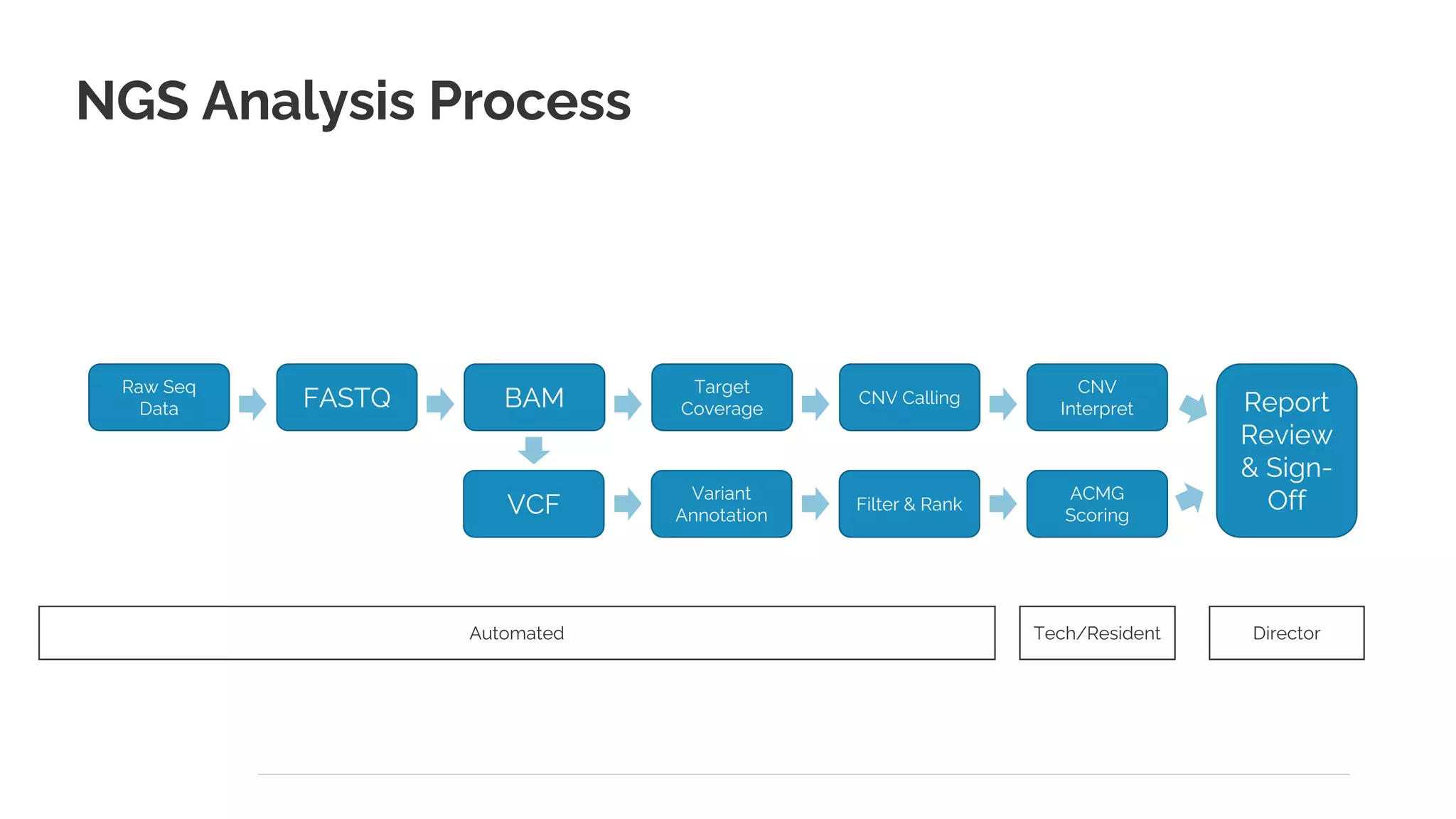
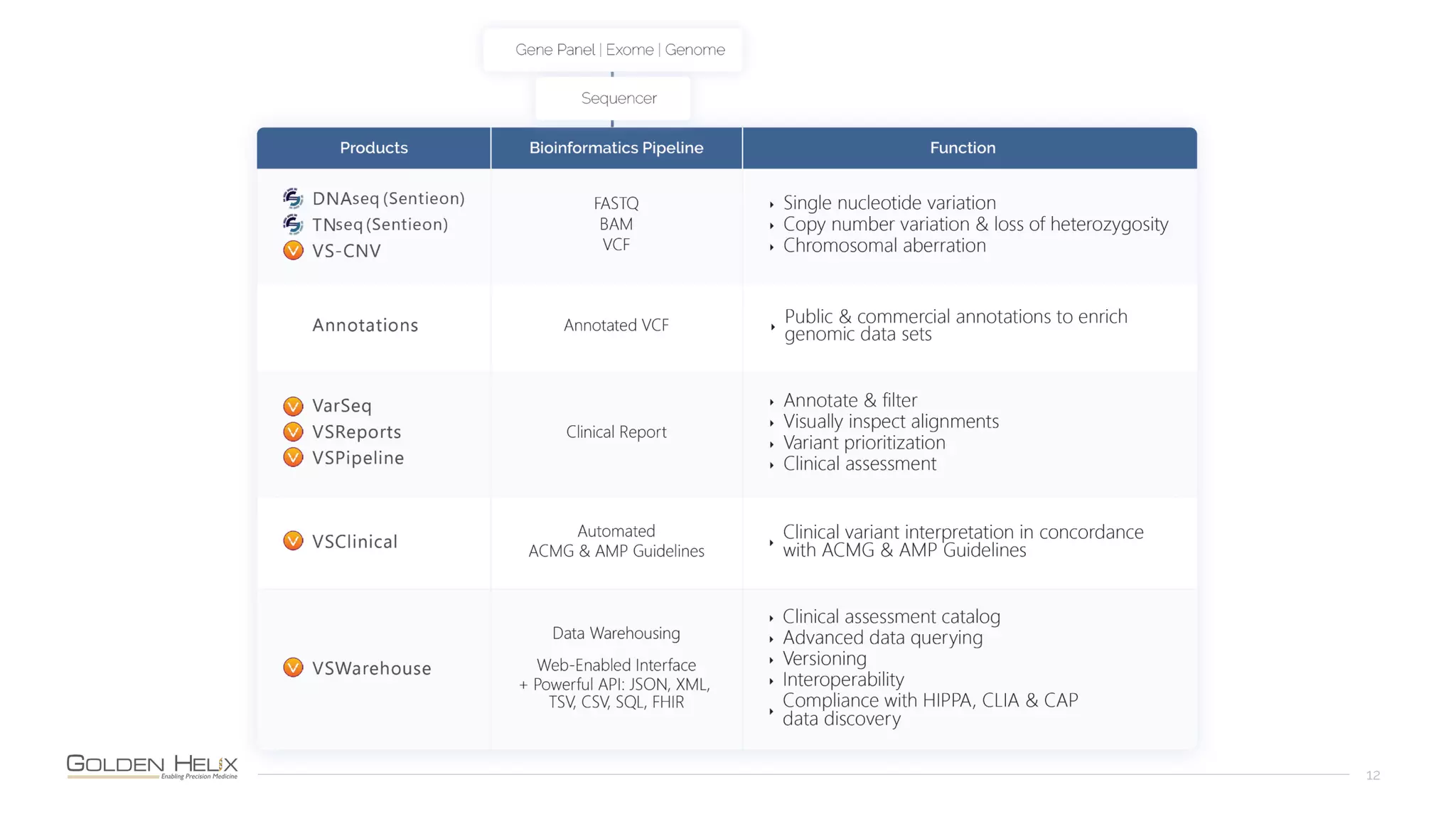
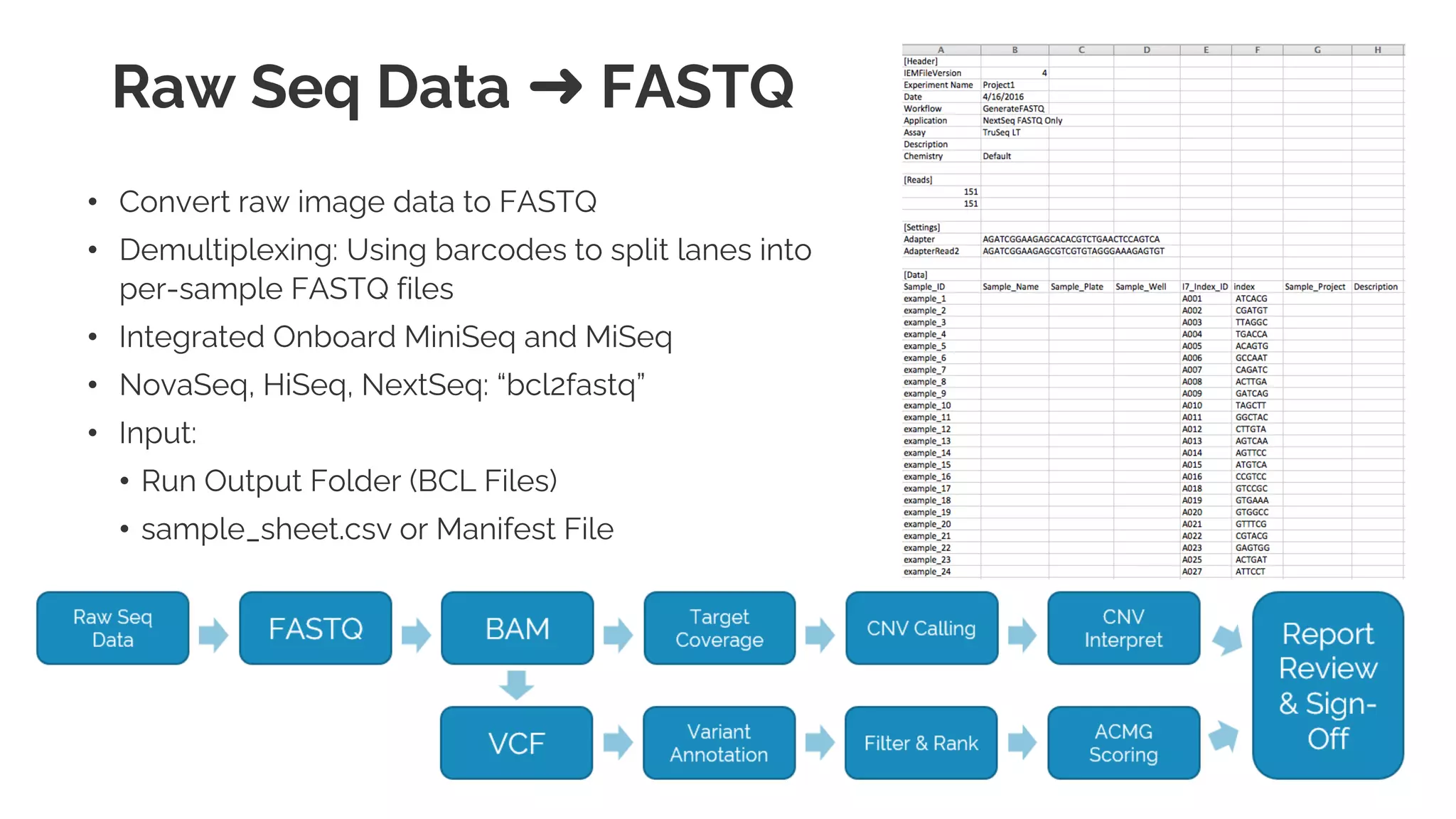
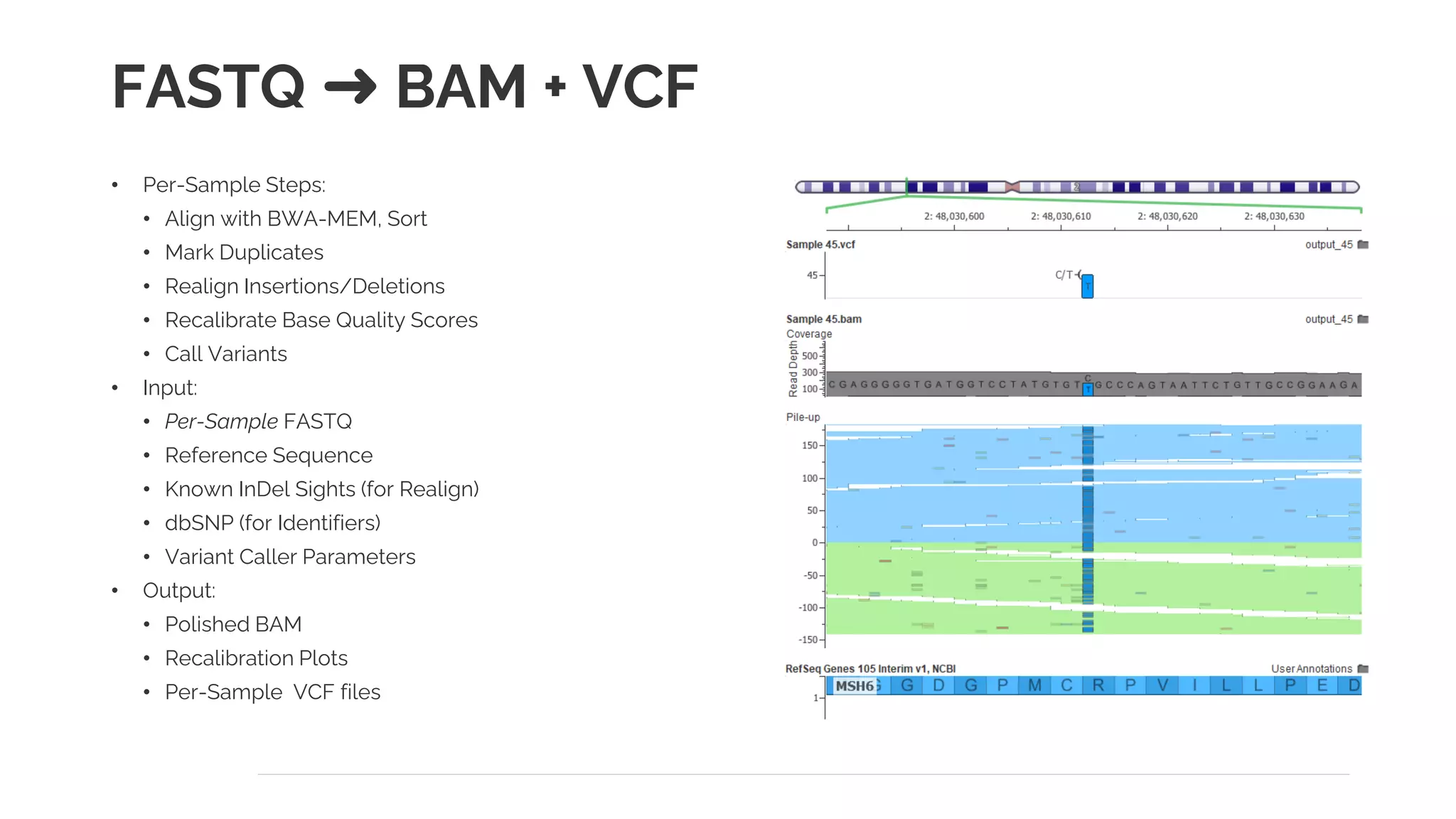
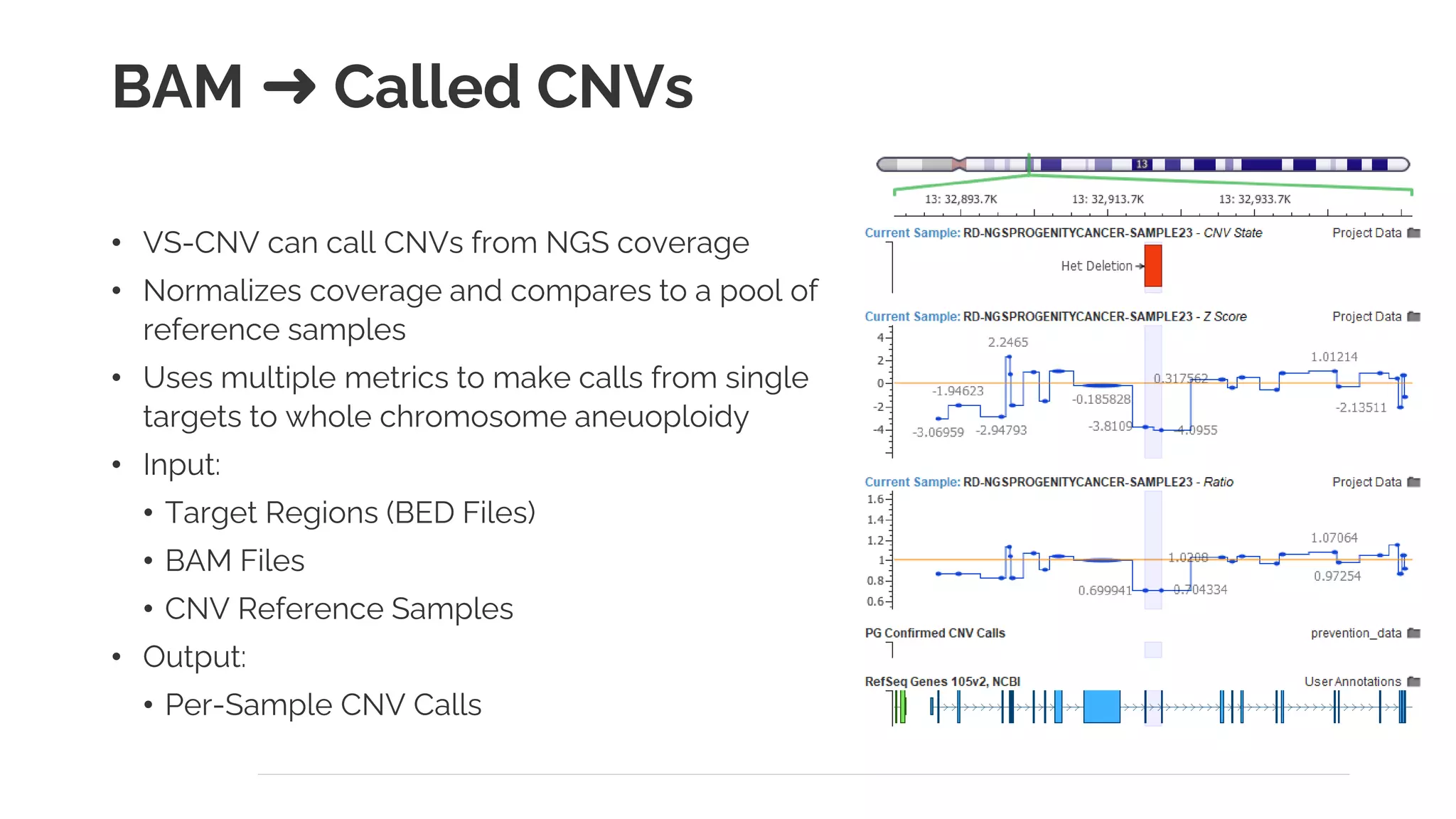
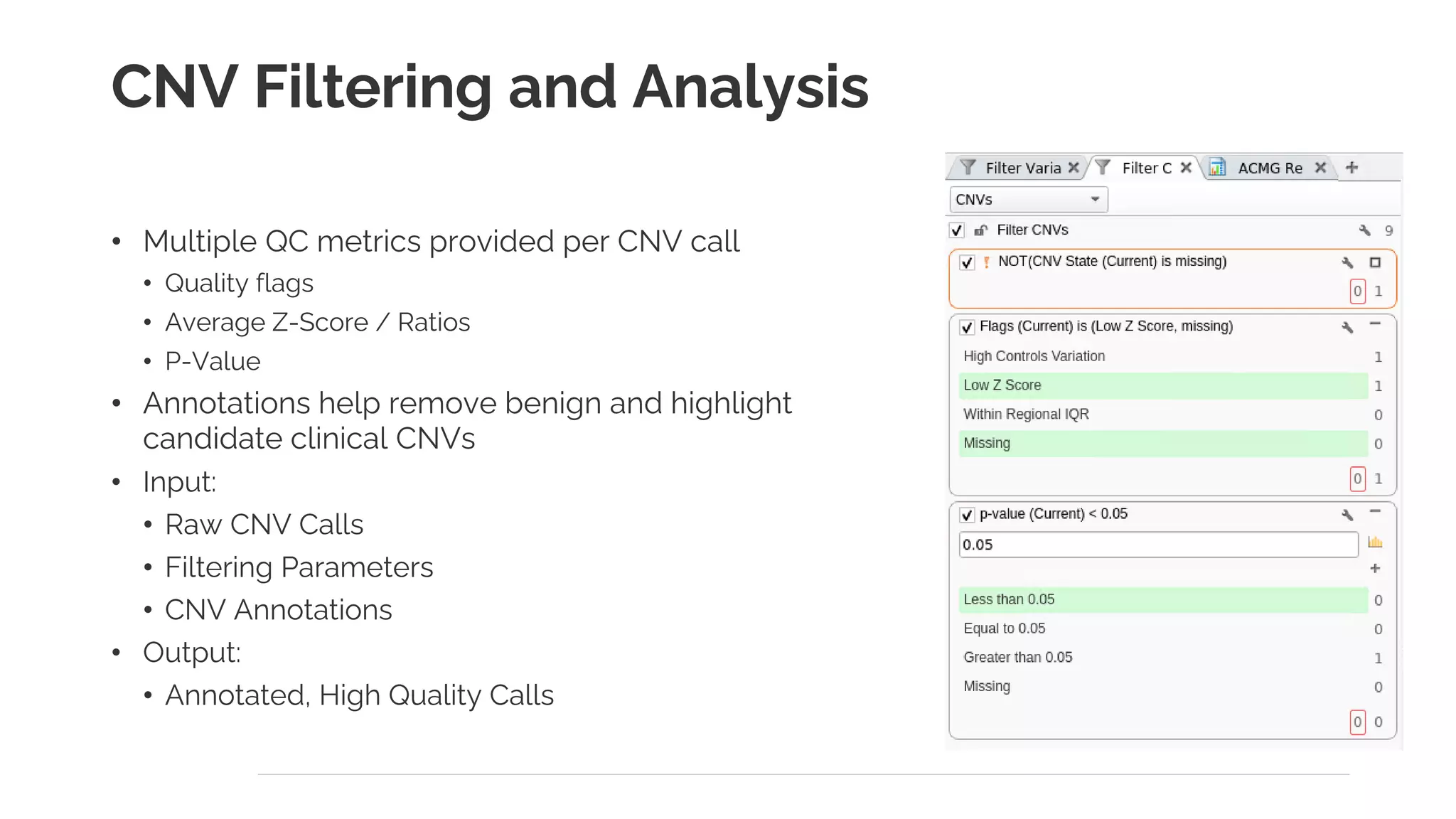
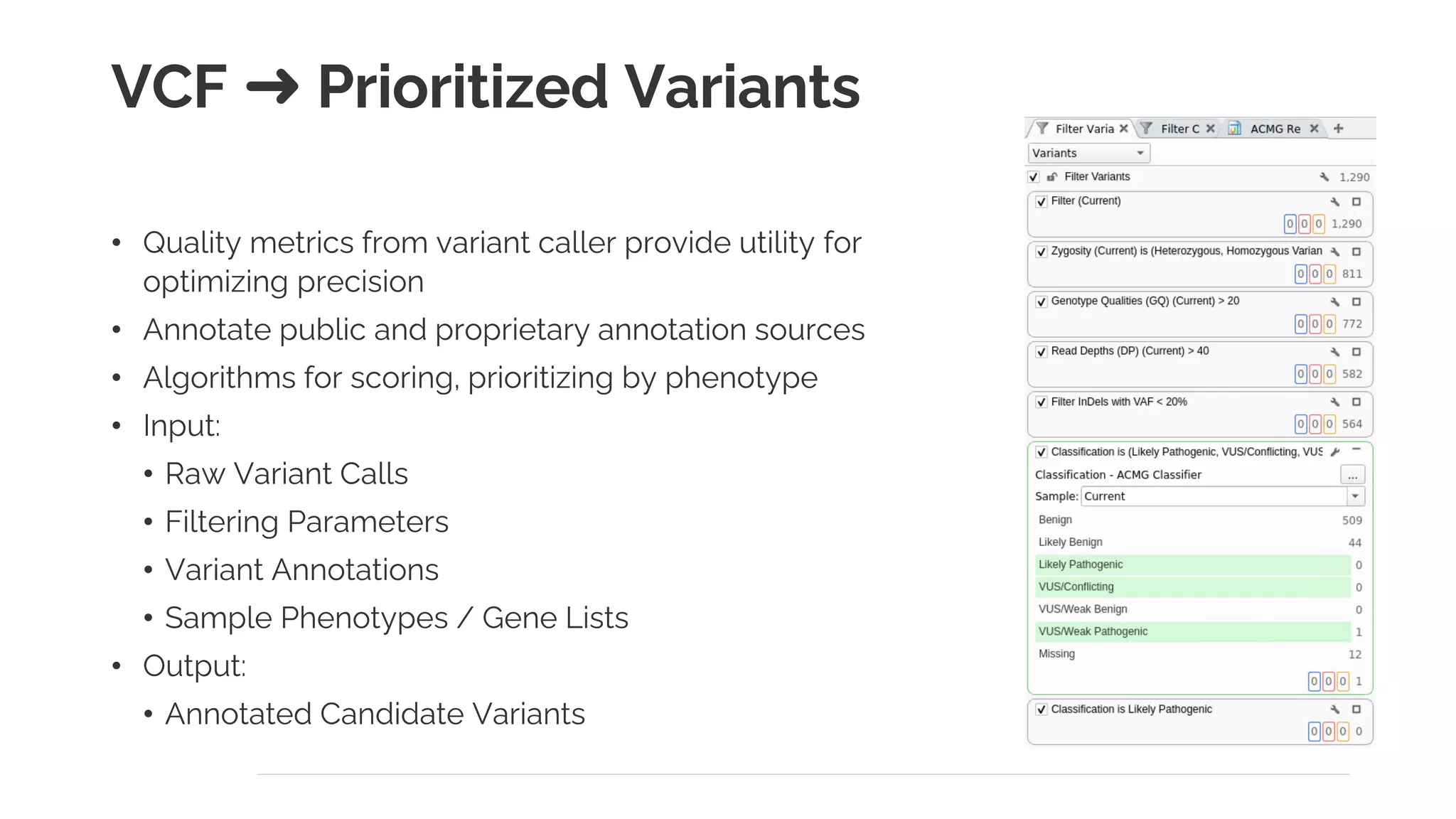
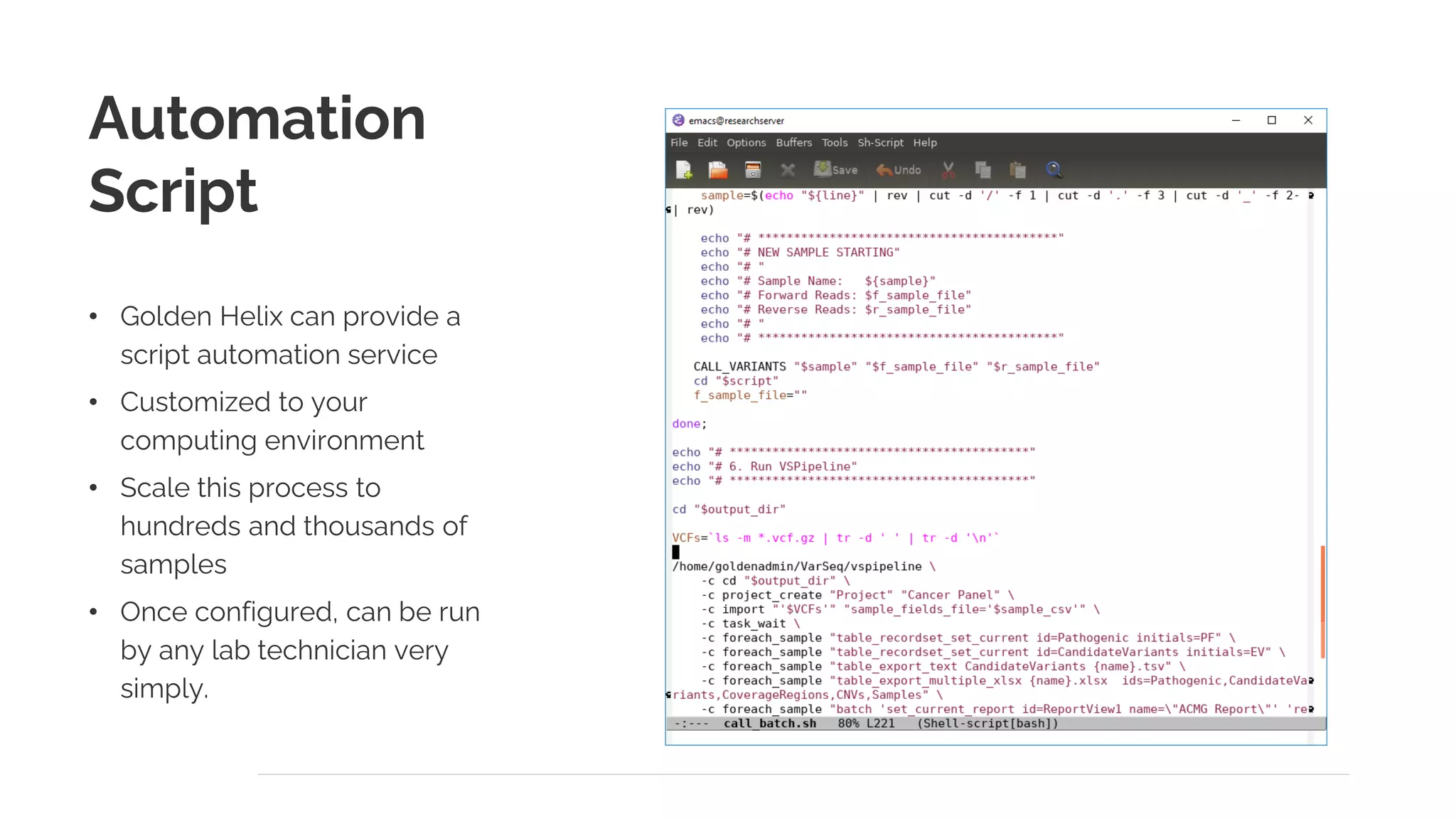
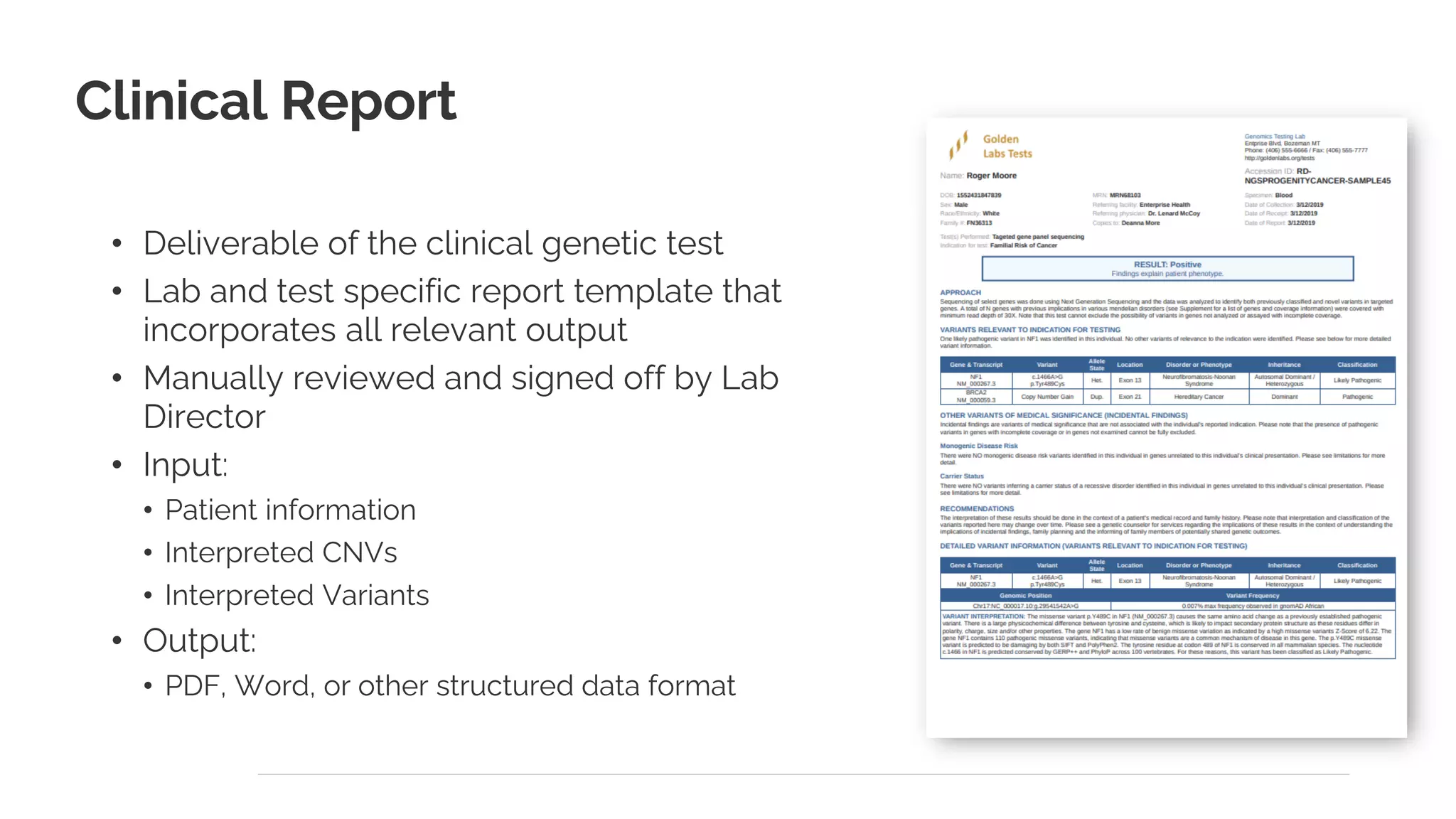
The document presents a discussion on automating clinical workflows using the VarSeq suite, led by Dr. Nate Fortier of Golden Helix. It outlines the benefits of automation in increasing lab throughput and reducing human error, along with a detailed overview of the NGS analysis process including variant calling and CNV analysis. Additionally, it highlights the support from various NIH grants and invites attendees to visit their booth for further engagement.