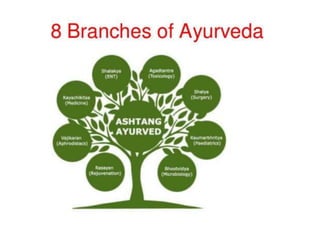
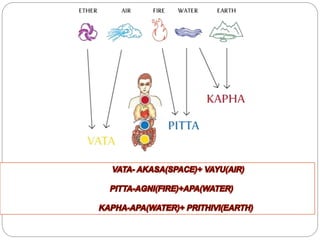
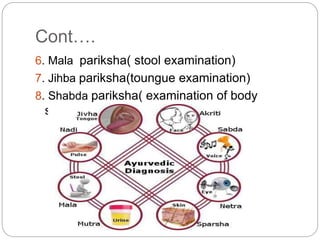
Ayurveda is an ancient Indian system of medicine that focuses on prevention and holistic healing. It believes that health results from a delicate balance between the mind, body, and spirit. Ayurvedic treatment aims to restore this balance through diet, herbs, yoga, massage, and meditation. Diagnosis evaluates the three doshas - vata, pitta, and kapha - which represent biological functions. Treatments are personalized and aim to improve digestion and eliminate toxins. Ayurveda uses plant, animal, and mineral substances but should only be practiced under the guidance of a qualified practitioner.