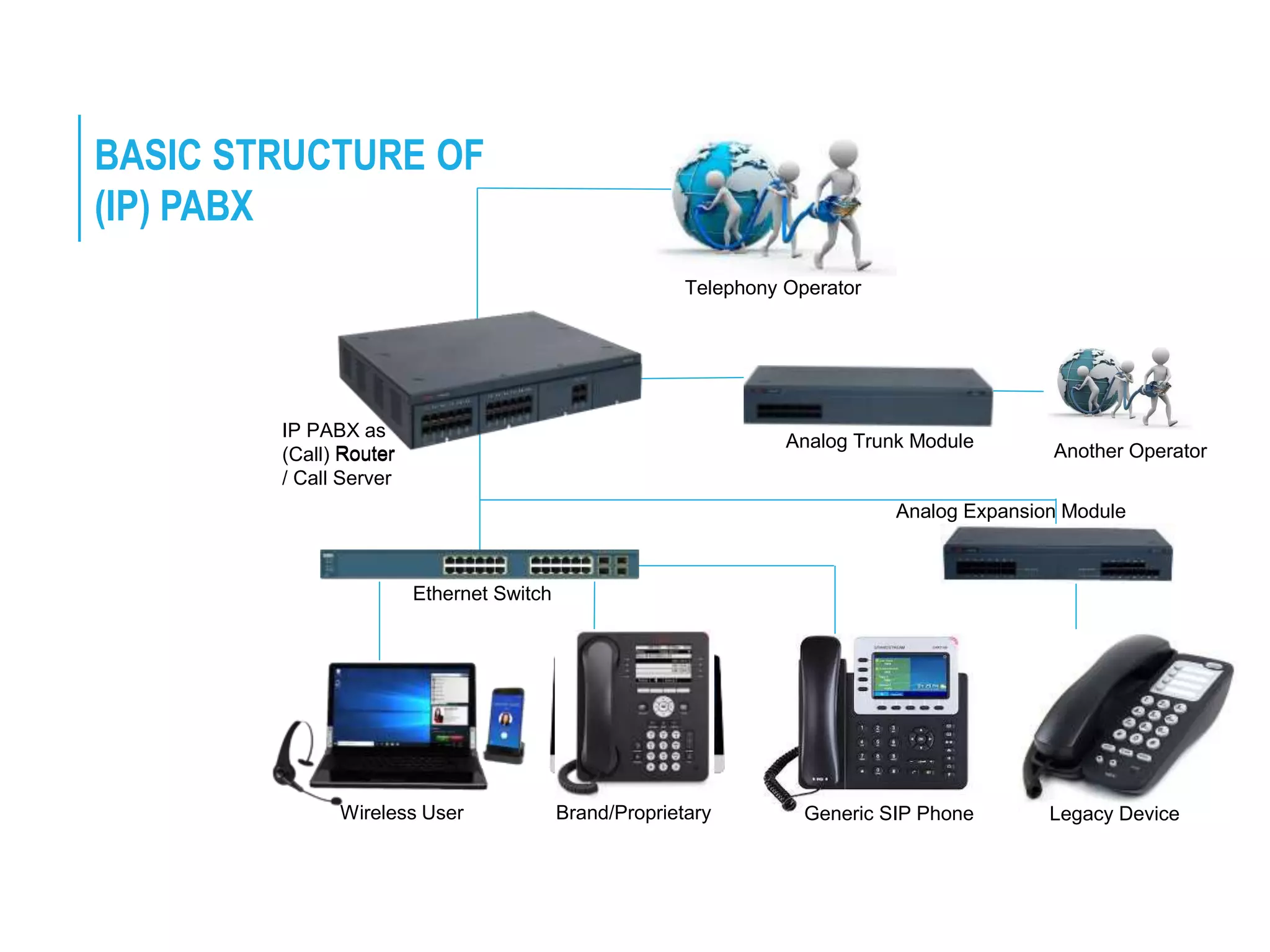
The document provides an overview of Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) systems, particularly focusing on Avaya IP Office technology and its evolution in Bangladesh's telecommunication landscape. It explains the functionality of PABX, which enables efficient call routing and management in large organizations, and outlines specific components of the Avaya IP Office system, including various modules and devices for improved VoIP communication. Key features include its support for both analog and IP phones, essential for modern telephony services.