Embed presentation
Download to read offline








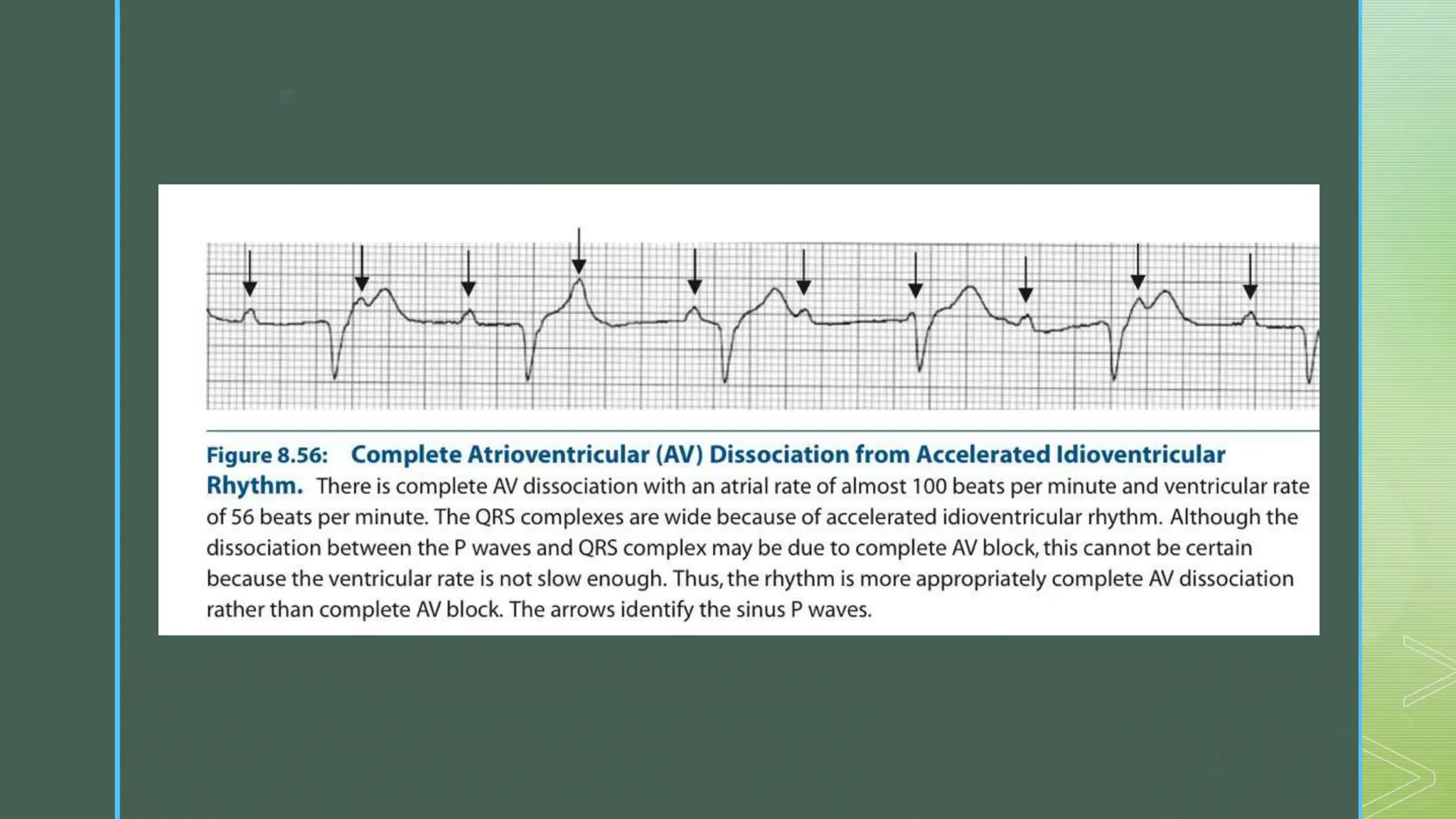
Complete AV dissociation is a broad term referring to any arrhythmia where the atria and ventricles contract independently of each other. It can be caused by AV block or the ventricles beating too fast such that atrial signals fall within their refractory period. On ECG, P waves and QRS complexes are completely dissociated with no relationship. The underlying rhythm in complete AV dissociation may be ventricular tachycardia, junctional tachycardia, accelerated junctional rhythm, accelerated ventricular rhythm, or complete AV block.








