The document discusses automated validation techniques for internet security protocols, specifically through the Avispa tool developed at the University of Bochum. It highlights various formal methods for analyzing security protocols, theoretical approaches like the Dolev-Yao intruder model, and the architecture of Avispa. The tool aims to provide effective analysis of security protocols while accommodating new developments and security challenges.

![Formal Methods for Security Protocol Analysis
Computational Models
Formal Models
Logic-based (e.g., BAN Logic [BAN89] )
Algebraic-based (e.g., NRL Protocol Analyser)
Inductive Proofs (Lawrence C. Paulson)
Model Checking (e.g., AVISPA OFMC)
Finite-State machines
Constraint-based
3
12.07.2006 Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and A
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deltchevavispappt-120505060627-phpapp02/85/Automated-Validation-of-Internet-Security-Protocols-and-Applications-AVISPA-slides-3-320.jpg)
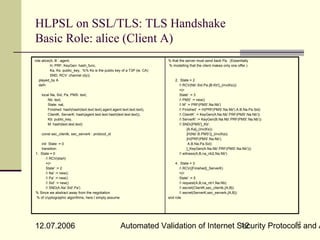
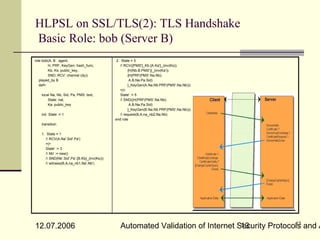
![Theoretical approaches : Dolev-Yao Intruder Model
The Dolev-Yao intruder [DY83]
Intruder has full controll over the network
Intruder can play role(s) of (normal) principals
Intruder cannot break cryptography
Unsatifying:
naively enumerates all intruder‘s messages
leads to enormous branching of the search tree
Standard Dolev-Yao abstraction lacks
cryptographic justification
Some Security Protocols secure in Dolev-Yao
model, become insecure using some provable crypto-
primitives
4
12.07.2006 Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and A
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deltchevavispappt-120505060627-phpapp02/85/Automated-Validation-of-Internet-Security-Protocols-and-Applications-AVISPA-slides-4-320.jpg)

![Model checkers: Example Implementations
Maude
Not exclusively a security protocol model checker
Instead of, it is an executable specification language, which
is based on rewriting logic
Hermes
check secrecy properties of protocols
Tested on 15 of the Clark/Jacob library [CJ97]
Finds attacks on 6 of 8 protocols
AVISPA
Uses two languages for protocol specification
Tested on 46 of 51 protocols of Clark/Jacob library
Finds attacks on all 32 of the 46 tested protocols
6
12.07.2006 Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and A
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deltchevavispappt-120505060627-phpapp02/85/Automated-Validation-of-Internet-Security-Protocols-and-Applications-AVISPA-slides-6-320.jpg)

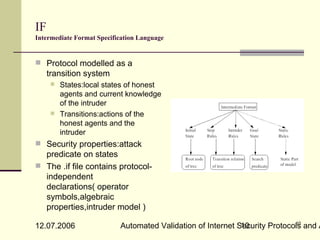
![AVISPA: Architecture
HLPSL: High Level Protocol
Specification Language
HLPSL2IF: Translator to IF
Format
IF: The Intermediate Format
Language
Translator to Subtools
OFMC (On-The-Fly-Model-
Checker) [MVO05]
ATSE (CL-based attack
searcher)
SATMC (SAT-based Model
checker)
TA4SP(Tree Automata-
based Protocol Analyser)
OF: The output format
8
12.07.2006 Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and A
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deltchevavispappt-120505060627-phpapp02/85/Automated-Validation-of-Internet-Security-Protocols-and-Applications-AVISPA-slides-8-320.jpg)

![Lazy Intruder Model
represents optimisation search technique
without excluding any attacks [BMV04]
exploits the fact, that certain
parts of the intruder‘s messages are irrelevant
for the receiver
Data constructors build data without
evaluating their arguments
Allow one to represent and compute with
infinite data (e.g., streams or infinite
trees), generating arbitrary prefixes of data on
demand
11
12.07.2006 Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and A
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deltchevavispappt-120505060627-phpapp02/85/Automated-Validation-of-Internet-Security-Protocols-and-Applications-AVISPA-slides-11-320.jpg)



![Automated analysis of Security protocols
References
[CJ97] John Clark and Jeremy [MVO05] Automated Validation
Jacob. A survey of authentication of Security Protocols(AVASP),
protocol literature : Version 1.0., Mördersheim/Vigano’/Oheimb
November 1997 apr. 2005
http://www-users.cs.york.ac.uk/ [BMV04] OFMC: A symbolic
jac/papers/drareview.ps.gz model checker for security
[M94] Catherine Meadows: Formal protocols,
Verification of Cryptographic Basin/Mördersheim/Vigano’
Protocols: A Survey. ASIACRYPT dec 2004
1994 [BB] Remote Timing Attacks
[TA02] Servey in Formal Analysis of are Practical, Brumley/Boneh
Security Properties of Cryptographic [CHVV] Password Interception
Protocols,Tarigan 2002 in a SSL/TLS Channel,
[DY83] D. Dolev, A. Yao, On the Canvel/Hiltgen/Vaudenay/
Security of Public Key Protocols, Vuagnoux
IEEE Trans. on Information Theory, [KPR] Attacking RSA-based
1983 Sessions in SSL/TLS,
[BAN89] Michael Burrows, Martin Klima/Pokorny’/Rosa
Abadi, and Roger Needham. A logic [WS] Analysis of the SSL 3.0
of authentication. Technical protocol,
Report 39, Digital Systems Wagner/Schneider
Research Center, february 1989
[AJ04] Three Tools for Model-
RFC 2246 "The TLS Protocol
Checking Security protocols, Version 1.0" , jan 1999
Arruda/Juma, jan 2004
17
12.07.2006 Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and A
17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/deltchevavispappt-120505060627-phpapp02/85/Automated-Validation-of-Internet-Security-Protocols-and-Applications-AVISPA-slides-17-320.jpg)