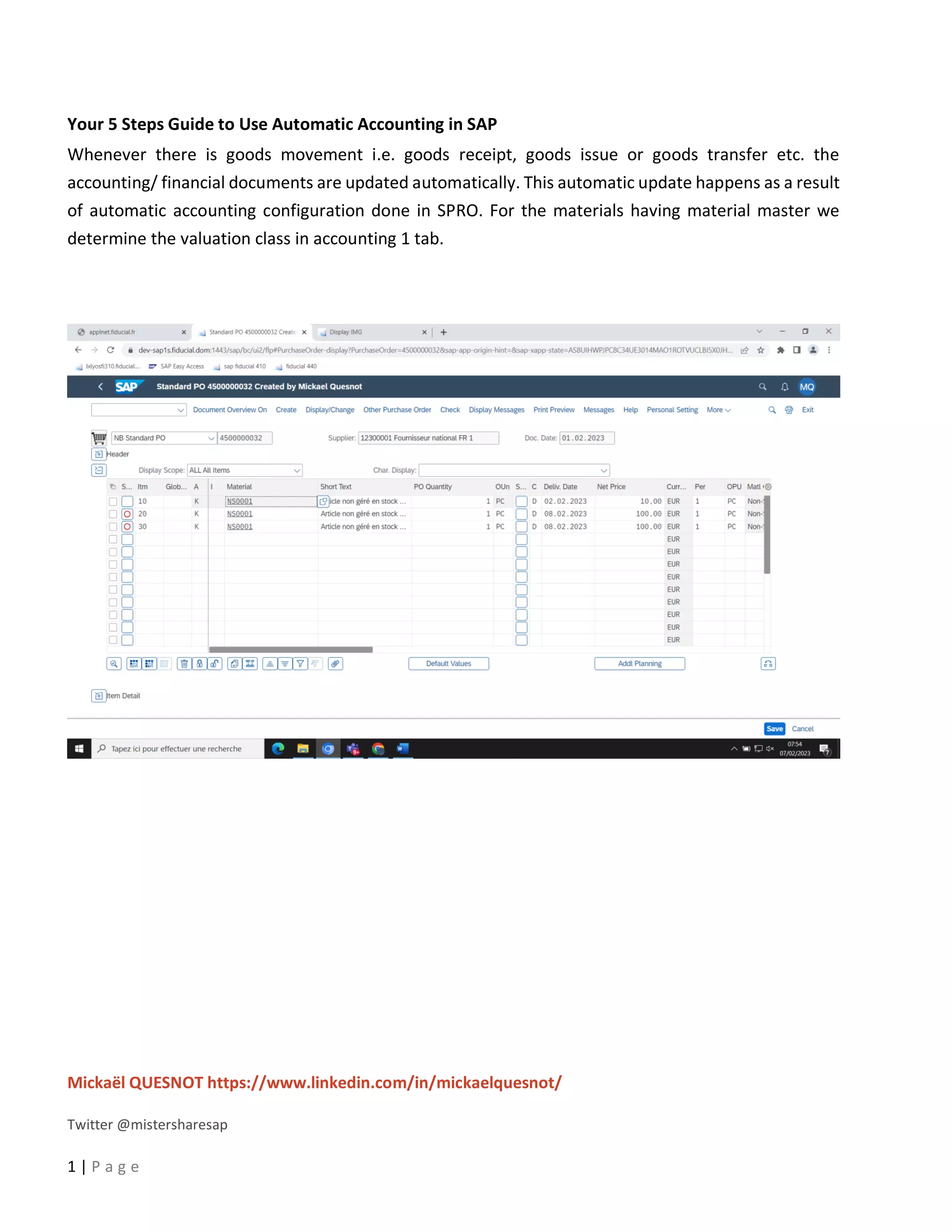
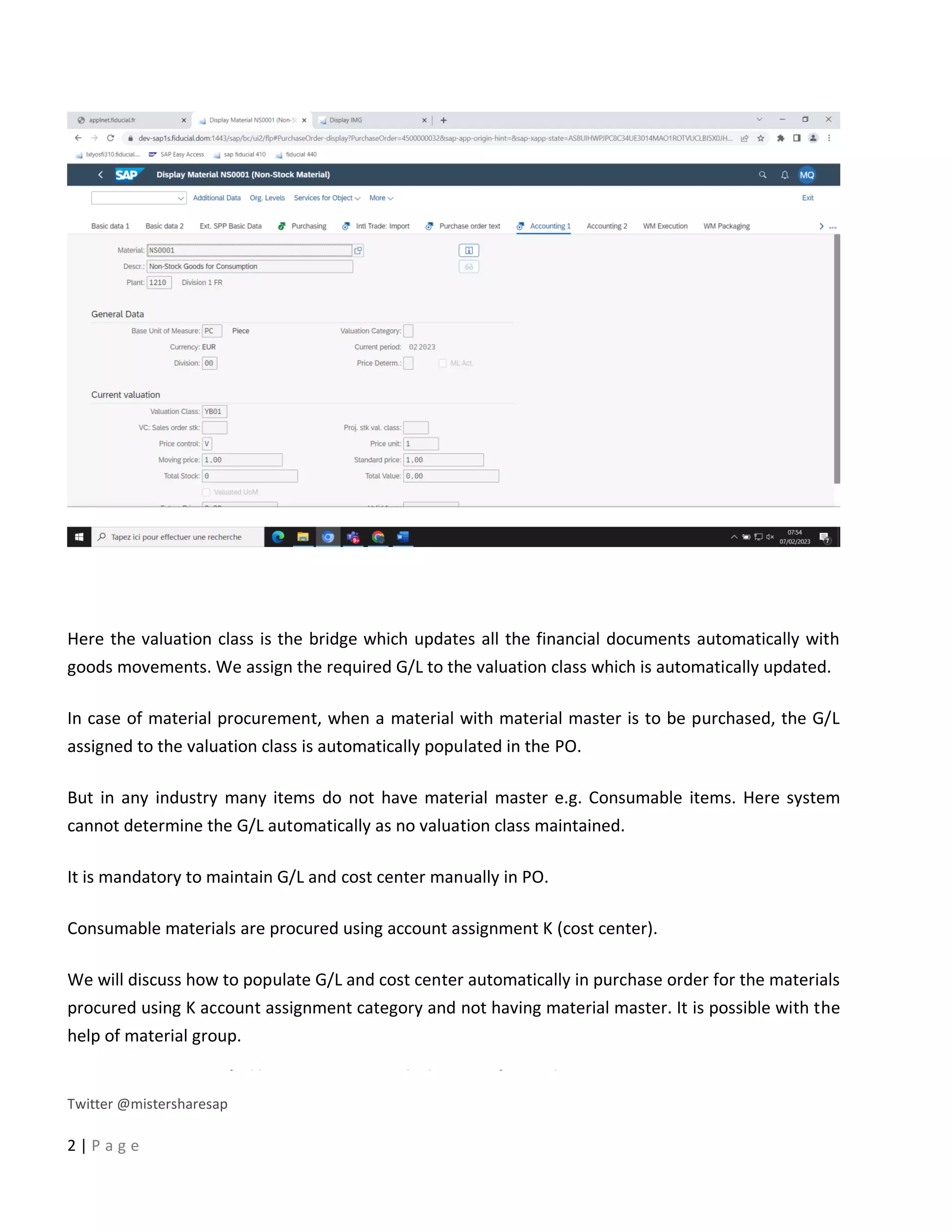
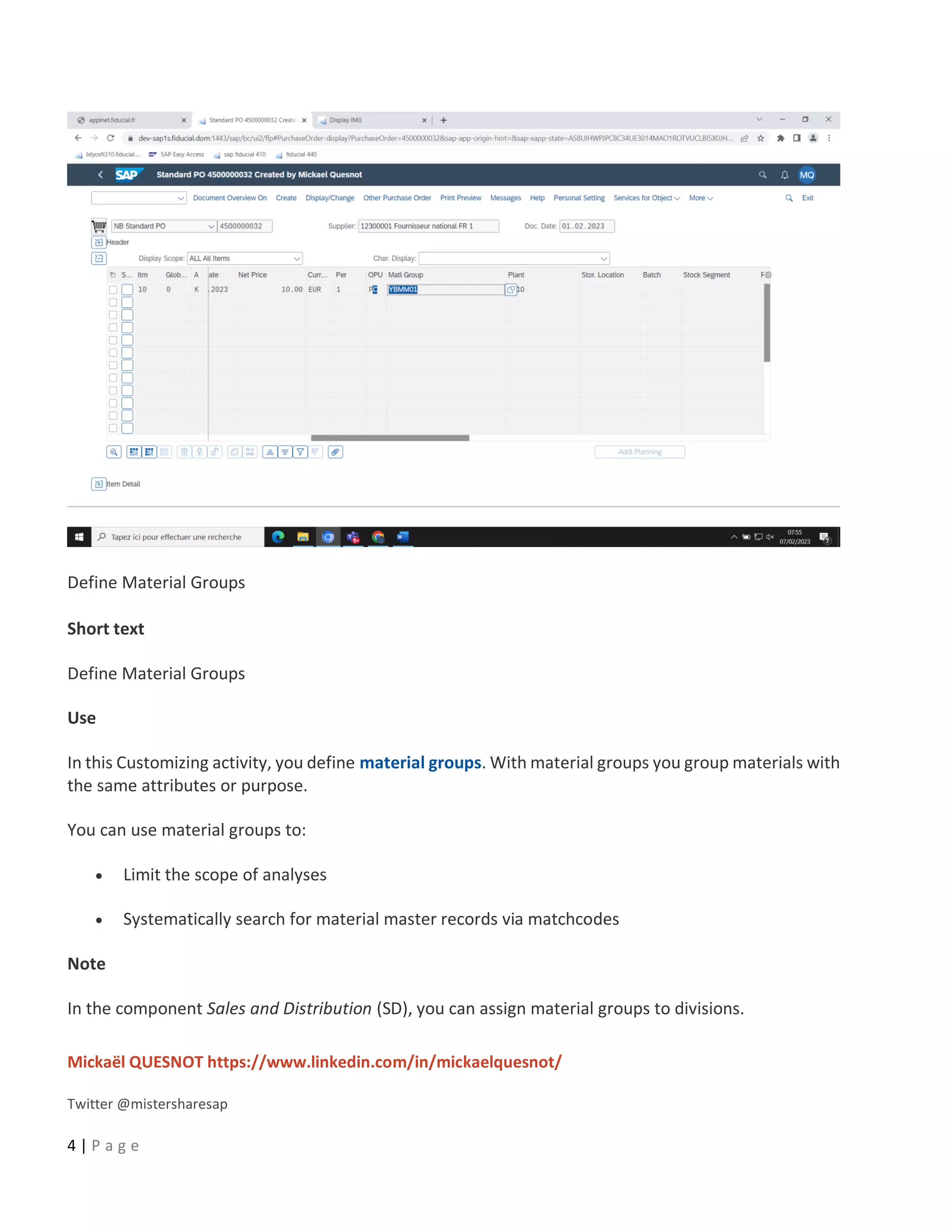
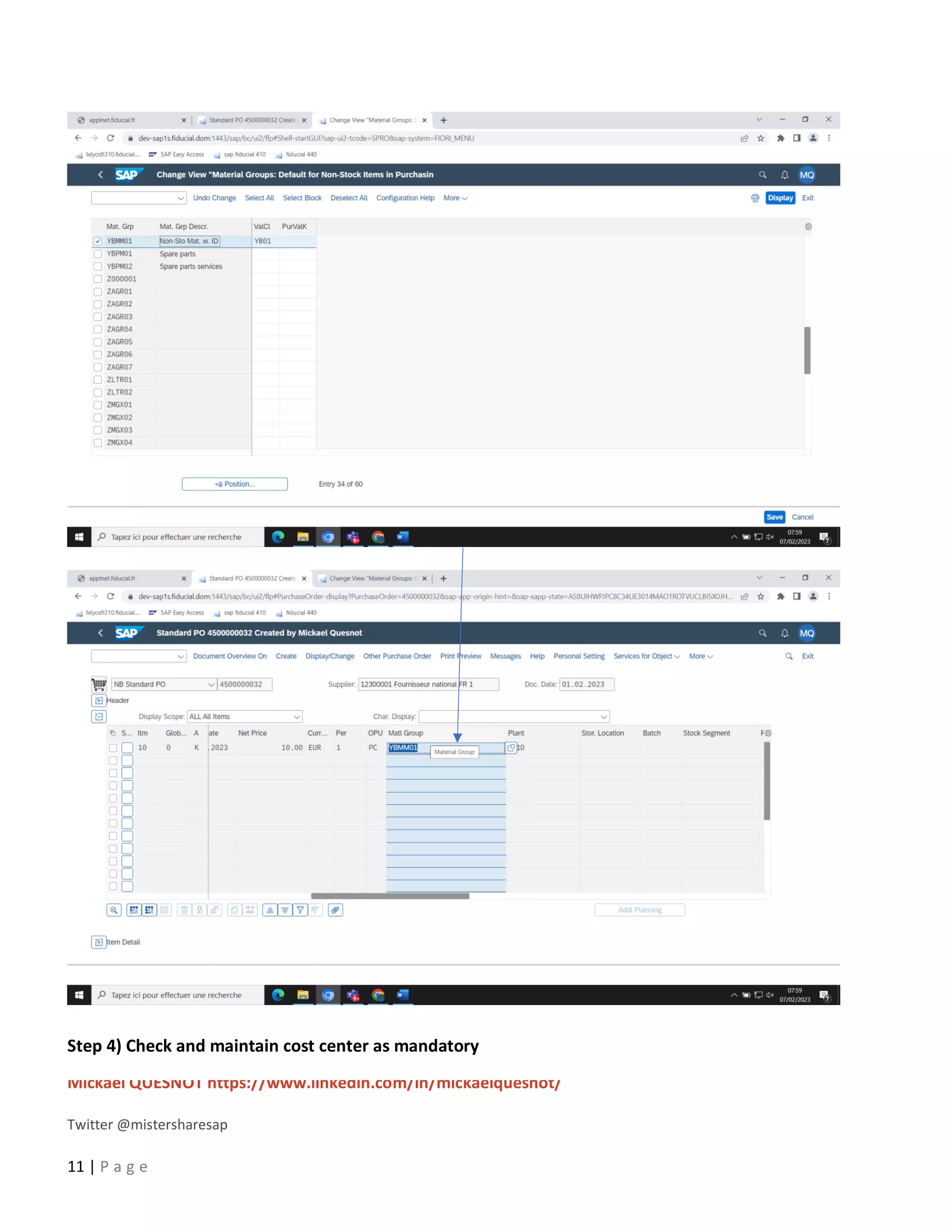
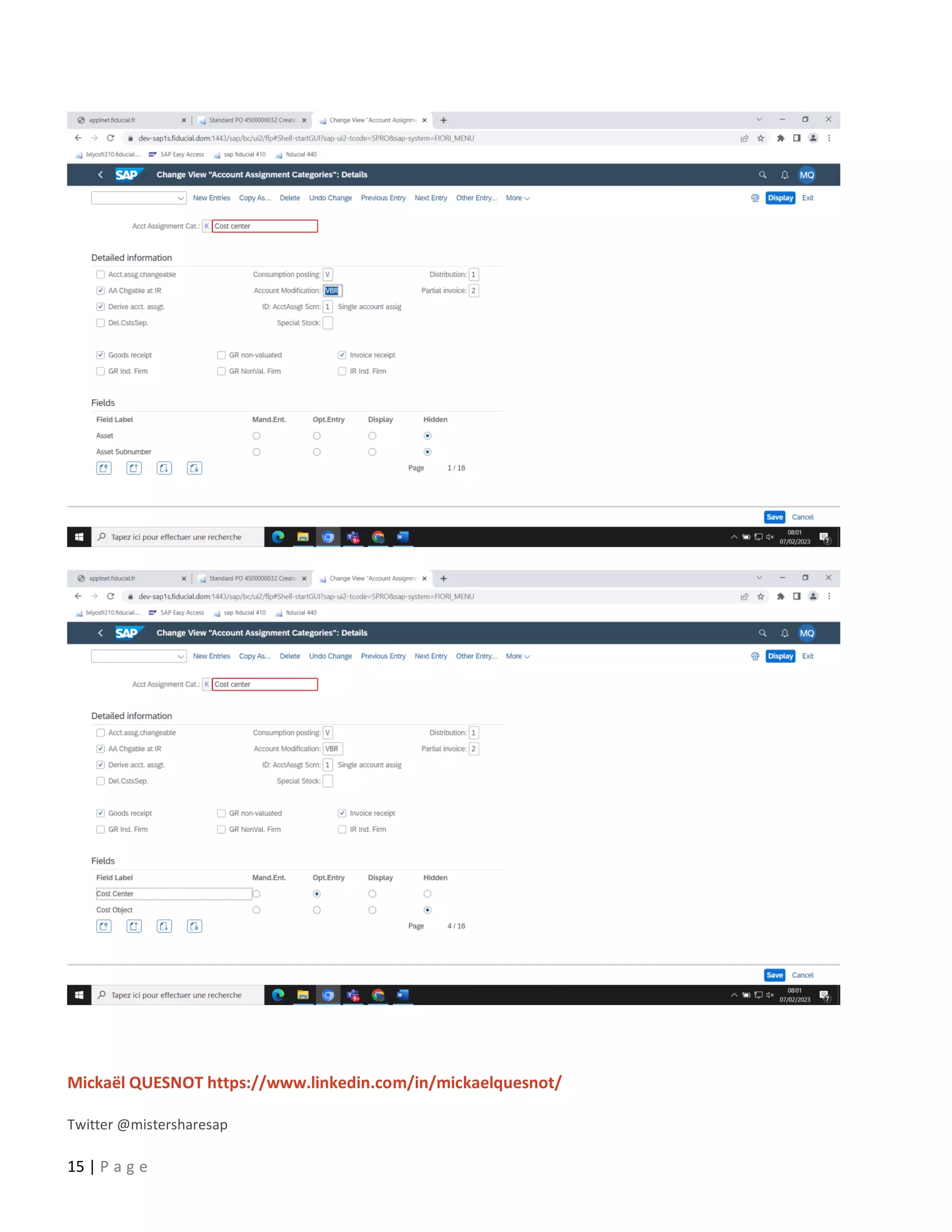
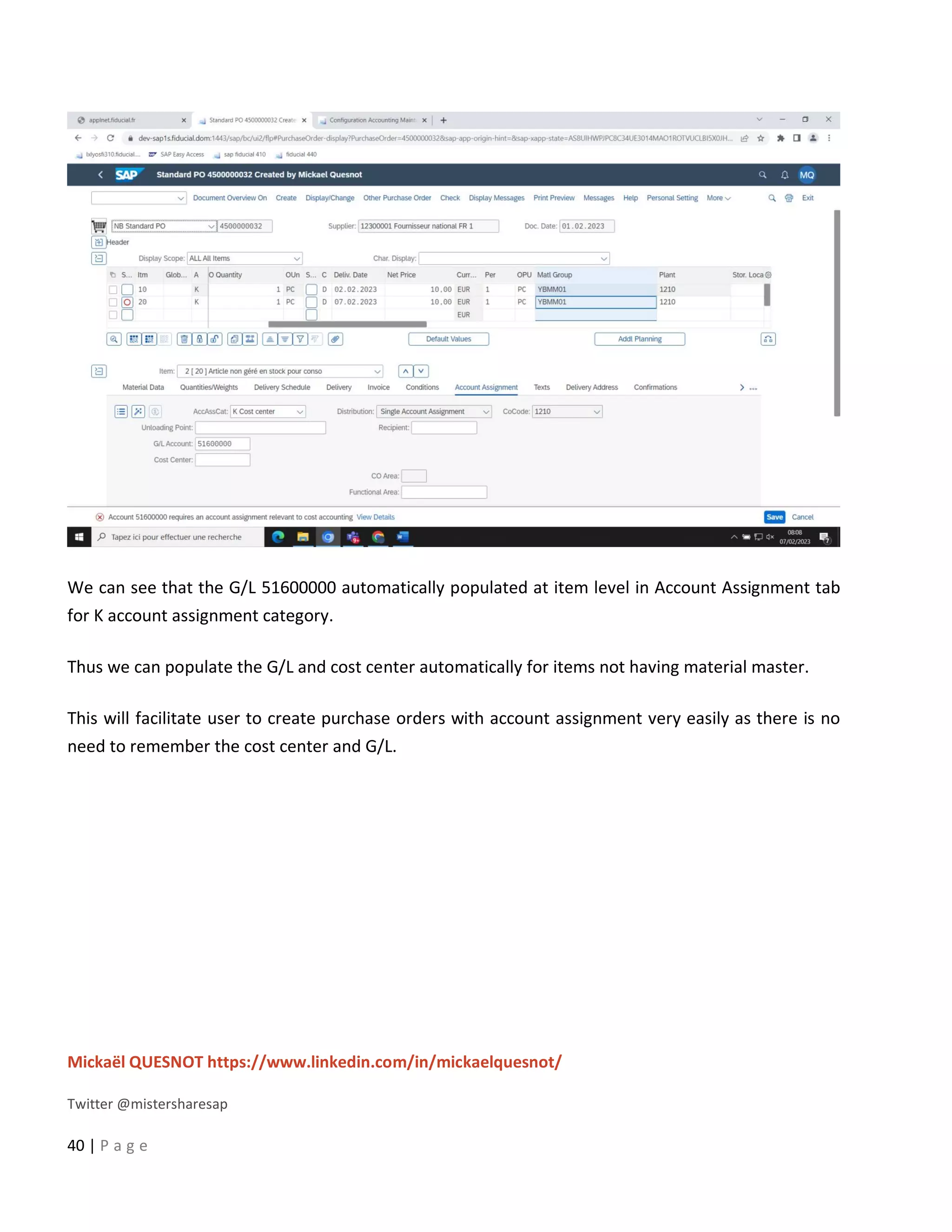
This document provides a 5-step guide to configure automatic accounting in SAP for materials that do not have a material master. The steps are: 1) Create a material group for consumable items procured using account assignment category K. 2) Create a new valuation class and assign it to the material group. 3) Assign a G/L and cost center to the valuation class. 4) Configure the system to derive the cost center automatically. 5) Maintain G/L accounts for the new valuation class to enable automatic postings. Following these steps allows automatic population of G/L and cost center for purchase orders of items without a material master.