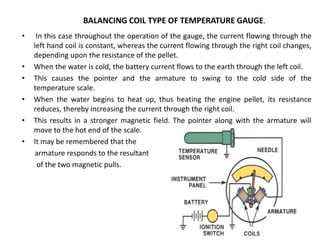
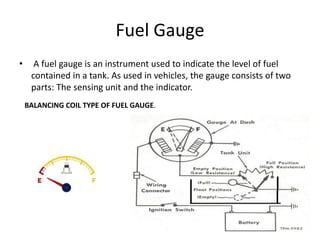
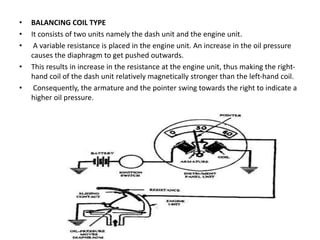
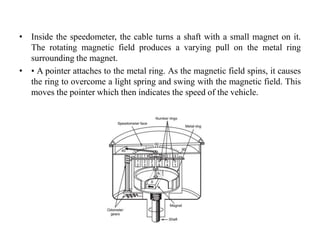
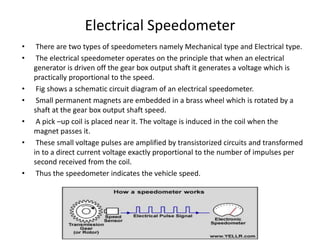
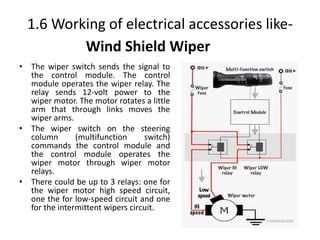
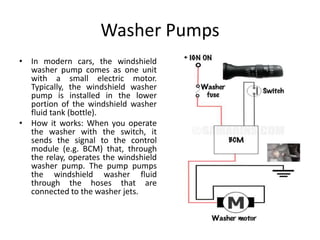
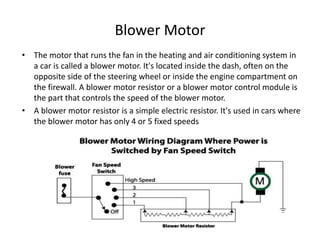
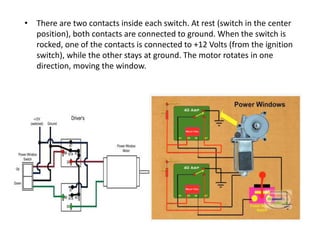
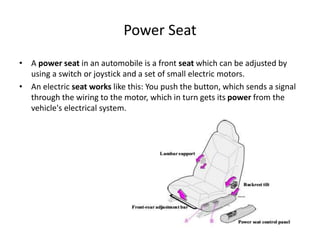
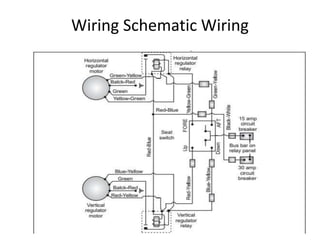
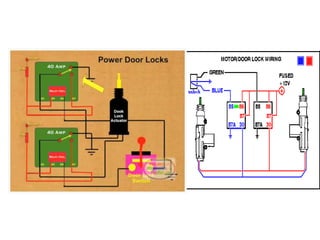
This document provides an overview of electrical and electronic components in automobiles. It discusses the purpose and operation of switches, relays, solenoids, buzzers, resistors, and circuit protection devices. It then explains the working of various electromagnetic gauges like temperature gauges, fuel gauges, oil pressure gauges, and speedometers. Features of scan testers are outlined. Finally, the operation of various electrical accessories is described, including windshield wipers, washer pumps, blower motors, electrochromic mirrors, power windows, power seats, and power door locks.