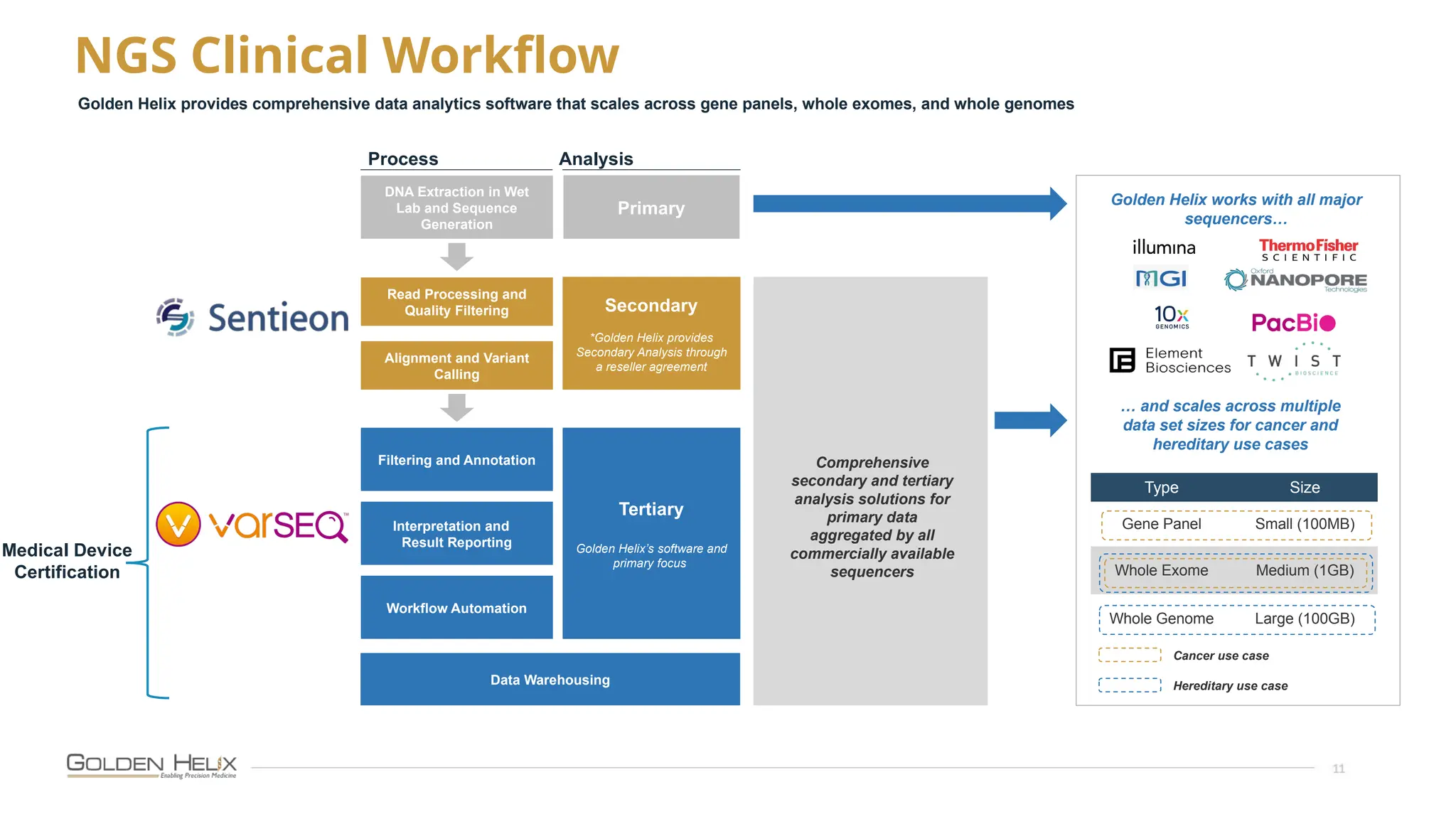
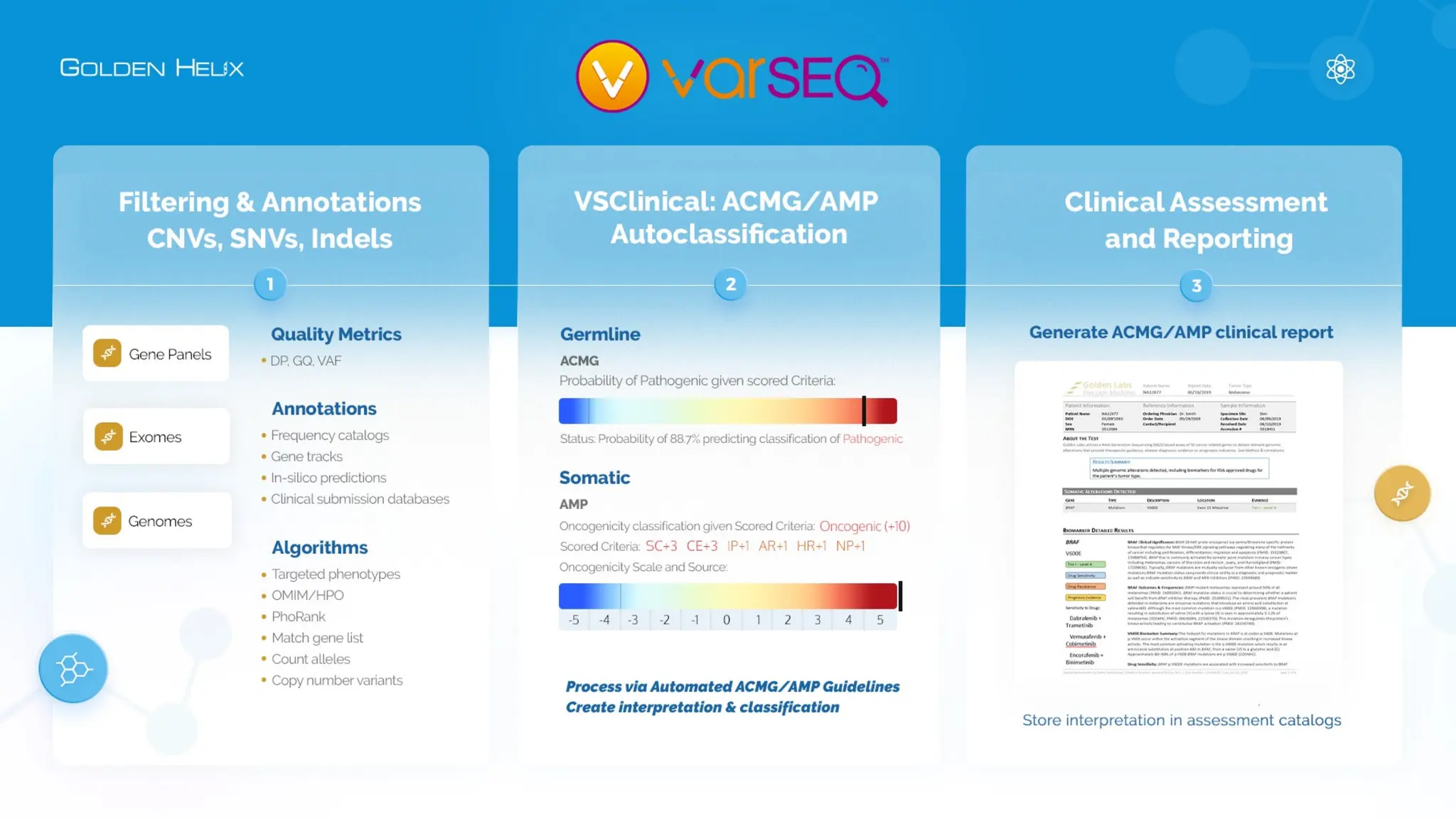
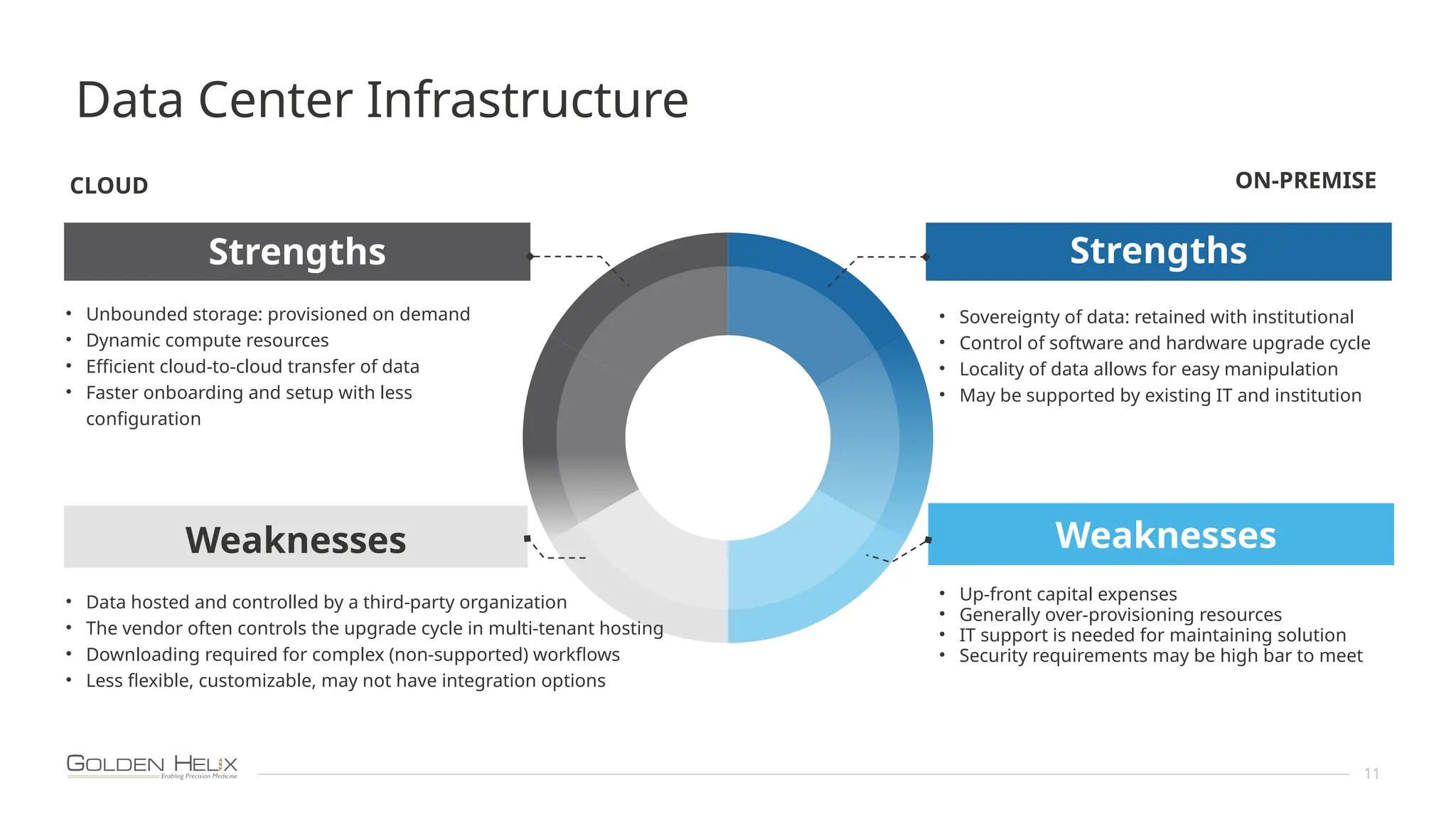
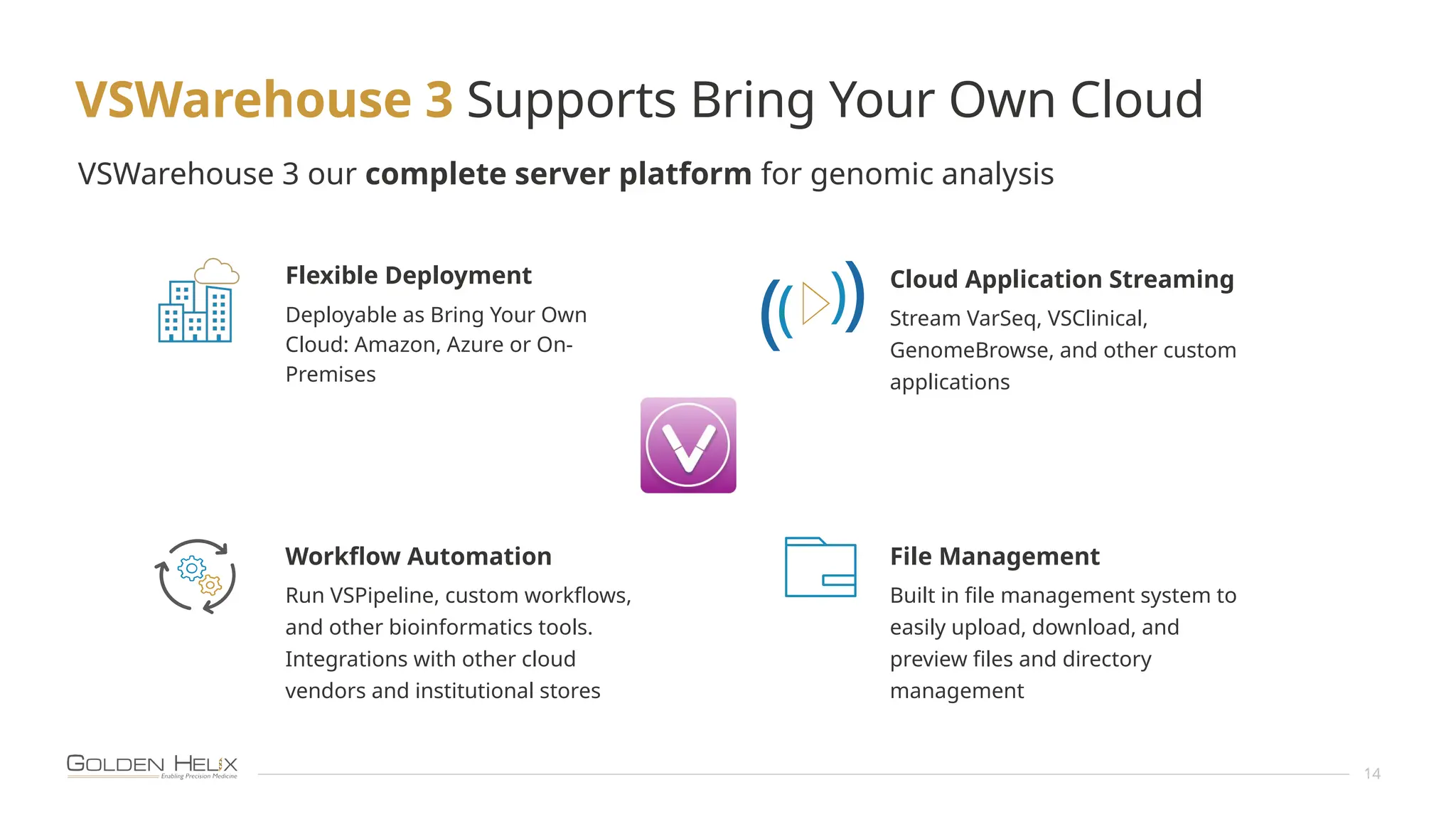
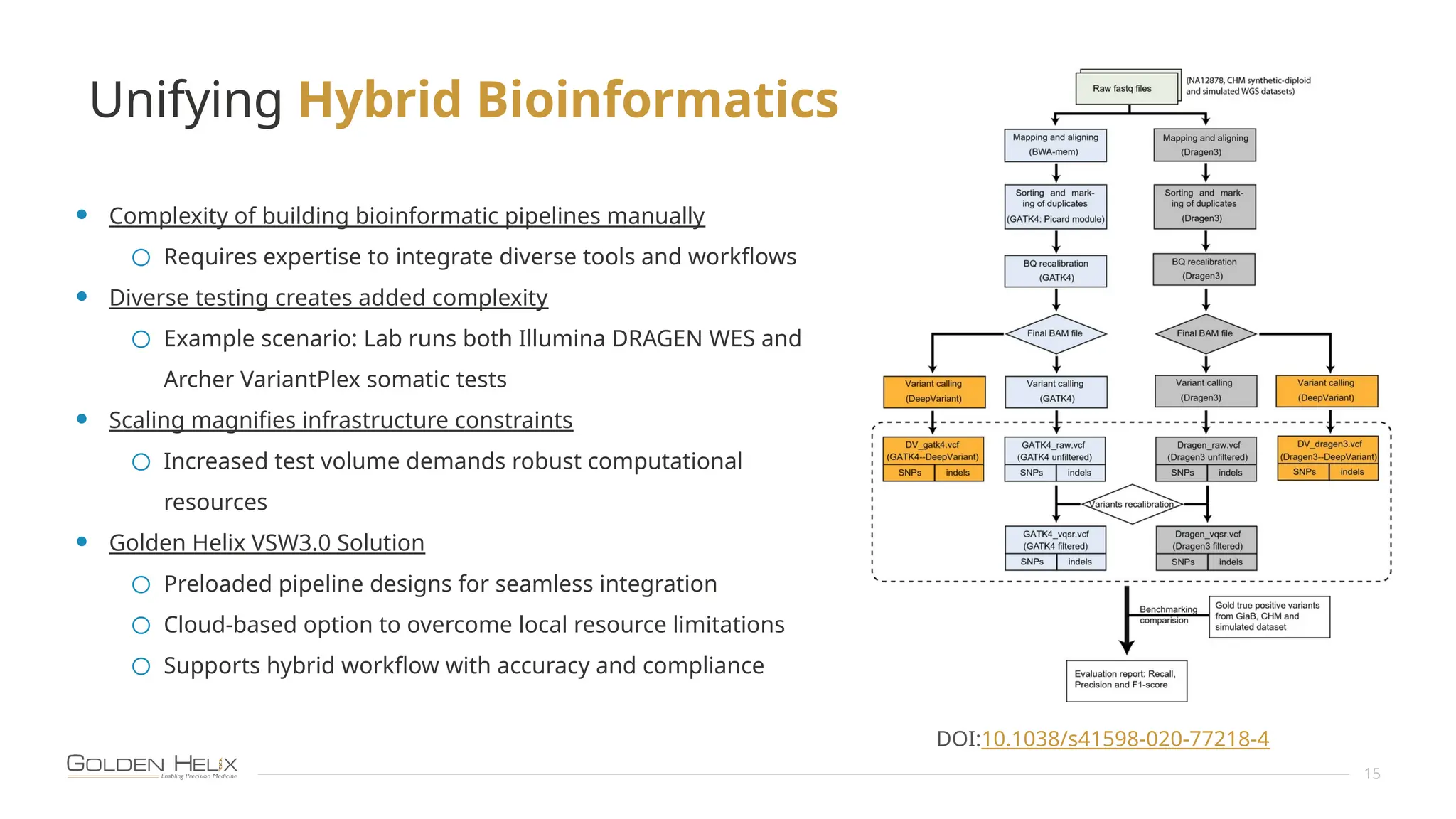
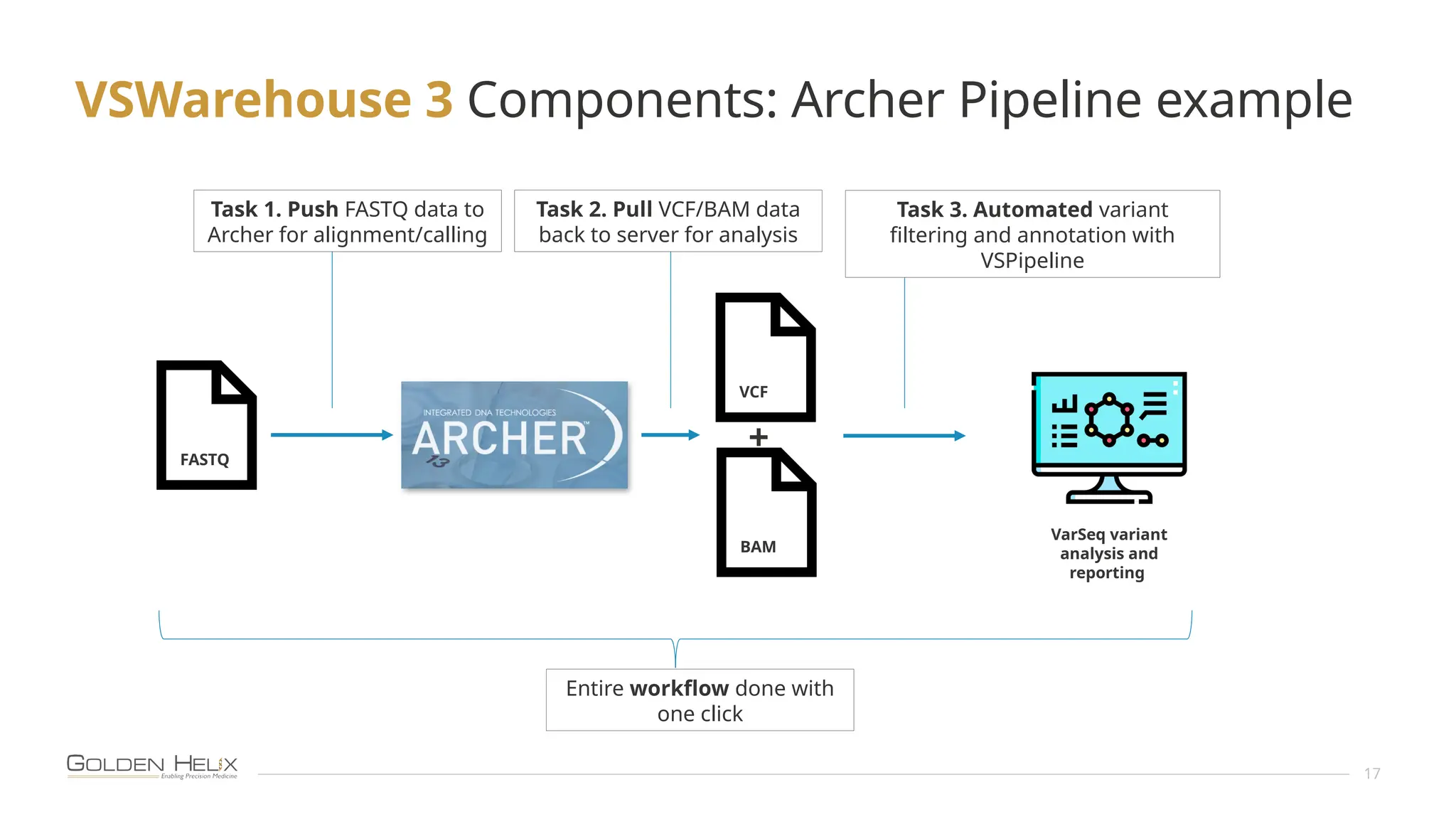
The document presents an overview of Golden Helix's VSWarehouse 3.0, a cloud-based bioinformatics solution for next-generation sequencing (NGS) data analysis. It highlights the company's focus on automating workflows for genetic analysis across various applications, from hereditary disease testing to oncology. Supported by NIH funding, the software offers clinical compliance through preloaded pipeline designs and aims to simplify deployment and integration of bioinformatics tools in a scalable manner.