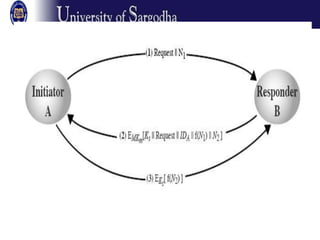
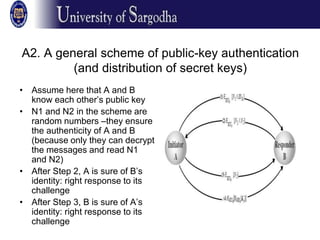
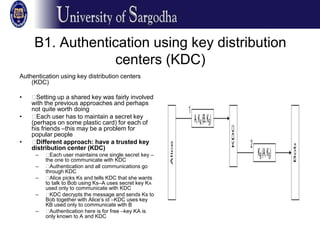
Authentication protocols allow communicating parties to verify each other's identities and establish secret session keys. They address confidentiality and timeliness issues like replay attacks. Approaches include timestamps and challenge-response protocols. Public key authentication enables parties knowing each other's public keys to mutually authenticate. Diffie-Hellman key exchange establishes a secret key based on each party's public key. Key distribution centers and protocols like Kerberos allow authentication through a trusted third party without pre-shared keys. Digital signatures authenticate message content and author, preventing later repudiation, while being verifiable by third parties. Direct signatures involve encrypting a message hash with a private key, while arbitrated signatures involve a trusted arbiter.