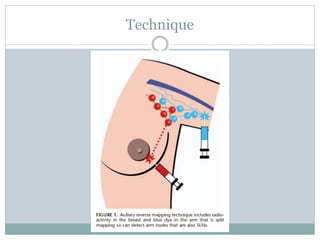
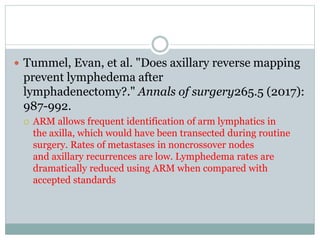
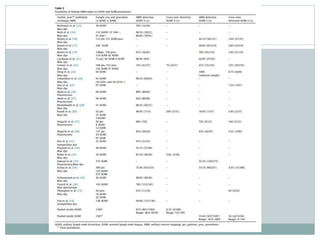
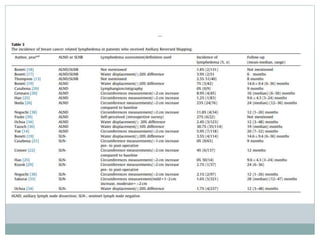
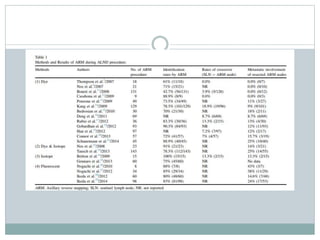
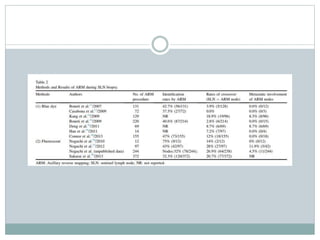
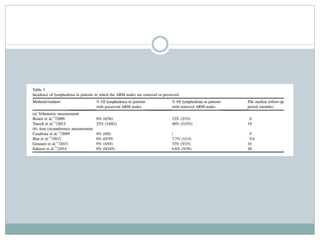
The document discusses the axillary reverse mapping (ARM) technique used during surgical procedures for breast cancer, highlighting its method, safety, and potential to reduce lymphedema rates. Studies cited show that while ARM is feasible and helps identify arm lymphatics, concerns exist regarding crossover nodes and oncological safety, particularly in patients with clinically positive breast cancer. Overall, although ARM has a theoretical benefit for lymphedema prevention, the evidence supporting its efficacy is limited due to variability in study methods and definitions.