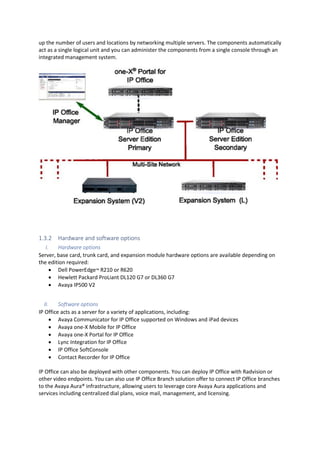
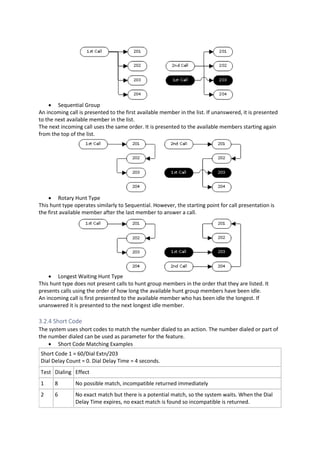
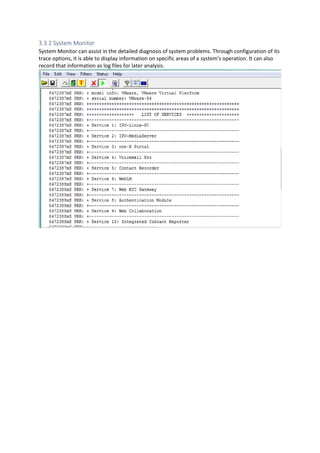
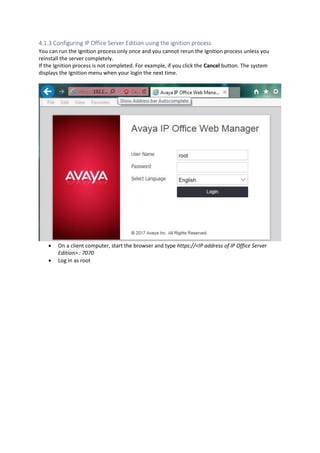
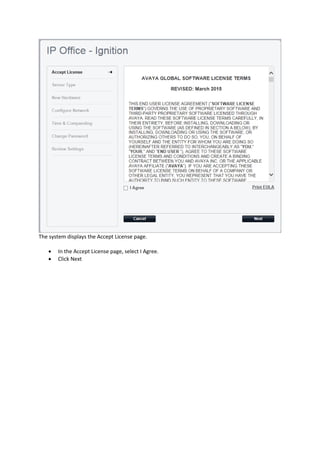
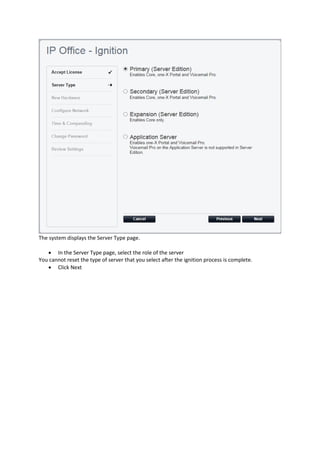
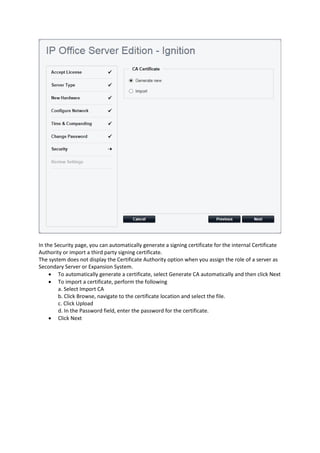
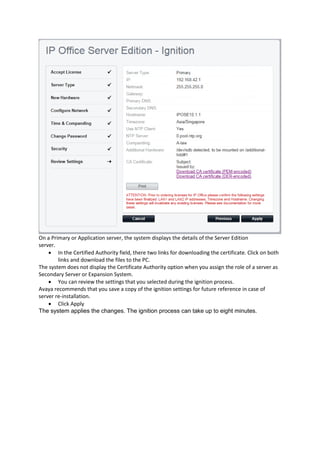
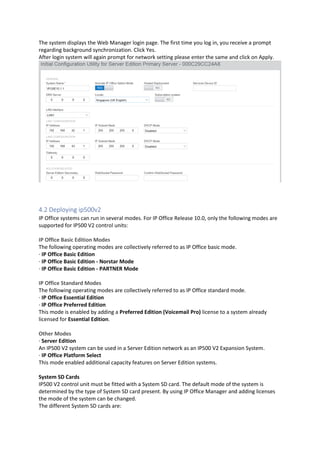
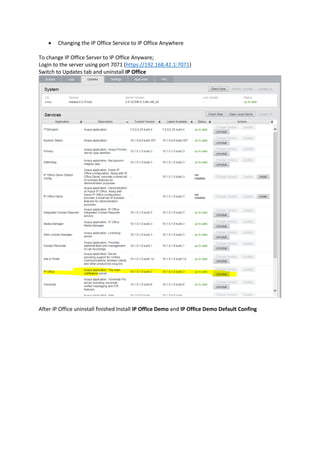
This document provides a high-level overview and introduction of the Avaya IP Office unified communications platform. It describes the various editions available from Basic to Server Edition, the hardware and software components, and reference configurations. Licensing and deployment options are also summarized. The document is intended to familiarize technical persons with the IP Office solution.