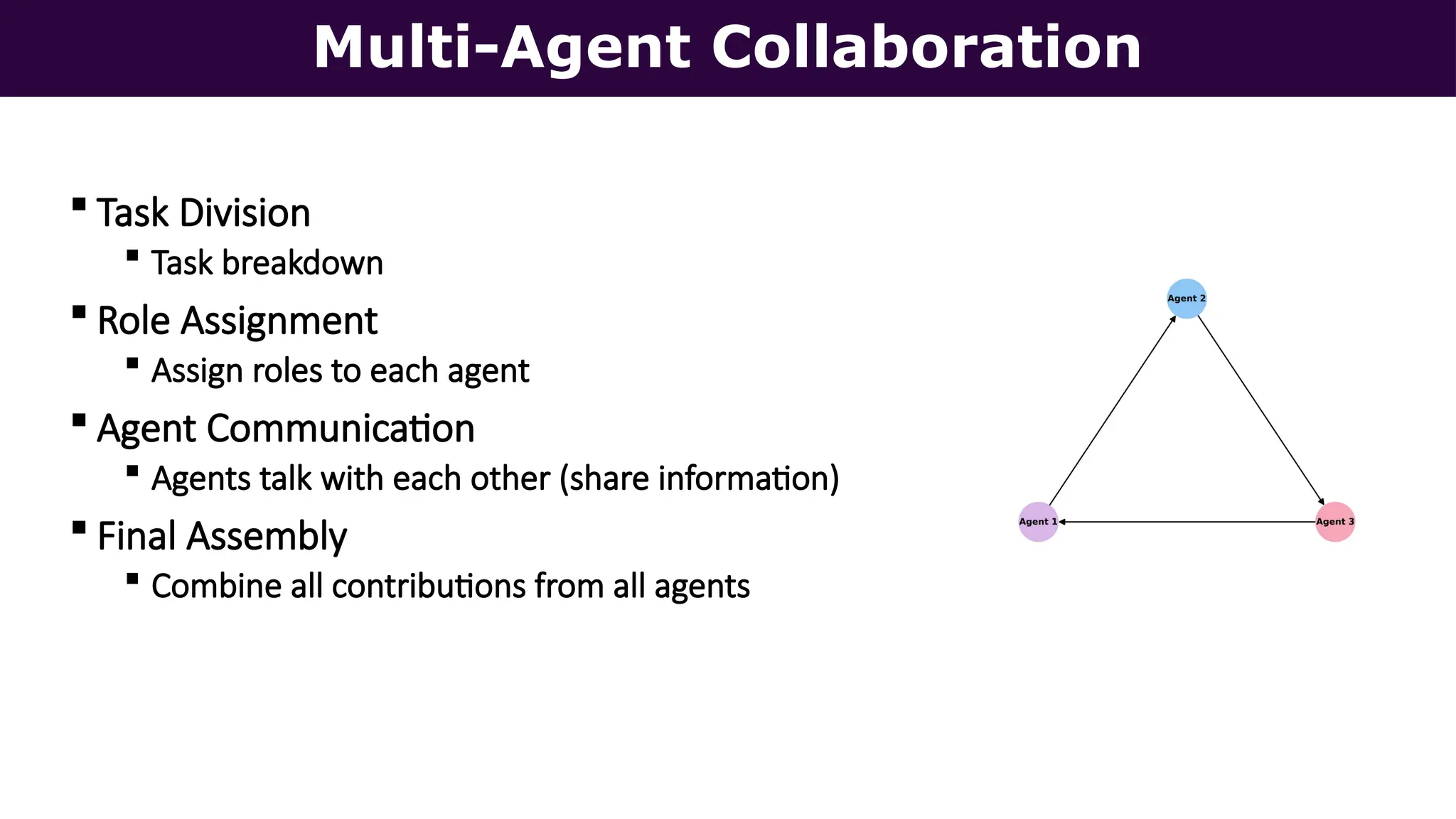
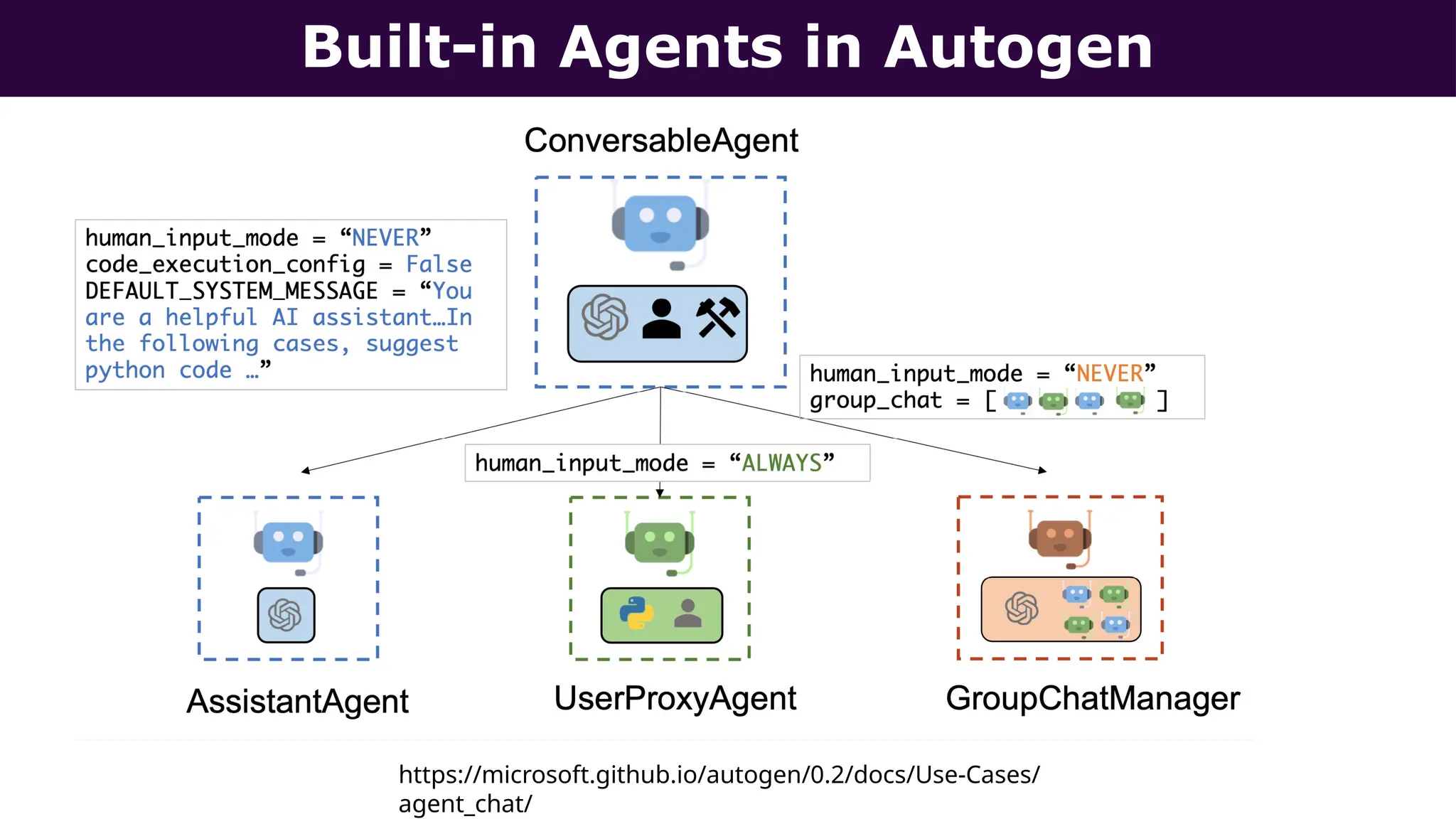
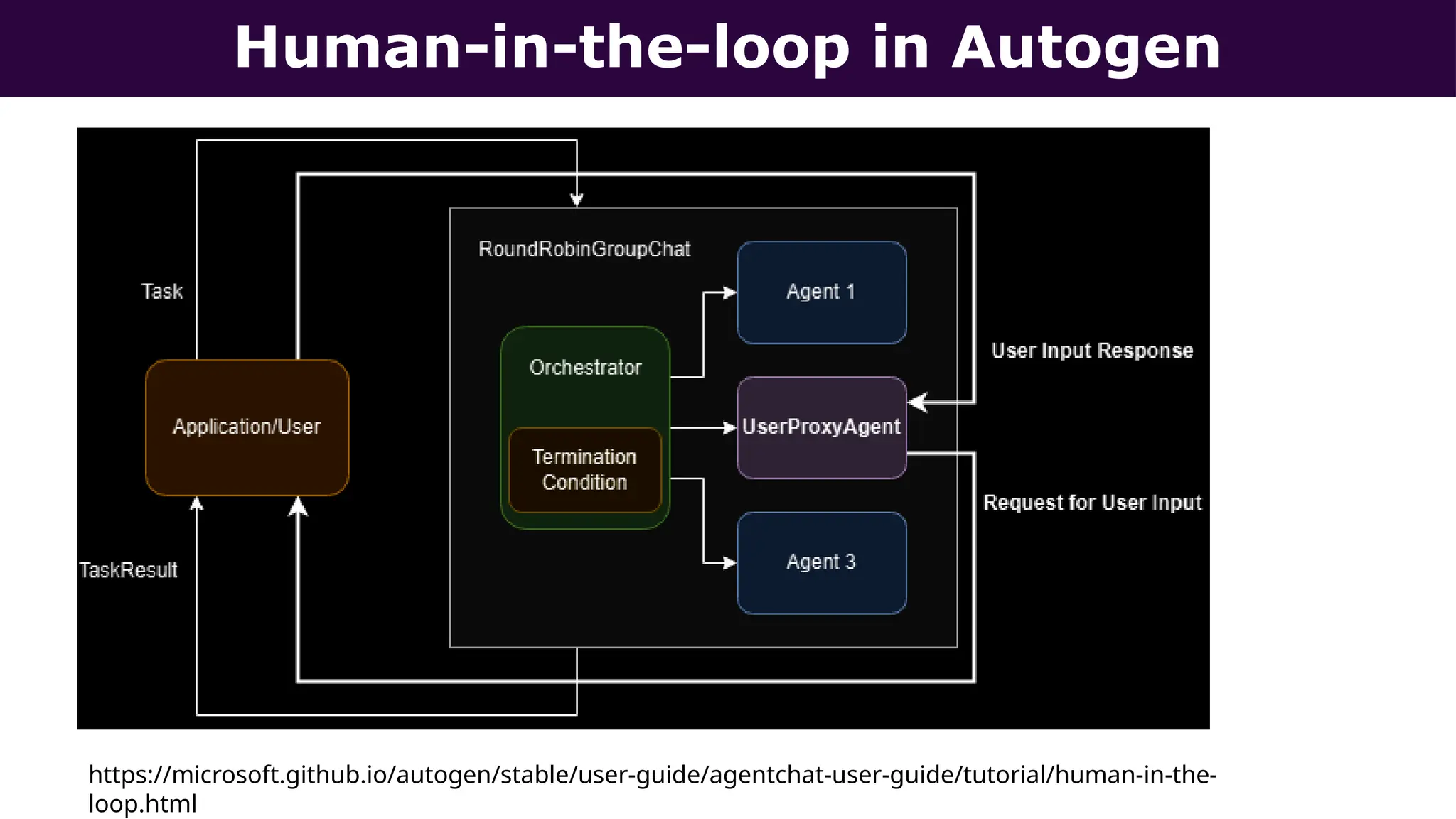
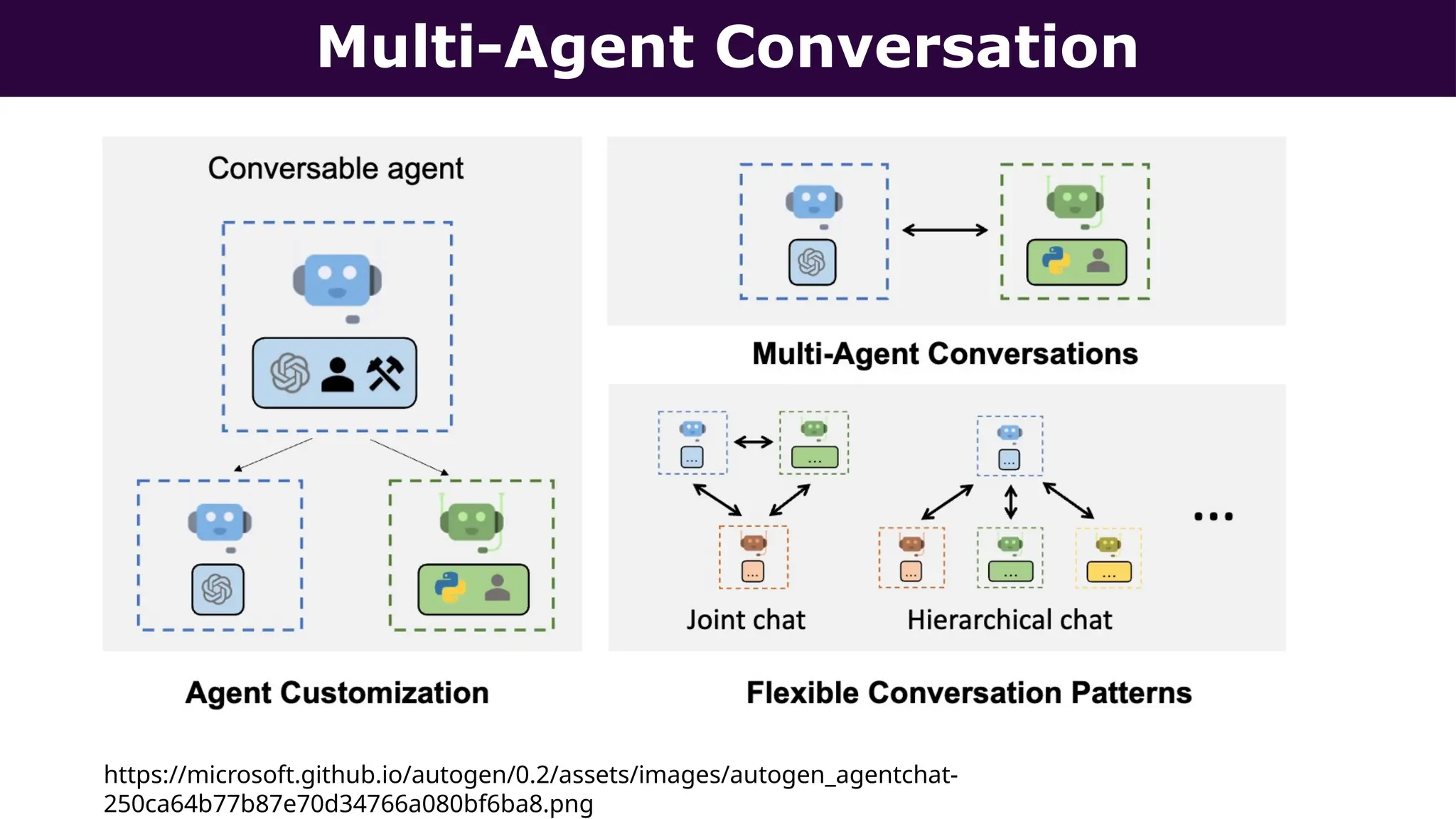
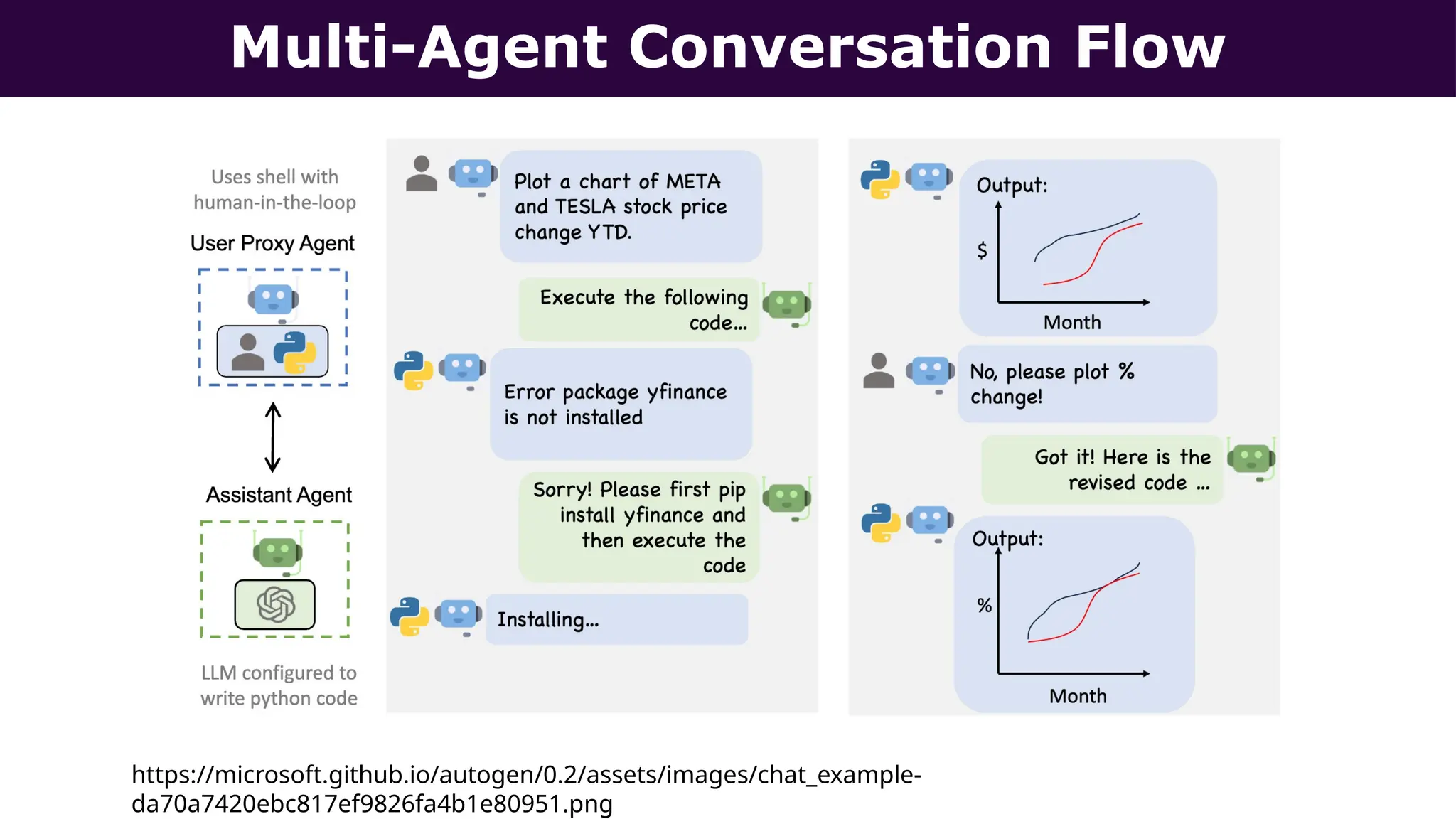
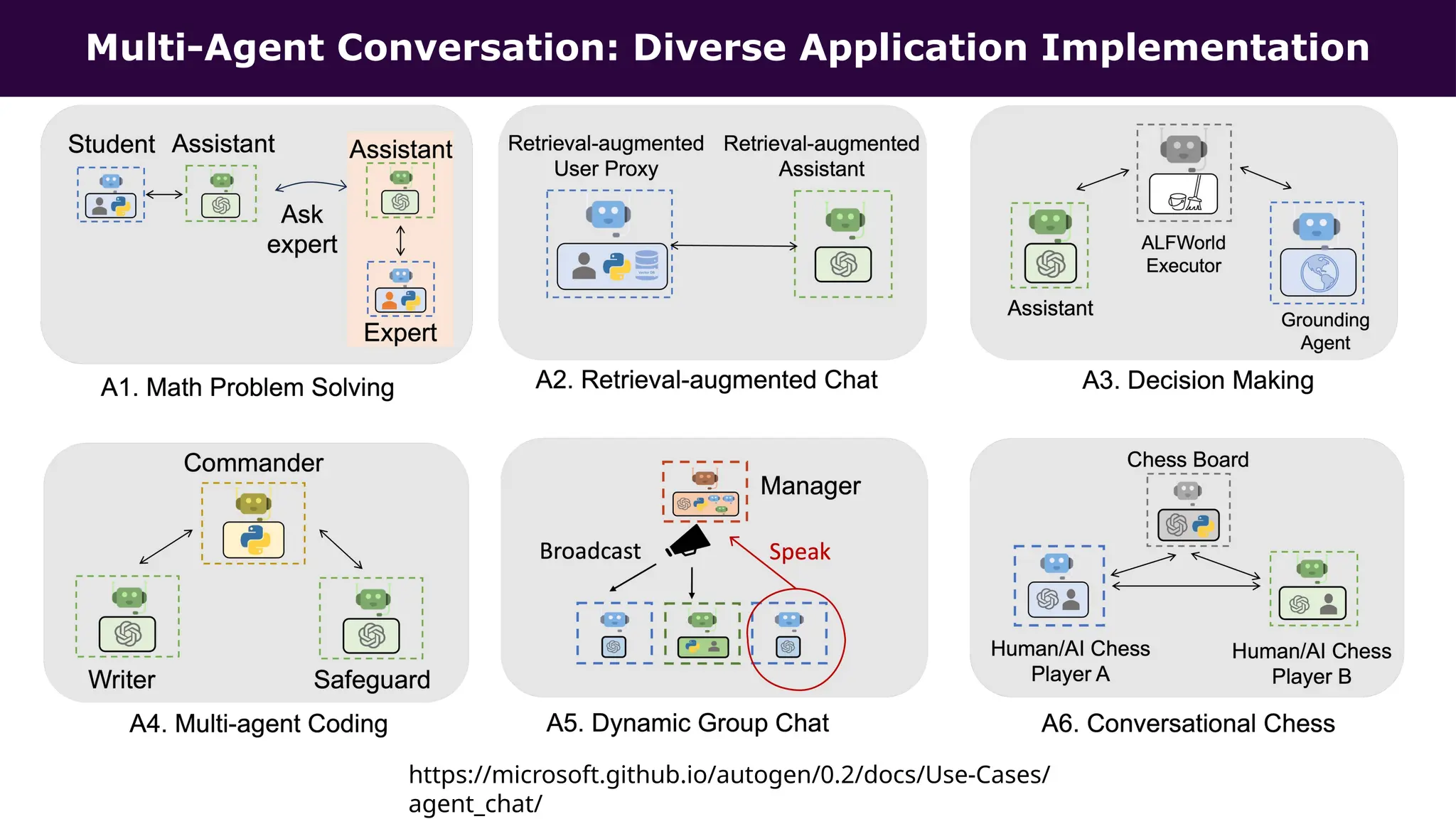
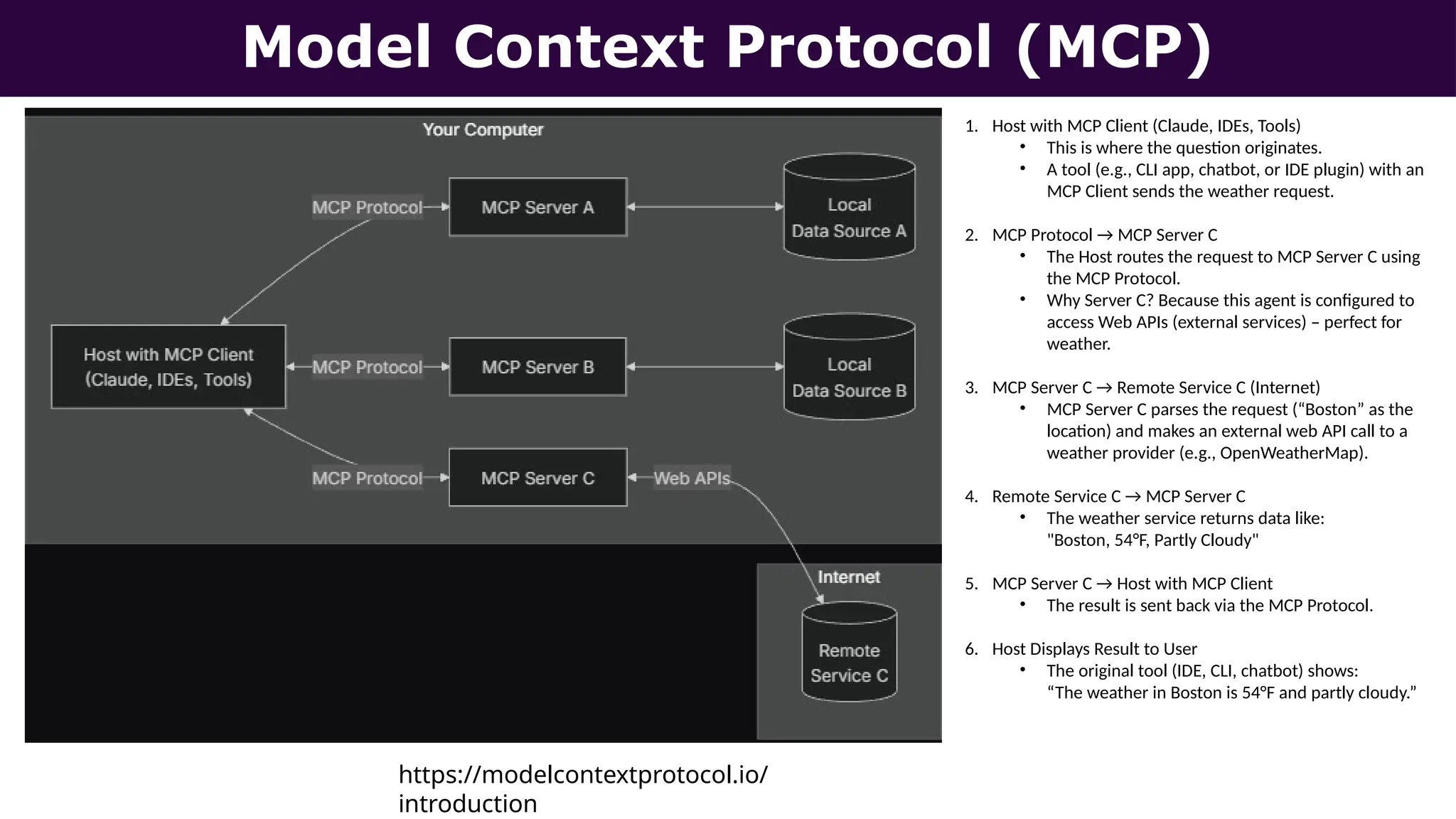
This presentation, delivered at Boston Code Camp 38, explores scalable multi-agent AI systems using Microsoft's AutoGen framework. It covers core concepts of AI agents, the building blocks of modern AI architectures, and how to orchestrate multi-agent collaboration using LLMs, tools, and human-in-the-loop workflows. Includes real-world use cases and implementation patterns.