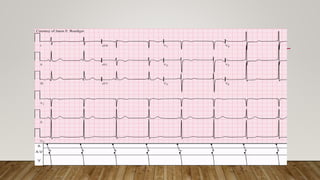
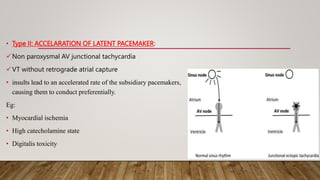
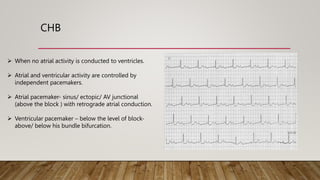
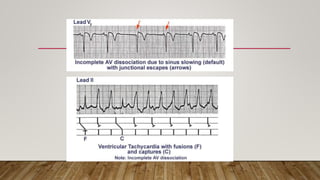
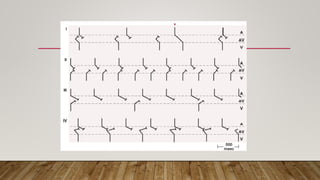
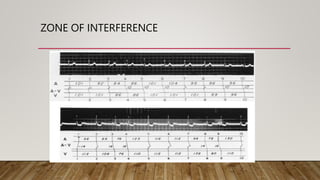
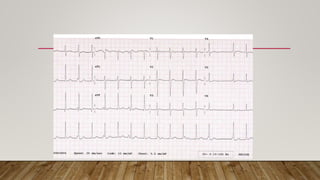
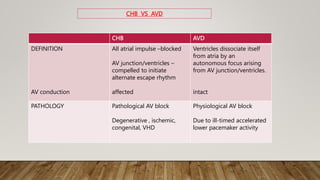
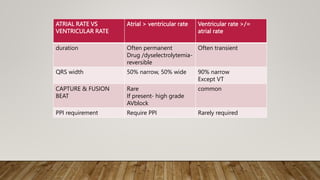
AV dissociation occurs when the atria and ventricles contract independently due to impaired conduction between the two. It is caused by one of three mechanisms: 1) conduction block at the AV node, 2) interference from an accelerated lower pacemaker like VT or AVNRT, or 3) complete heart block. There are four types of AV dissociation based on cause. Type I occurs when sinus bradycardia allows an escape junctional rhythm. Type II is due to acceleration of a latent pacemaker. Type III is complete heart block. Type IV is a combination of causes like digitalis toxicity leading to various arrhythmias and conduction abnormalities.